
1. Draw a neat diagram representing electromagnetic waves propagating along the z-axis.
2. Distinguish between p-type semiconductor and n-type semiconductor.
3. A bar magnet of magnetic moment 5.0A${m^2}$ has the pole 20cm apart. Calculate the pole strength.
Answer
574.5k+ views
Hint: The question has three parts we will first make a diagram of wave having electric and magnetic field lines perpendicular to each other and then distinguishing between p-type having holes as majority charge carriers and n-type as electron majority charge carriers and then calculating the pole strength which is the divide of magnetic moment with the distance between poles.
Complete step by step solution:
Step 1:
We are given three question and we are going to solve it one by one
Neat diagram representing electromagnetic waves propagating along z-axis.
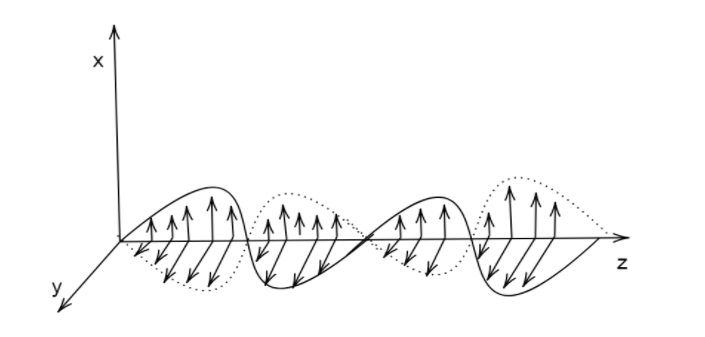
These are the electromagnetic waves propagating along the z-axis direction in a sinusoidal wave form.
The arrows are the electric and magnetic fields which are perpendicular with each other.
Step 2:
Distinguish between p-type and n-type
Step 3:
A bar magnet of magnetic moment 5.0A${m^2}$ has the pole 20cm apart. Calculate the pole strength
The magnetic moment is defined as the product of pole strength and distance between the poles.
This implies the pole strength =$\dfrac{{magnetic{\text{ }}moment{\text{ }}}}{{distance{\text{ }}between{\text{ }}poles}}$ …….. (1)
The magnetic moment given is 5 A${m^2}$ and distance between poles is 20 cm or 0.2 m
Substituting in (1) we get, the pole strength=$\dfrac{5}{{0.2}}$ , this gives 25 A${m^{ - 2}}$
Hence, the pole strength is 25$A{m^{ - 2}}$
Note:
Semiconductors are especially made up of germanium and silicon because they have free electrons in their outer shell and hence offer conductivity. Germanium at a given temperature offers more free electrons than silicon. That’s why they are widely used in transistors and other electronic devices.
Complete step by step solution:
Step 1:
We are given three question and we are going to solve it one by one
Neat diagram representing electromagnetic waves propagating along z-axis.

These are the electromagnetic waves propagating along the z-axis direction in a sinusoidal wave form.
The arrows are the electric and magnetic fields which are perpendicular with each other.
Step 2:
Distinguish between p-type and n-type
| P-TYPE | N-TYPE |
| In P-type the holes are the majority charge carriers and electrons are the minority charge carriers. | In N-type it is opposite to the P-type. It has majority electrons carriers and holes are the minority charge carriers. |
| It is an extrinsic semiconductor which is obtained by doping trivalent impurity atoms such as boron, gallium, indium, etc. to the pure germanium or silicon semiconductors | It is an extrinsic semiconductor which is obtained by doping the impurity pentavalent impurity atoms such as antimony, arsenic etc. to the pure germanium or silicon semiconductors. |
| The impurity atoms added create vacancies of electrons (holes) in the structure and are called acceptor atoms. | The impurity atoms added, provide extra electrons in the structure, and are called donor atoms. |
Step 3:
A bar magnet of magnetic moment 5.0A${m^2}$ has the pole 20cm apart. Calculate the pole strength
The magnetic moment is defined as the product of pole strength and distance between the poles.
This implies the pole strength =$\dfrac{{magnetic{\text{ }}moment{\text{ }}}}{{distance{\text{ }}between{\text{ }}poles}}$ …….. (1)
The magnetic moment given is 5 A${m^2}$ and distance between poles is 20 cm or 0.2 m
Substituting in (1) we get, the pole strength=$\dfrac{5}{{0.2}}$ , this gives 25 A${m^{ - 2}}$
Hence, the pole strength is 25$A{m^{ - 2}}$
Note:
Semiconductors are especially made up of germanium and silicon because they have free electrons in their outer shell and hence offer conductivity. Germanium at a given temperature offers more free electrons than silicon. That’s why they are widely used in transistors and other electronic devices.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers

Coming together federation is practiced in A India class 12 social science CBSE

How was the Civil Disobedience Movement different from class 12 social science CBSE

How is democracy better than other forms of government class 12 social science CBSE

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE




