




Why the Back Matters: Protecting Your Spine and Health
Do you ever wonder how your back muscles support such a large amount of your weight and are liable for such movements? If yes, you might know the main thing behind it is the human body's back. Your spine and trunk are supported by some muscles. You receive aid from others with breathing, standing up straight, and moving your body. Since your back muscles support such a large amount of your weight, wounds to these muscles are normal.
Back Muscles Pain
These wounds can cause low back pain. To stay away from injury and keep your back muscles healthy, you should warm up before physical activity and keep different muscles in your body strong. It is making almost half of your body weight. They work by forming layers that will work together to help us in our body movement.
Anatomy of Back Muscles
Your back muscles start under your skull, reaching across your shoulders and down to your lower back over your hips. These muscles append to your ribs, vertebra (bones in your spine), shoulder bones, and neck. In your back, there are three muscular groups. They belong to the skeletal muscle class of muscles. As a feature of your outer muscle-skeletal system, these muscles give structure to bones and other soft tissues. Many fibres make up skeletal muscles.
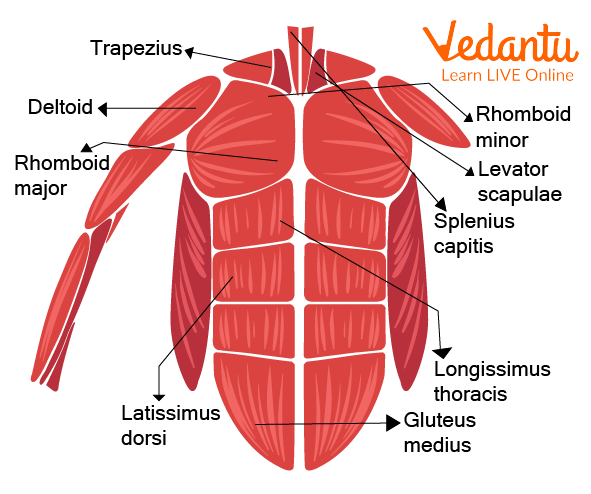
Back Muscles
How Do the Muscles on Your Back Look?
Muscles in the human body back belong to the skeletal muscle class of muscles. These muscles support bones and other soft tissues as part of your musculoskeletal system. Skeletal muscles are made up of numerous distinct fibres. These fibres group together to provide the impression of stripes or striae. These muscles are cylindrical, voluntary and multinucleated.
Uses of Back Muscles
The uses of back muscles are as follows:
Back muscles help us to move our body and bend the body.
They also help in rotating our trunk and standing up straight.
They also support our spine.
Some Interesting Facts About Muscles
Let's dig deeper into some of the unknown facts about Muscles:
There are about 600 muscles in the human body.
Three main types from them are skeletal, smooth and cardiac muscles.
The largest muscle in the human body is the gluteus maximus or buttock muscles.
Our back muscles are the structural support of our trunks.
These muscles assist us with moving our body, including our head, neck, shoulders, arms, and legs.
Our back muscles work to permit us to twist around, turn our heads and extend our backs. These muscles additionally help us to sit and stand upright.
Back muscles are an essential part of our body; they support our spine and assist us with breathing.
Summary
Different types of muscles protect our body parts. Back muscles make up almost half of your body weight. These muscles are under your control and allow you to move your body as you wish. The large muscles present at the top of the leg are very strong. The largest muscle in the human body is the gluteus maximus or buttock muscles.
An injury to your back muscles can cause muscle pain and firmness at any place in your back, muscle weakness, diminished mobility, restricted movement, swelling and even tenderness. Always take care during heavy exercises and weight lifting to avoid back muscle injury. We hope this article will clear all your doubts regarding the back muscles of the human body.
FAQs on Understanding the Human Body Back: Structure & Key Roles
1. What is the human back, and what are its main parts?
The human back is the posterior area of the body, extending from the neck to the pelvis. It serves as the body's central support structure. Its main parts include the backbone (also called the spine), a complex network of muscles that allow for movement and provide support, and the skin covering them.
2. Why is our backbone so important for our body?
The backbone, or spine, is crucial because it performs several vital functions. It provides the primary structural support for our body, allowing us to stand upright. It also offers flexibility, enabling us to bend and twist. Most importantly, it forms a protective bony canal for the spinal cord, which sends messages between the brain and the body.
3. What do the muscles in our back do?
The muscles in our back work together with the spine to help us move. They are responsible for actions like bending over, twisting from side to side, standing up straight, and lifting objects. Strong back muscles are essential for maintaining good posture and preventing injury to the spine.
4. How can we keep our back strong and healthy every day?
We can keep our back strong and healthy by following a few simple habits:
Maintaining Good Posture: Always try to sit and stand up straight, with your shoulders back.
Lifting Correctly: When picking up something heavy, bend your knees and use your leg muscles, not your back.
Staying Active: Regular exercise and stretching help keep your back muscles flexible and strong.
Eating a Balanced Diet: Proper nutrition helps build strong bones and muscles throughout the body, including the back.
5. Why is the backbone made of many small bones instead of one long bone?
The backbone is made of 33 small, stacked bones called vertebrae. This design is a clever example of natural engineering. If the spine were one single, long bone, we would be very rigid and unable to bend, twist, or absorb shock from walking and running. The series of vertebrae allows for a wide range of motion and flexibility while still providing strong support.
6. What is the difference between the backbone and the spinal cord?
The backbone (or spine) and the spinal cord are related but different parts. The backbone is the bony structure made of vertebrae that provides support and flexibility. The spinal cord is a bundle of nerves that runs through a canal in the center of the backbone. The backbone’s main job is to protect the delicate spinal cord, which acts like a superhighway for messages traveling between your brain and the rest of your body.
7. What happens if we don't take care of our back?
If we don't maintain good posture or lift heavy objects incorrectly, we can strain our back muscles. This can lead to pain, stiffness, and difficulty in moving. Over time, poor back care can weaken the muscles that support the spine, increasing the risk of more serious injuries. Taking care of our back is important for staying active and pain-free throughout life.









