




An Introduction to the Muscular System
Muscle fibres are specialised cells that make up the muscular system. Their main function is contractility, that is they contract which results in movement of our body. Movement is controlled by muscles, which are attached to bones or internal organs and blood vessels. Muscle contraction causes nearly all movement in the body. The action of cilia, the flagellum on sperm cells, and amoeboid movement of some white blood cells are exceptions to this rule.
Walking and running are obvious movements produced by the coordinated action of joints, bones, and skeletal muscles. Skeletal muscles also make more subtle movements, which result in different facial expressions, eye movements, and respiration.
The Muscular System
Muscles in the Human Body
Muscles are made of strong tissue that can contract in a controlled manner. Your muscular system has a variety of functions and muscle types. All muscle tissues are made up of contracting cells. Muscle tissues become shorter when the cells of a muscle contract. When the cells relax, the muscle tissues return to their original length.
Functions of the Muscular System
Movement
Many of your muscles aid in movement. The majority of these muscles are attached to the bones. These muscles are responsible for the movement of your skeleton.
When muscles contract, bones move. This movement can be quick, like when you run. Slow movement, such as when stretching, is also possible.
Many muscles in your body are not connected to bones.
Muscular System Function
Stability
Muscles attached to your bones support your body and aid in your balance.
Tendons are the fibrous bands that connect muscles to bones.
Tendons collaborate with muscles to keep your joints stable as your body moves.
Tendons also aid in keeping your body in proper posture or shape.
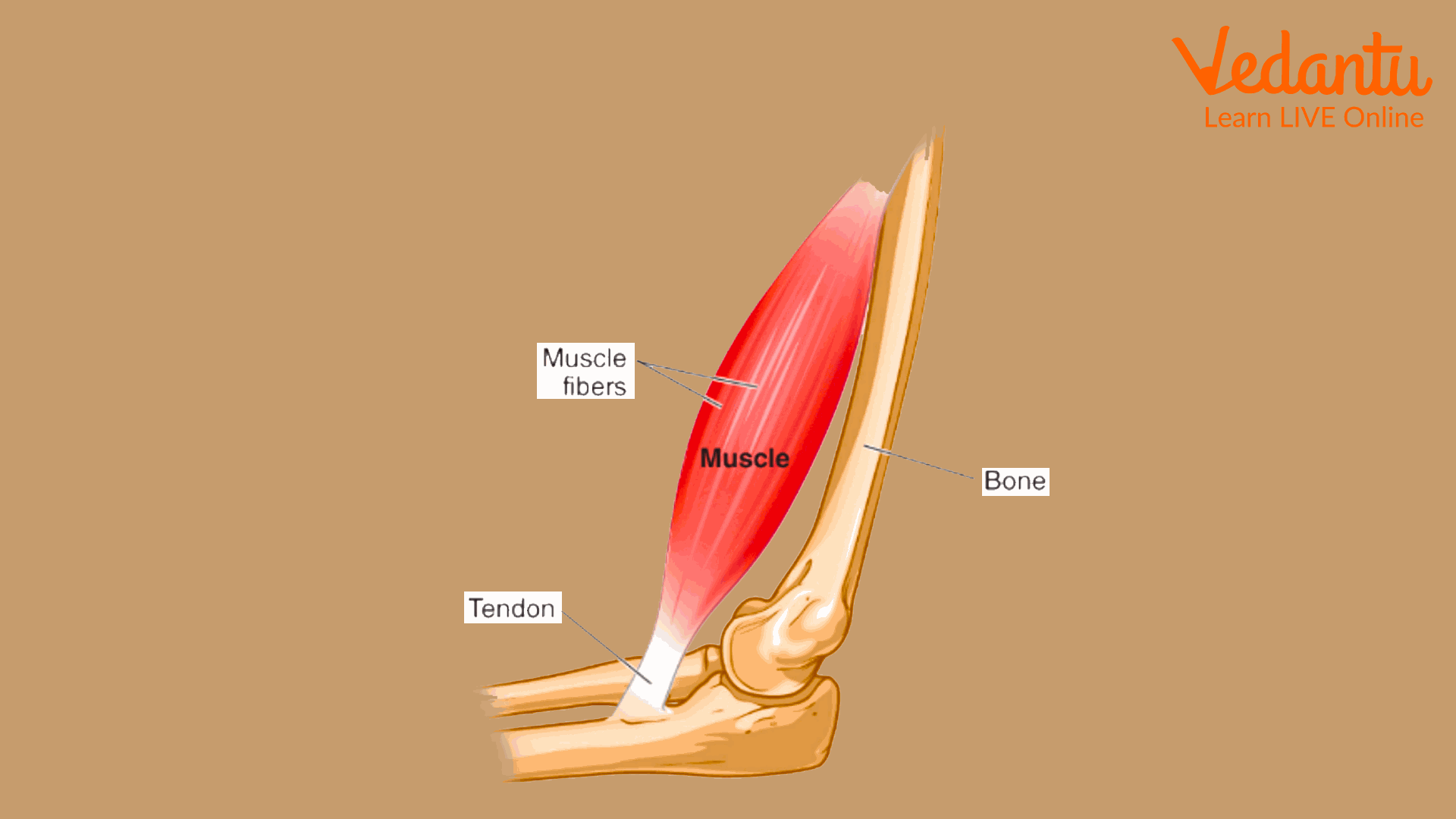
Tendons Collaborate
Protection
Muscles guard your body. They cover the majority of your skeleton.
Muscles also cover the majority of your body's organs.
Muscles are similar to a layer of padding. They protect your internal organs by encircling your abdomen, chest, and back.
The Muscular System Diagram
Temperature Regulation
Your muscular system aids your body in maintaining an internal temperature within a specific range.
Have You Ever Felt Cold and Shivered?
Shivering is caused by muscles contracting rapidly. This process converts chemical energy to thermal energy—the thermal energy released aids in maintaining your body's temperature.
This is significant because a human's body temperature must remain constant at around 37 degrees Celsius for the body to function appropriately.
During exercise, muscles also convert chemical energy to thermal energy. This is why you feel warm after exercising.
Feeling Cold and Shivering
Muscle Types
Skeletal Muscles - These are the muscles that allow us to move. They wrap around our skeleton and move our bones. Striped muscles are so-called because they have long dark and light bands of fibres that look striped. These muscles are voluntary because we control them directly with brain signals.
Smooth Muscles - Smooth muscles are unique muscles that do not connect to bones but control organs in our bodies. These muscles function without our conscious awareness.
Cardiac Muscle - This unique muscle transports our heart and blood throughout our bodies.
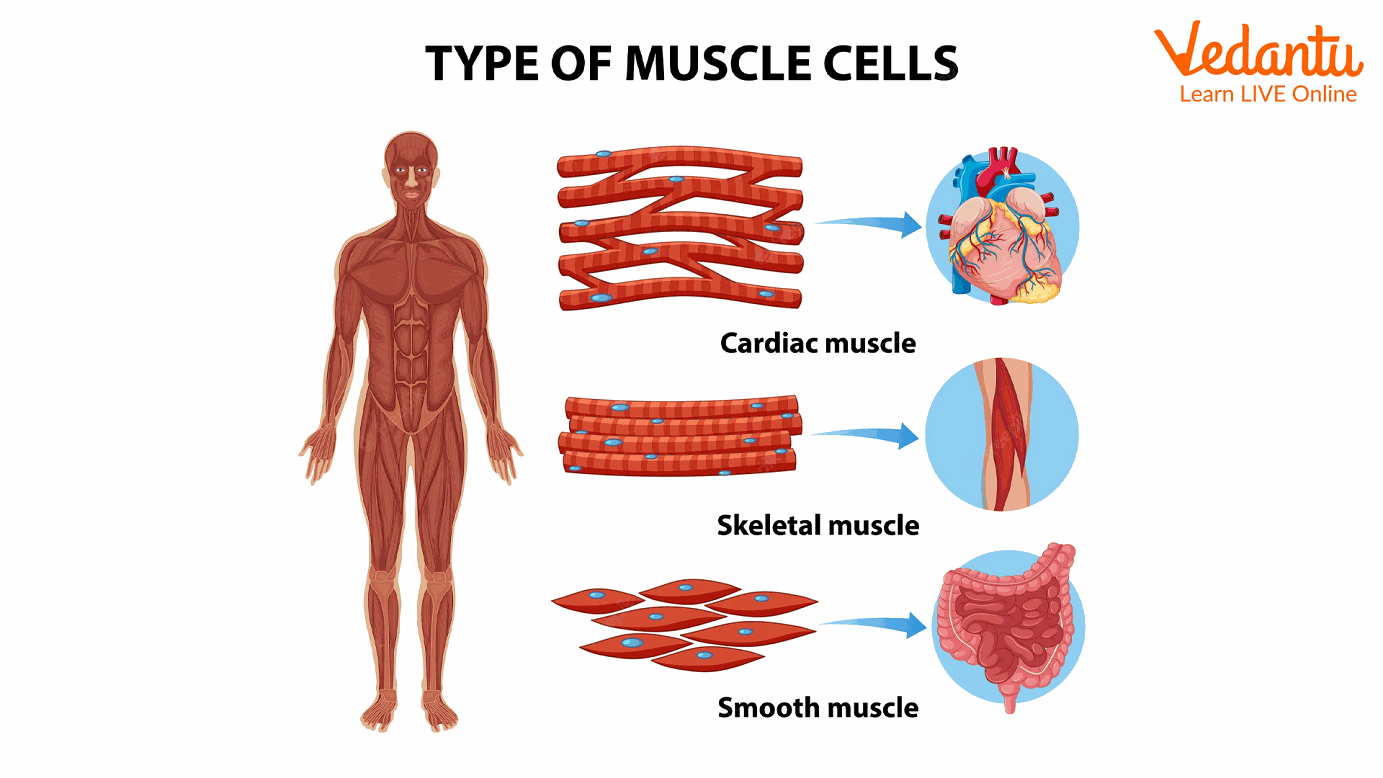
Types of Muscles
Solved Questions
1. Muscles are classified into three types in the body:
A) Smooth muscle, sports muscles, and skeletal muscles
B) Smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, and skeletal muscle
C) Smooth muscle, running muscle, and face muscles
D) Smooth muscle, flexible muscle, and strength muscle
Ans: B) Smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, and skeletal muscle
2. Which muscle aids in shoulder movement?
A) Smooth muscle
B) Deltoid muscle
C) Quadriceps
D) Tendons
Ans: B) Deltoid muscle
3. Which muscle type is found in your digestive system?
A) Rectus abdominus
B) Cardiac muscle
C) Smooth muscle
D) Stomach muscles
Ans: C) Smooth muscle
Summary
The muscular system is a complicated network of muscles essential to the human body. Muscles are involved in everything you do. They regulate your heartbeat and breathing, aid digestion, and allow you to move. Like the rest of your body, muscles benefit from regular exercise and a nutritious diet.
FAQs on Surprising Muscle Facts
1. What are the main functions of the muscular system in our body?
The muscular system has several vital functions. Its primary role is to enable movement, from walking and running to fine actions like writing. Muscles also help maintain posture, stabilise joints, protect internal organs, and generate heat to keep our body temperature stable.
2. What are the three types of muscles found in the human body?
The human body has three distinct types of muscles, each with a specific purpose:
- Skeletal Muscle: These are voluntary muscles attached to our bones by tendons. They allow us to control our movements, such as lifting an arm or kicking a ball.
- Smooth Muscle: This is involuntary muscle found in the walls of internal organs like the stomach, intestines, and blood vessels. It works automatically to perform functions like digestion.
- Cardiac Muscle: This special involuntary muscle is found only in the heart. It is responsible for pumping blood throughout the body and is designed to never get tired.
3. What is considered the strongest muscle in the human body?
This is a surprising question because strength can be measured in different ways. The masseter (jaw muscle) can exert the most pressure. The gluteus maximus (in the buttocks) is the largest muscle by volume and generates great force for powerful movements. However, many consider the uterine muscle one of the strongest for its size, especially during childbirth.
4. Why do muscles sometimes feel sore a day or two after a lot of exercise?
The soreness you feel after strenuous exercise is called Delayed Onset Muscle Soreness (DOMS). It is not caused by lactic acid buildup. Instead, it's the result of microscopic tears in the muscle fibres. This is a normal part of the muscle-building process, as the body repairs these tiny tears, making the muscle stronger than before.
5. What is the smallest muscle in the body and what surprising job does it do?
The smallest muscle in the human body is the stapedius, located in the middle ear. It's less than 2 millimetres long and its important job is to stabilise the smallest bone in the body (the stapes), which helps protect the inner ear from loud, damaging noises.
6. How are the muscles that help us digest food different from our leg muscles?
The main difference lies in their control and structure. Leg muscles are skeletal muscles, which are voluntary—you consciously decide when to move them. The muscles that aid digestion are smooth muscles, which are involuntary. They work automatically without you having to think about them, pushing food through your digestive system.
7. Is it true that it takes more muscles to frown than to smile?
This is a popular myth. While the exact numbers can vary between individuals, scientific analysis suggests that smiling is generally more efficient. A simple smile typically uses around 10 to 12 muscles, whereas a frown can engage over 40 different facial muscles. So, smiling is actually the easier facial expression!
8. Can muscles turn into fat if a person stops exercising?
No, muscles cannot turn into fat, and fat cannot turn into muscle. They are two completely different types of biological tissue. When you stop exercising, muscle cells may shrink in size (a process called atrophy), while fat cells may grow larger if you consume more calories than you burn. This can create the illusion of muscle being replaced by fat, but they are separate processes.









