




What Leads to the Depletion of Groundwater Resources?
For our luck, earth is a watery planet. But only 3% of water can be useful to human beings. Rest 97% of the water is salt water. We people depend on water for many things like drinking and irrigation and water is essential in various industrial processes. The unsustained use or overpumping of groundwater and the modernisation will end up in scarcity of freshwater. Beneath our feet, we have a water table and its level is falling down day by day. In this article, we will discuss the water table, its depletion, and what are the reasons of depletion of water table.
What is a Water Table?
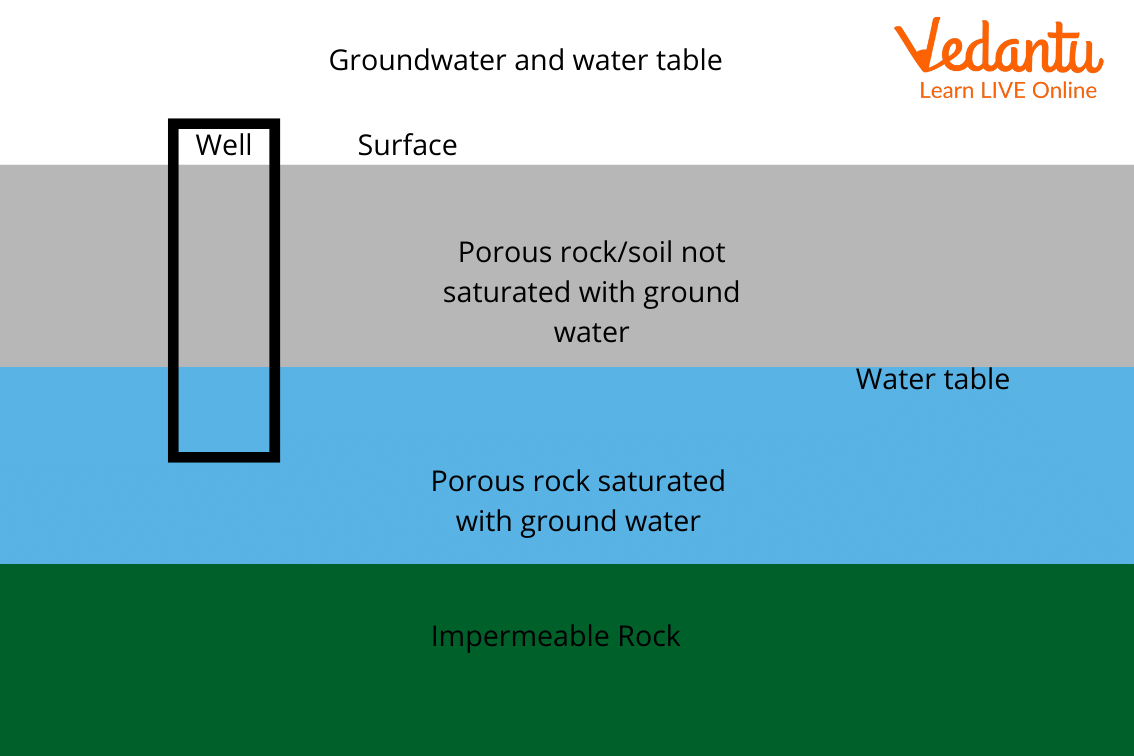
The water table can be defined as an underground boundary where atmospheric pressure and water pressure are equal. It is the boundary between the soil surface and areas of sediments and rocks, where groundwater gets saturated. So above the water table soil surface came and below it, sedimentary rocks came. The soil surface is not saturated with water. It contains both water and oxygen. Hence, the soil surface is called an unsaturated zone or zone of aeration.
In the area below the water table, sedimentary rocks are present and the spaces between them are completely filled with water; this is called the saturated zone. Local geology can affect the shape and size of the water table. For example, the water table under hills is curved and drops under valleys. The water below the water table is a result of the water seeping from the soil surface. That process is called precipitation.
The level of the water table may vary according to the seasons. For example, the water table level will be high during winter and spring. Because during this season, snow will melt and precipitation will be high. During the irrigation of crops also, the water table level increases because more water seeps out from the soil surface to the area underneath the water table. The water table level will also be influenced by the use of wells for the use of underground water for drinking and irrigation.
In order to determine the effect of seasons, climate, or human impact, the depth of the water table can be measured in the existing wells. If water is extracted in an unsustainable manner from the wells, it causes the permanent destruction of the water table. The greater extraction of groundwater compared to the rate of replenishment from precipitation causes the depletion of the water table.
Water Table Diagram
Water Table Diagram
Above the water table, soil surface and beneath the water table sedimentary rocks filled with groundwater are present. The areas where underground water meets the land surface springs are forming through which groundwater flows out and eventually reaches a river or stream. Springs are the natural flow of underground water from the underground water sources to the land surface.
Depletion of Water Table
Depletion means a reduction in the quantity or number of something. Depletion of the water table means a significant reduction in the amount of groundwater. The water table gets depleted if the rate of intake underwater is much higher than the water seeps into the soil and recharges the aquifers. There are many reasons for the depletion of the water table. Deforestation and overpumping of groundwater can be considered the main causes of the depletion of the water table. If we plant more trees, we will get a sufficient amount of rainfall since trees help in the evapotranspiration of water. Hence, groundwater will not be depleted due to afforestation.
What are the Causes of Water Table Depletion?
The reasons for the depletion of the water table are deforestation and over pumping of water. Along with that, irregular climate, increased agricultural uses, increased population, and water pollution are also reasons for the depletion of the water table. Let's check all the causes of the depletion of the water table one by one.
Over Pumping of Water from the Ground: Due to the increased population density, the need for people in various fields like agriculture and industrialisation also increases. For the daily consumption of drinking needs and various needs in agricultural and industrial fields, we people start using groundwater in a huge amount and this results in the overpumping of groundwater. The frequent pumping of groundwater leads to difficulties to recharge the groundwater by itself. This is one of the main causes of the depletion of the water table.
Deforestation: The high demand for industrialisation and urbanisation leads to deforestation, that is cutting down the trees of forests to make bare lands. Trees have a key role in bringing rainfall. If there is a reduction in the number of trees, the rate of evapotranspiration will be less and this leads to less rainfall. If the rainfall is less, only less amount of water will seep into the ground and recharge the aquifers. Hence, deforestation is also one of the main causes of the depletion of the water table.
Irregular Climate: The water table recharges primarily by rainfall. If we get poor monsoons, then only less water seeps into the ground. Also, poor monsoon leads to drought. Poor monsoon also forces farmers to dig so deeply to get groundwater which results in the further pushing down of water tables deeper down.
Increased Agricultural Needs: It is a result of the population explosion. As the population increases, the food requirement also increases. To cultivate more food products, a high amount of groundwater is required. This leads to the overpumping of groundwater from aquifers and aquifers don't get enough time to recharge by themselves.
Decreased Recharging Time of Aquifers: Aquifers are the largest reservoir of groundwater. Higher population, increased agricultural needs, urbanisation, and industrialisation lead to the overuse of groundwater, hence aquifers do not get time to recharge by themselves. This leads to the depletion of the water table.
Interesting Facts
On the earth, only 3% of water is freshwater and 97% of water is saline.
Qatar is the prime country which faces a higher water crisis.
Key Features
The water table is the underground boundary between the soil surface and sedimentary rocks which are saturated with groundwater.
The decline in the level of the water table is called depletion of the water table.
Deforestation and overpumping of groundwater are the main causes of the depletion of the water table.
FAQs on Depletion of Water Table: Causes, Consequences & Solutions
1. What is meant by the depletion of the water table?
Depletion of the water table refers to the lowering of the upper level of groundwater in an area. This occurs when the rate at which water is extracted from the ground (through pumping for agriculture, industry, and domestic use) is significantly higher than the rate at which it is replenished by natural processes like rainfall seeping into the soil. A continuously falling water table indicates an imbalance in the groundwater budget.
2. What are the main causes of water table depletion?
The primary causes of water table depletion are linked to human activities and environmental changes. Key factors include:
- Over-extraction of Groundwater: Pumping large amounts of water for irrigation, industrial processes, and growing urban populations is the single biggest cause.
- Deforestation: Trees help water seep into the ground. Removing forests reduces groundwater recharge and increases surface runoff.
- Urbanisation: Concrete roads and buildings prevent rainwater from infiltrating the soil, which is essential for replenishing the water table.
- Changes in Cropping Patterns: Shifting to water-intensive crops increases the demand for irrigation, leading to excessive groundwater pumping.
3. What are the major consequences of a depleting water table?
A falling water table has several serious consequences for the environment and society:
- Increased Pumping Costs: Wells need to be dug deeper, and more energy is required to pump water to the surface.
- Water Scarcity: It can lead to a severe shortage of fresh water for drinking and daily needs, impacting communities and agriculture.
- Deterioration of Water Quality: As the water level drops, the concentration of harmful minerals and pollutants in the remaining groundwater can increase.
- Land Subsidence: The ground can sink when the water that helps support the soil and rock is removed. This can damage buildings, roads, and other infrastructure.
- Impact on Ecosystems: Rivers, lakes, and wetlands that are fed by groundwater can dry up, harming aquatic life and surrounding habitats.
4. What are some effective methods to control the depletion of the water table?
We can control water table depletion through responsible water management practices. Important methods include:
- Rainwater Harvesting: Collecting rainwater from rooftops and other surfaces and directing it into the ground to recharge aquifers.
- Afforestation: Planting more trees enhances water retention in the soil and promotes groundwater recharge.
- Water Conservation: Adopting water-saving habits at home and in industries, such as fixing leaks and using water-efficient appliances.
- Efficient Irrigation: Using modern techniques like drip irrigation and sprinklers in agriculture reduces water wastage compared to traditional flood irrigation.
- Wastewater Recycling: Treating and reusing wastewater for non-potable purposes like industrial cooling or gardening reduces the demand on fresh groundwater.
5. How does deforestation specifically contribute to the depletion of the water table?
Deforestation accelerates water table depletion in two main ways. Firstly, tree roots create channels in the soil that allow rainwater to infiltrate deep into the ground, replenishing the aquifers. When trees are cut down, the soil becomes compacted, and this natural recharge process is severely hindered. Secondly, the forest canopy slows down rainfall and reduces surface runoff, giving water more time to seep into the ground. Without trees, rainwater flows away quickly over the surface, causing soil erosion and preventing it from ever reaching the water table.
6. Is a falling water table the same as a drought? Explain the key difference.
No, a falling water table and a drought are related but distinct concepts. A drought is a temporary, short-term period of below-average rainfall, leading to a shortage of surface water. In contrast, a falling water table is a long-term decline in the level of underground water, primarily caused by over-extraction. While a prolonged drought can contribute to a falling water table by reducing recharge, a water table can continue to drop even during periods of normal rainfall if groundwater is being pumped out faster than it can be replaced.
7. How can building more concrete roads in a city negatively impact the local water table?
Concrete roads and pavements create an impermeable surface that acts as a barrier between rainwater and the soil. In a natural environment, a significant portion of rainfall would seep into the ground, a process called infiltration, which recharges the groundwater and maintains the water table. When a city expands with more concrete structures, rainwater can no longer penetrate the ground. Instead, it is channelled into storm drains and flows away as surface runoff, completely bypassing the natural groundwater replenishment cycle and contributing to the long-term depletion of the local water table.























