
How would zero velocity and non-zero acceleration be represented on a velocity-time graph?
Answer
563.1k+ views
Hint: The graph between velocity and time is a straight line graph and its slope is the tan of the angle made by the line with the x-axis. When acceleration is non zero, velocity changes continuously as long as acceleration is not zero. When acceleration is positive, velocity increases. While, when acceleration is negative, velocity decreases.
Complete answer:
Velocity is the change in displacement that takes place per unit time. Its SI unit is $m{{s}^{-1}}$.
$v=\dfrac{d}{t}$
Here, $v$ is the velocity
$d$ is the displacement of the object
$t$ is time taken
The acceleration is the change in velocity that takes place in unit time. Its SI unit is $m{{s}^{-2}}$
$a=\dfrac{v-u}{t}$
Here, $a$ is the acceleration
$v$ is the final velocity
$u$ is the initial velocity
$t$ is time taken
When a graph is drawn between velocity and time, the velocity is the dependent variable and hence taken on the y-axis while time is the independent variable taken on the x-axis.
Let us assume that the acceleration is a constant, therefore we can use the equation of motion,
$v=u+at$
Here, $v$ is the final velocity
$u$ is the initial velocity
$a$ is the acceleration
$t$ is the time taken
The above equation is similar to the equation of a line-
$y=mx+c$
$v=at+u$
Comparing both equations we can say that acceleration is the tangent of the line. Therefore, its graph will be-
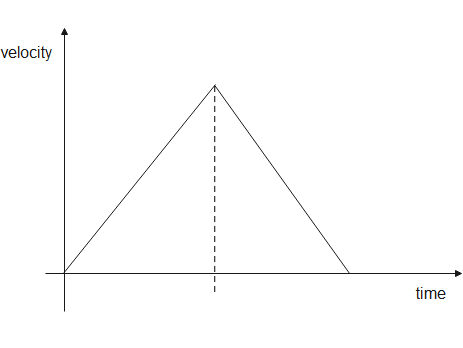
When tangent is positive, the line makes an acute angle with x-axis, when tangent is negative the line makes an obtuse angle with the y-axis.
For zero velocity, the x-axis is the line representing zero velocity as on x-axis $y=0$
Therefore, zero velocity is represented by the x-axis on the graph and accelerated motion is represented by a straight line.
Note:
If acceleration is non-zero, the graph will be a curve. When acceleration is acting on a body, external forces are acting on it by Newton’s second law. The slope of the graph between velocity and time is given by $\dfrac{dx}{dt}$ (the change in displacement is $dx$ and time taken is $dy$).
Complete answer:
Velocity is the change in displacement that takes place per unit time. Its SI unit is $m{{s}^{-1}}$.
$v=\dfrac{d}{t}$
Here, $v$ is the velocity
$d$ is the displacement of the object
$t$ is time taken
The acceleration is the change in velocity that takes place in unit time. Its SI unit is $m{{s}^{-2}}$
$a=\dfrac{v-u}{t}$
Here, $a$ is the acceleration
$v$ is the final velocity
$u$ is the initial velocity
$t$ is time taken
When a graph is drawn between velocity and time, the velocity is the dependent variable and hence taken on the y-axis while time is the independent variable taken on the x-axis.
Let us assume that the acceleration is a constant, therefore we can use the equation of motion,
$v=u+at$
Here, $v$ is the final velocity
$u$ is the initial velocity
$a$ is the acceleration
$t$ is the time taken
The above equation is similar to the equation of a line-
$y=mx+c$
$v=at+u$
Comparing both equations we can say that acceleration is the tangent of the line. Therefore, its graph will be-

When tangent is positive, the line makes an acute angle with x-axis, when tangent is negative the line makes an obtuse angle with the y-axis.
For zero velocity, the x-axis is the line representing zero velocity as on x-axis $y=0$
Therefore, zero velocity is represented by the x-axis on the graph and accelerated motion is represented by a straight line.
Note:
If acceleration is non-zero, the graph will be a curve. When acceleration is acting on a body, external forces are acting on it by Newton’s second law. The slope of the graph between velocity and time is given by $\dfrac{dx}{dt}$ (the change in displacement is $dx$ and time taken is $dy$).
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




