
Write the structure of tetra-tert butyl methane.
Answer
592.8k+ views
Hint: Nomenclature is a very important part of organic chemistry. This nomenclature not only for compounds but also for carbon atoms that make this compound. For nomenclature of carbon atoms, use the terms primary, secondary, tertiary, and quaternary to refer to the substitution level that carbon has in the molecule. Based on the classification of carbon atoms useful to determine the stability and predict the products in organic chemistry reactions.
Complete step by step solution:
Classifications of carbon atoms based on nomenclature are primary, secondary, tertiary, and quaternary. To describe how many carbon atoms are attached to given carbon, this classification is applied to only saturated hydrocarbons and its substitutions compounds like alkyl halides, alcohols, amines, etc.
The terminology of carbon-containing functional groups:
Primary carbon: a hydrogen atom on a carbon attached to one other carbon atom
Secondary carbon atom: hydrogen on a carbon attached to only two other carbon atoms
Tertiary carbon: a carbon atom attached to three other carbon atoms. Giving the name for saturated hydrocarbons starts prefix with tertiary, when a carbon bonded to the other four carbon atoms. This tertiary carbon appears in branched alkanes only, but not in linear alkanes.
Given the structure of tetra-tert butyl methane is:
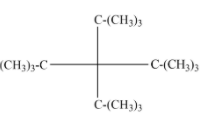
Note: The classification is important as it is applied in the classification of organic compounds with different functional groups. Especially for alcohols, amine, and alkyl halides and also applied for carbocations and carbanions. Due to the hyperconjugation from nearby C-H bonds, tertiary carbocation is more stable compared to primary, secondary, and methyl cation respectively.
Complete step by step solution:
Classifications of carbon atoms based on nomenclature are primary, secondary, tertiary, and quaternary. To describe how many carbon atoms are attached to given carbon, this classification is applied to only saturated hydrocarbons and its substitutions compounds like alkyl halides, alcohols, amines, etc.
The terminology of carbon-containing functional groups:
Primary carbon: a hydrogen atom on a carbon attached to one other carbon atom
Secondary carbon atom: hydrogen on a carbon attached to only two other carbon atoms
Tertiary carbon: a carbon atom attached to three other carbon atoms. Giving the name for saturated hydrocarbons starts prefix with tertiary, when a carbon bonded to the other four carbon atoms. This tertiary carbon appears in branched alkanes only, but not in linear alkanes.
Given the structure of tetra-tert butyl methane is:

Note: The classification is important as it is applied in the classification of organic compounds with different functional groups. Especially for alcohols, amine, and alkyl halides and also applied for carbocations and carbanions. Due to the hyperconjugation from nearby C-H bonds, tertiary carbocation is more stable compared to primary, secondary, and methyl cation respectively.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Name the part of the brain responsible for the precision class 11 biology CBSE

The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to AEffect class 11 biology CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

State and prove Bernoullis theorem class 11 physics CBSE

Actinoid contraction is more than lanthanoid contraction class 11 chemistry CBSE

Which out of the following hydrocarbons undergo addition class 11 chemistry CBSE




