
Write the Rutherford -Soddy law of radioactive decay and draw decay curve.
Answer
588.9k+ views
Hint:The Rutherford -Soddy law tells us about the radiation and decay of elements.
Formula used: \[N={{N}_{0}}{{e}^{-\lambda t}}\]
Complete Answer:
1) The radioactivity is based on counting of disintegration per second. The activity depends on the number of decays per second.
2) The law is the exponential decay law which states that a fixed fraction of elements will decay per unit time. Let us take the example, the half part of thorium decays and the remaining in the next four days and so on.
The derivation of the formula: -
\[\begin{align}
& -\dfrac{dN}{dt}\alpha N \\
& \Rightarrow -\dfrac{dN}{dt}=kN \\
& \Rightarrow \int\limits_{{{N}_{0}}}^{N}{\dfrac{dN}{N}}=\lambda \int\limits_{0}^{t}{dt} \\
& \Rightarrow N={{N}_{0}}{{e}^{-\lambda t}} \\
\end{align}\]
where, N= size of population of radioactive element , N₀= size of initial population of radioactive element, 𝝀 = decay constant.
This shows that the population decays exponentially at a rate that depends on the decay constant.
The time required for half of the population to decay is called the half-life which is given by
\[{{T}_{{}^{1}/{}_{2}}}=\dfrac{0.693}{\lambda }\]
The decay curve is shown in the figure below:
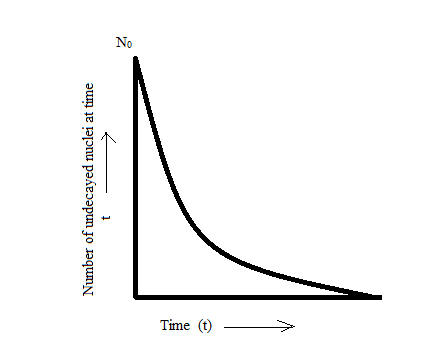
Note: Radioactivity property is exhibited by certain types of matter of emitting energy simultaneously. Half-life is the time required for an element to reduce to half of its initial value.
Formula used: \[N={{N}_{0}}{{e}^{-\lambda t}}\]
Complete Answer:
1) The radioactivity is based on counting of disintegration per second. The activity depends on the number of decays per second.
2) The law is the exponential decay law which states that a fixed fraction of elements will decay per unit time. Let us take the example, the half part of thorium decays and the remaining in the next four days and so on.
The derivation of the formula: -
\[\begin{align}
& -\dfrac{dN}{dt}\alpha N \\
& \Rightarrow -\dfrac{dN}{dt}=kN \\
& \Rightarrow \int\limits_{{{N}_{0}}}^{N}{\dfrac{dN}{N}}=\lambda \int\limits_{0}^{t}{dt} \\
& \Rightarrow N={{N}_{0}}{{e}^{-\lambda t}} \\
\end{align}\]
where, N= size of population of radioactive element , N₀= size of initial population of radioactive element, 𝝀 = decay constant.
This shows that the population decays exponentially at a rate that depends on the decay constant.
The time required for half of the population to decay is called the half-life which is given by
\[{{T}_{{}^{1}/{}_{2}}}=\dfrac{0.693}{\lambda }\]
The decay curve is shown in the figure below:

Note: Radioactivity property is exhibited by certain types of matter of emitting energy simultaneously. Half-life is the time required for an element to reduce to half of its initial value.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




