
Write the relation between object distance (u), image distance (v) and focal length (f) for a concave mirror.
Answer
596.7k+ views
Hint: A concave mirror is an inward angled mirror in the middle. In the calculations of concave mirrors, the formula we use is called the mirror equation. This equation defines how far an entity is from the mirror and how big or tiny the entity is (object size).
Complete answer:
The laws of reflection also refer to concave mirrors; but because the surface of the mirror is angled, depending on which section of the mirror the angle of light hits the surface is different. The angle of the mirror is often called an incident angle. The concave mirror enables light to be concentrated in the way a camera lens filters light and shapes a frame. Concave mirrors may produce actual pictures in comparison to a flat mirror, reflected in front of the mirror where the light focuses.
It produces an illusion that floats in the air in front of the mirror! You don't have to see this thing through the mirror at all so that is why it's a real image. That is very different when you gaze at a flat mirror from the virtual image you see.
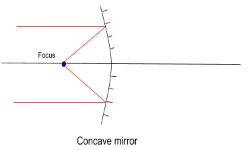
The relation between object distance, image distance and spherical mirror focal length is indicated by-
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{f} = \dfrac{1}{v} + \dfrac{1}{u}$
Where,
F= focal length of the concave mirror (distance between poles and the mirror 's centre focus)
u= distance of object (pole-to-object distance)
v= image distance (pole-image distance)
Note: A concave mirror, or converging mirror, has a reflecting surface that is recessed inward (away from the incident light). Concave mirrors reflect light inward to one focal point. They are used to focus light. Unlike convex mirrors, concave mirrors show different image types depending on the distance between the object and the mirror.
Complete answer:
The laws of reflection also refer to concave mirrors; but because the surface of the mirror is angled, depending on which section of the mirror the angle of light hits the surface is different. The angle of the mirror is often called an incident angle. The concave mirror enables light to be concentrated in the way a camera lens filters light and shapes a frame. Concave mirrors may produce actual pictures in comparison to a flat mirror, reflected in front of the mirror where the light focuses.
It produces an illusion that floats in the air in front of the mirror! You don't have to see this thing through the mirror at all so that is why it's a real image. That is very different when you gaze at a flat mirror from the virtual image you see.

The relation between object distance, image distance and spherical mirror focal length is indicated by-
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{f} = \dfrac{1}{v} + \dfrac{1}{u}$
Where,
F= focal length of the concave mirror (distance between poles and the mirror 's centre focus)
u= distance of object (pole-to-object distance)
v= image distance (pole-image distance)
Note: A concave mirror, or converging mirror, has a reflecting surface that is recessed inward (away from the incident light). Concave mirrors reflect light inward to one focal point. They are used to focus light. Unlike convex mirrors, concave mirrors show different image types depending on the distance between the object and the mirror.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

State and prove converse of BPT Basic Proportionality class 10 maths CBSE




