
How do you write the orbital diagram for hydrogen?
Answer
564.3k+ views
Hint: The answer is based on the concept of the Pauli’s exclusion principle which states that no two electrons in the same atom can have all the quantum numbers same.
Complete answer:
The concept of Pauli’s exclusion principle and also Hund’s rule and many other concepts which come under the general chemistry part are very familiar with us.
- Now, let us see what Pauli's exclusion principle says and how the orbital diagrams can be drawn for the hydrogen atom.
- Pauli’s exclusion principle states that no two electrons in an atom can have all the quantum numbers same.
In other words, this can be stated that,
a) No more than two electrons can occupy the same orbital
b) Two electrons in the same orbital must have the opposite spins.
- Therefore, according to this rule we can assign the electrons in the orbital.
- Now, the given question has hydrogen where the atomic number of this atom is 1 and thus it has only one electron in its orbit.
- The number of protons in an atom depicts the atomic number and also the total number of protons in an atom will be always equal to the number of electrons, that is they are always equal in number.
- Therefore, there is one proton and one electron in an atom. The electronic configuration of hydrogen can be written as $1{{s}^{1}}$ that is it has one orbital with a single electron in it.
This can be represented in the orbital form as shown below,
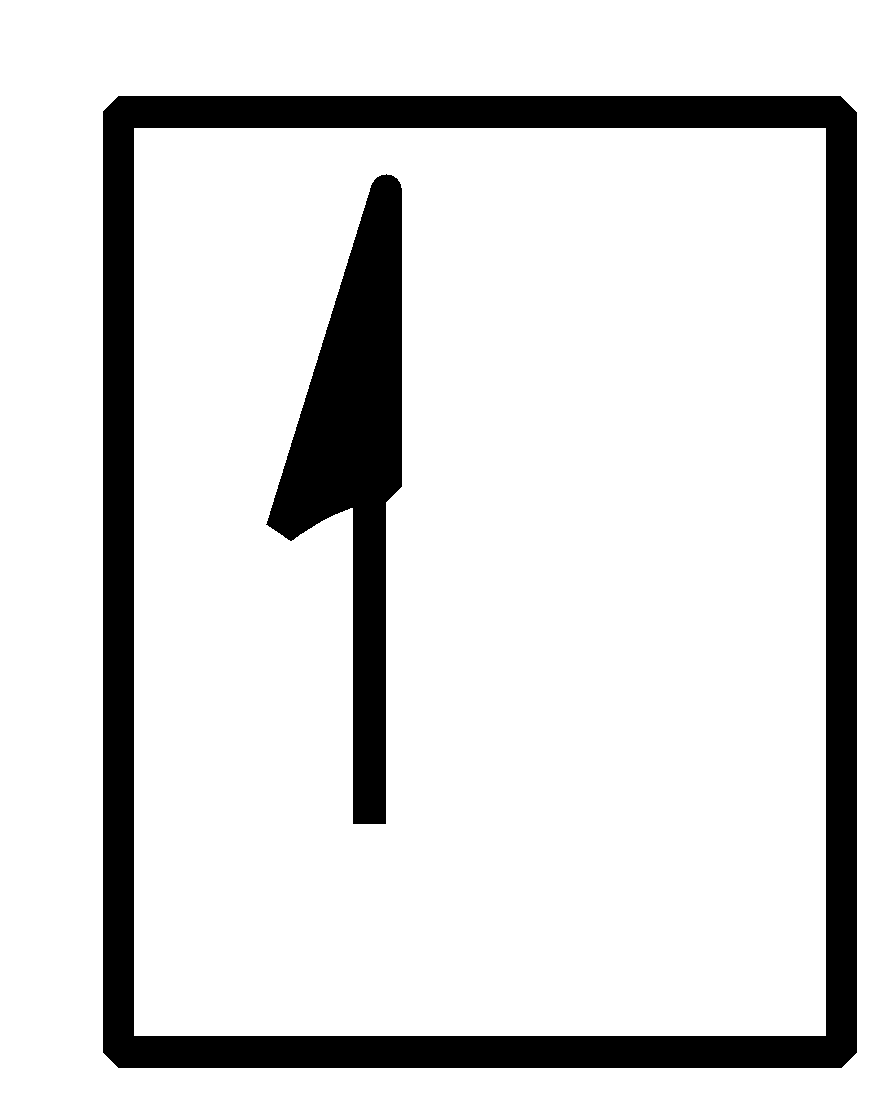
Note:
Note that while assigning the electrons in the orbital form, three rules are to be kept in mind and also to be followed that are- Aufbau principle, Pauli’s exclusion principle and also the Hund’s rule.
Complete answer:
The concept of Pauli’s exclusion principle and also Hund’s rule and many other concepts which come under the general chemistry part are very familiar with us.
- Now, let us see what Pauli's exclusion principle says and how the orbital diagrams can be drawn for the hydrogen atom.
- Pauli’s exclusion principle states that no two electrons in an atom can have all the quantum numbers same.
In other words, this can be stated that,
a) No more than two electrons can occupy the same orbital
b) Two electrons in the same orbital must have the opposite spins.
- Therefore, according to this rule we can assign the electrons in the orbital.
- Now, the given question has hydrogen where the atomic number of this atom is 1 and thus it has only one electron in its orbit.
- The number of protons in an atom depicts the atomic number and also the total number of protons in an atom will be always equal to the number of electrons, that is they are always equal in number.
- Therefore, there is one proton and one electron in an atom. The electronic configuration of hydrogen can be written as $1{{s}^{1}}$ that is it has one orbital with a single electron in it.
This can be represented in the orbital form as shown below,

Note:
Note that while assigning the electrons in the orbital form, three rules are to be kept in mind and also to be followed that are- Aufbau principle, Pauli’s exclusion principle and also the Hund’s rule.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Accountancy: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




