
Write the name and symbol of the following elements.
The metalloid in the third period: ___________.
Answer
600.6k+ views
Hint: The elements whose properties are intermediate between metals and nonmetals are called metalloids. In the modern periodic table, there are a total 7 metalloids which are arranged diagonally in p-block.
Complete step by step answer:
In the modern form of periodic table, total 7 elements are found whose properties are intermediate between metals and nonmetals. These are called metalloids.
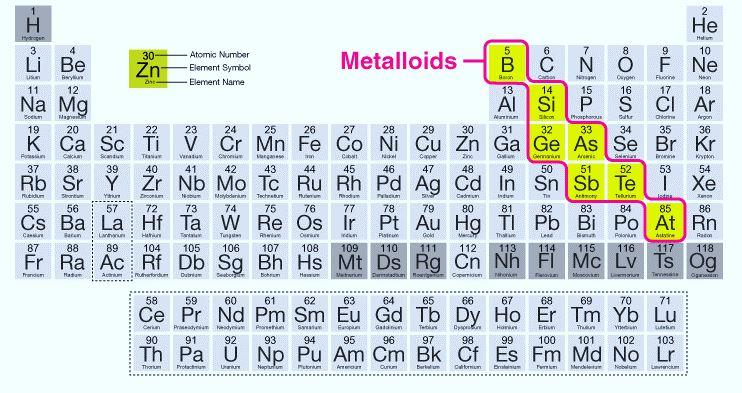
So, we have metalloids - Boron (B), Silicon (Si), Germanium (Ge), Arsenic (As), Antimony (Sb), Tellurium (Te) and Astatine (At).
Out of these, Silicon is a metalloid in the third period.
Silicon belongs to the third period, 14th group. The elements in this group are also known as Carbon family. Atomic number of Silicon is 14 and its electronic configuration is \[{\text{1}}{{\text{s}}^2}{\text{ 2}}{{\text{s}}^2}{\text{ 2}}{{\text{p}}^6}{\text{ 3}}{{\text{s}}^2}{\text{ 3}}{{\text{p}}^2}\].
Additional information: Metalloids generally have metallic appearance but they are brittle. Their chemical properties show close similarity with non-metals. Metalloids are mostly used as alloys, biological agents and catalysts. They are of extreme use in semiconductors and electronics. In the modern periodic table, metalloids lie on either side of the line dividing metals from nonmetals.
Silicon is a brittle, crystalline solid with a bluish grey metallic lustre. It rarely occurs in its purest form in earth’s crust. It is mostly found as dust, sand and clay. In these forms, it is used in construction works. Cast iron contains silicon. Silicon is also widely used in making semiconductors and in production of fire bricks.
Note: Total 7 metalloids are found in the modern periodic table, out of this, Silicon is from the third period. Silicon has tremendous uses, especially in semiconductors.
Complete step by step answer:
In the modern form of periodic table, total 7 elements are found whose properties are intermediate between metals and nonmetals. These are called metalloids.

So, we have metalloids - Boron (B), Silicon (Si), Germanium (Ge), Arsenic (As), Antimony (Sb), Tellurium (Te) and Astatine (At).
Out of these, Silicon is a metalloid in the third period.
Silicon belongs to the third period, 14th group. The elements in this group are also known as Carbon family. Atomic number of Silicon is 14 and its electronic configuration is \[{\text{1}}{{\text{s}}^2}{\text{ 2}}{{\text{s}}^2}{\text{ 2}}{{\text{p}}^6}{\text{ 3}}{{\text{s}}^2}{\text{ 3}}{{\text{p}}^2}\].
Additional information: Metalloids generally have metallic appearance but they are brittle. Their chemical properties show close similarity with non-metals. Metalloids are mostly used as alloys, biological agents and catalysts. They are of extreme use in semiconductors and electronics. In the modern periodic table, metalloids lie on either side of the line dividing metals from nonmetals.
Silicon is a brittle, crystalline solid with a bluish grey metallic lustre. It rarely occurs in its purest form in earth’s crust. It is mostly found as dust, sand and clay. In these forms, it is used in construction works. Cast iron contains silicon. Silicon is also widely used in making semiconductors and in production of fire bricks.
Note: Total 7 metalloids are found in the modern periodic table, out of this, Silicon is from the third period. Silicon has tremendous uses, especially in semiconductors.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




