
Write the equation involved in the following reactions:
(i) Reimer-Tiemann reaction
(ii) Kolbe’s reaction
Answer
530.3k+ views
Hint: You can use these hints to make this question easier for you (i) Formylation of phenols with chloroform is known as Reimer- Tiemann reaction. (ii) Kolbe process is a reaction that proceeds by heating sodium phenoxide with carbon dioxide.
Complete step by step answer:
Let’s discuss each reaction with proper mechanism -
Reimer-Tiemann reaction - The Reimer–Tiemann reaction is a chemical reaction used for the ortho-formylation of phenols; with the simplest example being the conversion of phenol to salicylaldehyde.
When phenols i.e. $C_6H_5OH$ is treated with $CHCl_3$ (chloroform) in the presence of NaOH (sodium hydroxide), an aldehyde group (-CHO) is introduced at the ortho position of benzene ring leading to the formation of o-hydroxybenzaldehyde (salicylaldehyde).
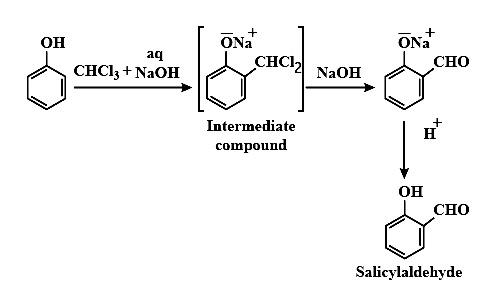
Kolbe’s reaction - Kolbe process or Kolbe–Schmitt reaction is a carboxylation chemical reaction that proceeds by heating sodium phenoxide with carbon dioxide under pressure, then treating the product with sulfuric acid.
The final product is an aromatic hydroxy acid which is also known as salicylic acid.

Therefore, we wrote the equation involved in the Reimer-Tiemann reaction and Kolbe’s reaction.
Additional information:
The Kolbe electrolysis involves the formation of symmetrical hydrocarbons through the coupling of radicals generated from carboxylic acid at an anode via electrolysis. This reaction is useful for the preparation of hydrocarbons.
Note: Here we observe that in the Reimer Tiemann reaction the ortho product is major.
Because the inductive effect dies with distance, so the ortho position will be more electron-rich as compared to the para position, and the incoming electrophile (carbene) will attack the ortho carbon. That's why ortho isomer is the major product.
Complete step by step answer:
Let’s discuss each reaction with proper mechanism -
Reimer-Tiemann reaction - The Reimer–Tiemann reaction is a chemical reaction used for the ortho-formylation of phenols; with the simplest example being the conversion of phenol to salicylaldehyde.
When phenols i.e. $C_6H_5OH$ is treated with $CHCl_3$ (chloroform) in the presence of NaOH (sodium hydroxide), an aldehyde group (-CHO) is introduced at the ortho position of benzene ring leading to the formation of o-hydroxybenzaldehyde (salicylaldehyde).

Kolbe’s reaction - Kolbe process or Kolbe–Schmitt reaction is a carboxylation chemical reaction that proceeds by heating sodium phenoxide with carbon dioxide under pressure, then treating the product with sulfuric acid.
The final product is an aromatic hydroxy acid which is also known as salicylic acid.

Therefore, we wrote the equation involved in the Reimer-Tiemann reaction and Kolbe’s reaction.
Additional information:
The Kolbe electrolysis involves the formation of symmetrical hydrocarbons through the coupling of radicals generated from carboxylic acid at an anode via electrolysis. This reaction is useful for the preparation of hydrocarbons.
Note: Here we observe that in the Reimer Tiemann reaction the ortho product is major.
Because the inductive effect dies with distance, so the ortho position will be more electron-rich as compared to the para position, and the incoming electrophile (carbene) will attack the ortho carbon. That's why ortho isomer is the major product.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




