
How do you write the equation for a hyperbola given vertices (0, -4) and (0, 4), conjugate axis of length 14 units?
Answer
562.5k+ views
Hint: Consider the major axis of the hyperbola as y – axis and the conjugate axis as the x – axis. Write the general equation of the hyperbola for this condition as: - \[\dfrac{-{{x}^{2}}}{{{a}^{2}}}+\dfrac{{{y}^{2}}}{{{b}^{2}}}=1\]. Use the formula: - length of conjugate axis = 2a and substitute it with 14 to find the value of ‘a’. Now, find the distance of one of the vertices from the origin and equate it with ‘b’ to find its value. Finally, substitute the values of ‘a’ and ‘b’ in the general equation of hyperbola to get the answer.
Complete step by step answer:
Here, we have been provided with the vertices of a hyperbola and length of its conjugate axis and we have been asked to write the equation of this hyperbola.
Now, we can see that the vertices of the hyperbola provided are (0, -4) and (0, 4). Since these points will lie on the y – axis therefore we will assume the major axis of the hyperbola as y – axis and the conjugate axis as x – axis. Let us draw a diagram of this type of hyperbola.
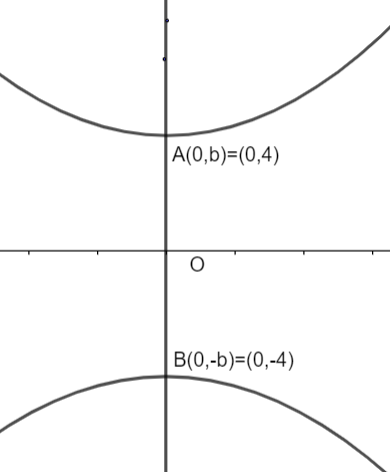
Now, general equation of this type of hyperbola is given as: - \[\dfrac{-{{x}^{2}}}{{{a}^{2}}}+\dfrac{{{y}^{2}}}{{{b}^{2}}}=1\], where ‘a’ denotes the half of the length of the conjugate axis and ‘b’ denotes the half of the length of the major axis, i.e., distance of the origin from one of the vertices. So, let us determine the values of ‘a’ and ‘b’.
\[\because \] Length of conjugate axis = 14 units
\[\Rightarrow \] Half of the length of conjugate axis = 7 units
\[\Rightarrow \] a = 7 units
Clearly, we can see that in the figure the length of vertex A or vertex B from the origin is 4 units. So, we have,
b = 4 units
Therefore, substituting the numerical values of ‘a’ and ‘b’ in the general equation of hyperbola, we get,
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{-{{x}^{2}}}{{{7}^{2}}}+\dfrac{{{y}^{2}}}{{{4}^{2}}}=1 \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{-{{x}^{2}}}{49}+\dfrac{{{y}^{2}}}{16}=1 \\
\end{align}\]
Hence, the above equation is our answer.
Note: One may note that there are two types of hyperbola, one in which the major axis lies on the x – axis and the other in which it lies on the y – axis. In the above question it was lying on the y – axis, if it would have lied on the x – axis then the general equation would have been \[\dfrac{{{x}^{2}}}{{{a}^{2}}}-\dfrac{{{y}^{2}}}{{{b}^{2}}}=1\]. The roles of ‘a’ and ‘b’ would have got reversed as the vertices would have been present on the x – axis. So, you must know about both the cases to detect the difference.
Complete step by step answer:
Here, we have been provided with the vertices of a hyperbola and length of its conjugate axis and we have been asked to write the equation of this hyperbola.
Now, we can see that the vertices of the hyperbola provided are (0, -4) and (0, 4). Since these points will lie on the y – axis therefore we will assume the major axis of the hyperbola as y – axis and the conjugate axis as x – axis. Let us draw a diagram of this type of hyperbola.

Now, general equation of this type of hyperbola is given as: - \[\dfrac{-{{x}^{2}}}{{{a}^{2}}}+\dfrac{{{y}^{2}}}{{{b}^{2}}}=1\], where ‘a’ denotes the half of the length of the conjugate axis and ‘b’ denotes the half of the length of the major axis, i.e., distance of the origin from one of the vertices. So, let us determine the values of ‘a’ and ‘b’.
\[\because \] Length of conjugate axis = 14 units
\[\Rightarrow \] Half of the length of conjugate axis = 7 units
\[\Rightarrow \] a = 7 units
Clearly, we can see that in the figure the length of vertex A or vertex B from the origin is 4 units. So, we have,
b = 4 units
Therefore, substituting the numerical values of ‘a’ and ‘b’ in the general equation of hyperbola, we get,
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{-{{x}^{2}}}{{{7}^{2}}}+\dfrac{{{y}^{2}}}{{{4}^{2}}}=1 \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{-{{x}^{2}}}{49}+\dfrac{{{y}^{2}}}{16}=1 \\
\end{align}\]
Hence, the above equation is our answer.
Note: One may note that there are two types of hyperbola, one in which the major axis lies on the x – axis and the other in which it lies on the y – axis. In the above question it was lying on the y – axis, if it would have lied on the x – axis then the general equation would have been \[\dfrac{{{x}^{2}}}{{{a}^{2}}}-\dfrac{{{y}^{2}}}{{{b}^{2}}}=1\]. The roles of ‘a’ and ‘b’ would have got reversed as the vertices would have been present on the x – axis. So, you must know about both the cases to detect the difference.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

What organs are located on the left side of your body class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a labelled diagram of the human heart and label class 11 biology CBSE

What is 1s 2s 2p 3s 3p class 11 chemistry CBSE




