
Write the electronic configuration based on molecular orbital theory for the molecular orbital of helium \[\text{H}{{\text{e}}_{\text{2}}}\] molecule. Calculate its bond order and comment on its magnetic property.
Answer
573k+ views
Hint:Molecular Orbital Theory is the quantum mechanical way of describing the electronic arrangement of the electrons in a molecule. The atomic orbitals combine to form low energy bonding and high energy antibonding orbitals.
Complete answer:
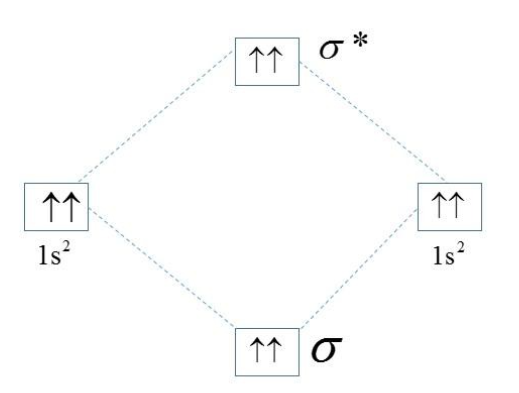
In the helium atom, there are two electrons in the valance 1s orbital. The other helium atom also has two electrons hence the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) of the 1s orbitals lead to the formation of a sigma bonding and antibonding orbitals. So one electron pair goes to the bonding while the other one goes to the antibonding molecular orbital. The bond order between any two atoms in a molecule has the formula,
$\text{B}\text{.O}\text{.=}\dfrac{\text{No}\text{. of bonding electrons -No}\text{. of antibonding electrons}}{\text{2}}$ .
For the helium atom, the number of bonding electrons and the number of antibonding electrons are the same and equal to two. Hence the bond order.
$\text{B}\text{.O}\text{.=}\dfrac{\text{2 - 2}}{\text{2}}=\dfrac{0}{2}$= 0.
Hence, there cannot be any bond between the helium atoms as the bond order between the atoms is zero. As there are no unpaired electrons in the atom of the helium, its magnetic moment is equal to zero.
Note:
According to the molecular orbital theory, the electrons in a molecule are arranged in three different molecular orbitals: the bonding, the anti-bonding, and the non-bonding molecular orbitals. The bonding and the antibonding orbitals can be further divided into sigma and pi molecular orbitals. These orbitals are as a result of the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) resulting from the bonds between different atoms.
Complete answer:
In the helium atom, there are two electrons in the valance 1s orbital. The other helium atom also has two electrons hence the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) of the 1s orbitals lead to the formation of a sigma bonding and antibonding orbitals. So one electron pair goes to the bonding while the other one goes to the antibonding molecular orbital. The bond order between any two atoms in a molecule has the formula,
$\text{B}\text{.O}\text{.=}\dfrac{\text{No}\text{. of bonding electrons -No}\text{. of antibonding electrons}}{\text{2}}$ .
For the helium atom, the number of bonding electrons and the number of antibonding electrons are the same and equal to two. Hence the bond order.
$\text{B}\text{.O}\text{.=}\dfrac{\text{2 - 2}}{\text{2}}=\dfrac{0}{2}$= 0.
Hence, there cannot be any bond between the helium atoms as the bond order between the atoms is zero. As there are no unpaired electrons in the atom of the helium, its magnetic moment is equal to zero.

Note:
According to the molecular orbital theory, the electrons in a molecule are arranged in three different molecular orbitals: the bonding, the anti-bonding, and the non-bonding molecular orbitals. The bonding and the antibonding orbitals can be further divided into sigma and pi molecular orbitals. These orbitals are as a result of the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) resulting from the bonds between different atoms.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

Name the part of the brain responsible for the precision class 11 biology CBSE

The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to AEffect class 11 biology CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE




