
Write the electron dot structure for magnesium and chlorine. Show the formation of magnesium chloride by the transfer of electrons. What are the ions present in this compound?
Answer
539.1k+ views
Hint: To draw the electron dot structure, we have to first write the electronic configuration of the element then find the valence shell and find the valence electrons. These electrons are drawn as dots around the symbol of the element. The electrons are transferred from the electron-rich to the electron-deficient element.
Complete answer:
First, we have to draw the electron dot structure of magnesium and chlorine, to draw electron dot structure we have to write the electron configuration of magnesium and chlorine.
Magnesium has atomic number 12, so there are 12 electrons in magnesium atom. Its electronic configuration will be:
$1{{s}^{2}}2{{s}^{2}}2{{p}^{6}}3{{s}^{2}}$
Chlorine has atomic number 17, so there are 17 electrons in chlorine atom. Its electronic configuration will be:
$1{{s}^{2}}2{{s}^{2}}2{{p}^{6}}3{{s}^{2}}3{{p}^{5}}$
In magnesium, valence electrons are 2 and in chlorine, valence electrons are 7
The electron dot structure of magnesium is given below:
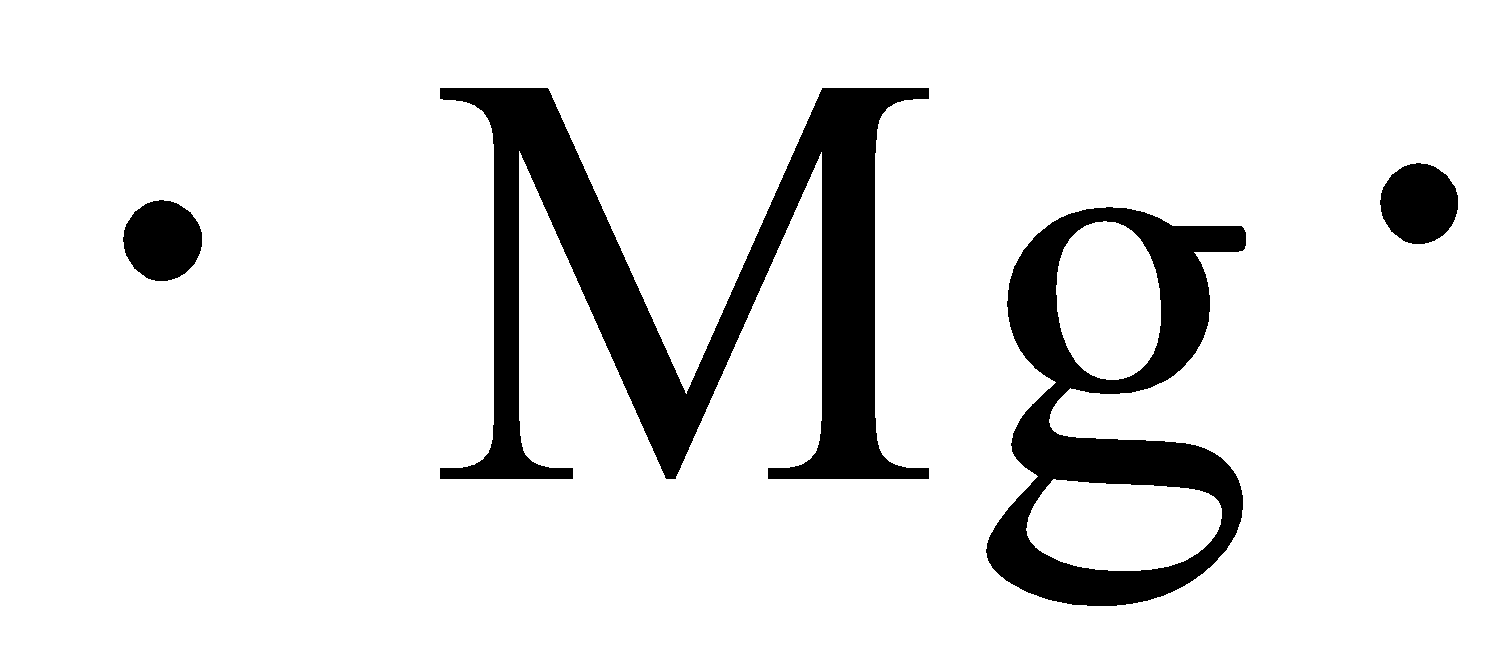
The electron dot structure of chlorine is given below:
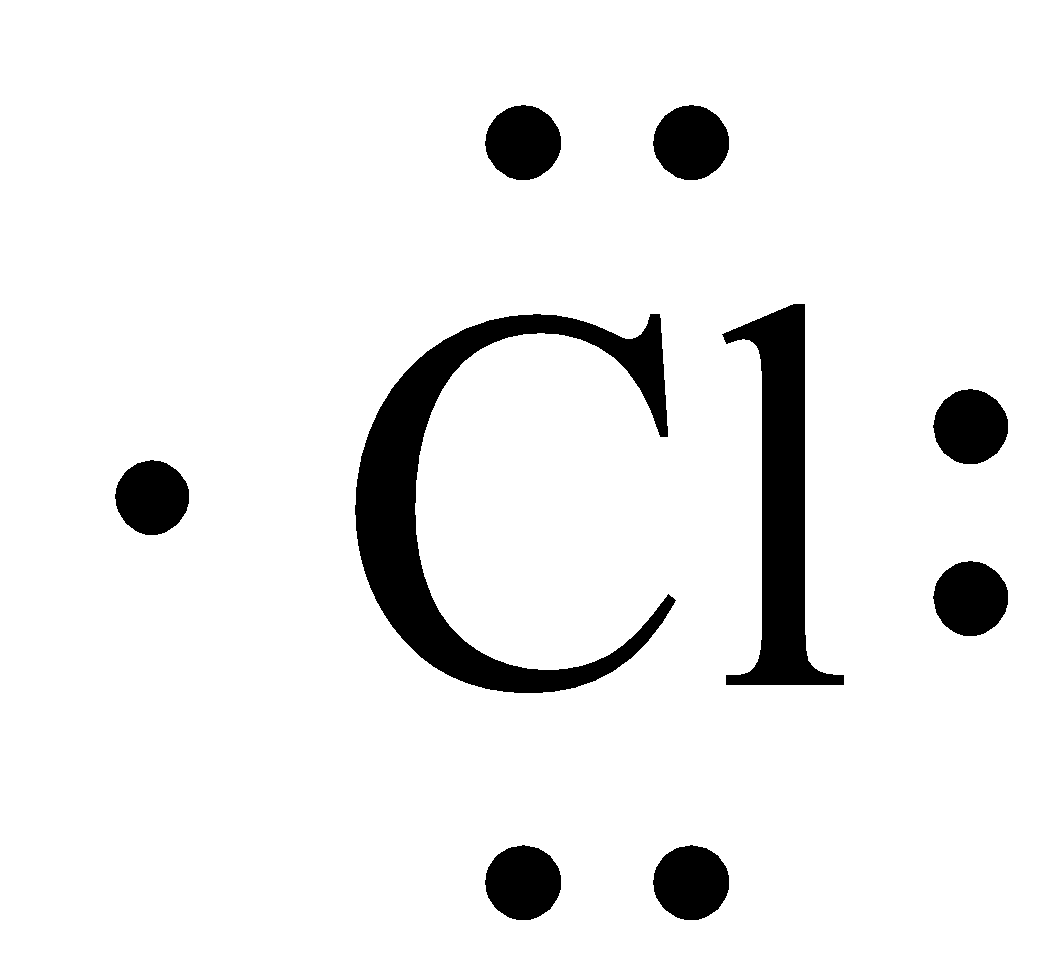
When 2 chlorine atoms and magnesium atoms combine by transfer of electrons then magnesium chloride is formed by transfer of electrons. Chlorine atom needs only one electron to complete its octet and magnesium cal removes two electrons to complete its octet. The transfer of electrons is given below:
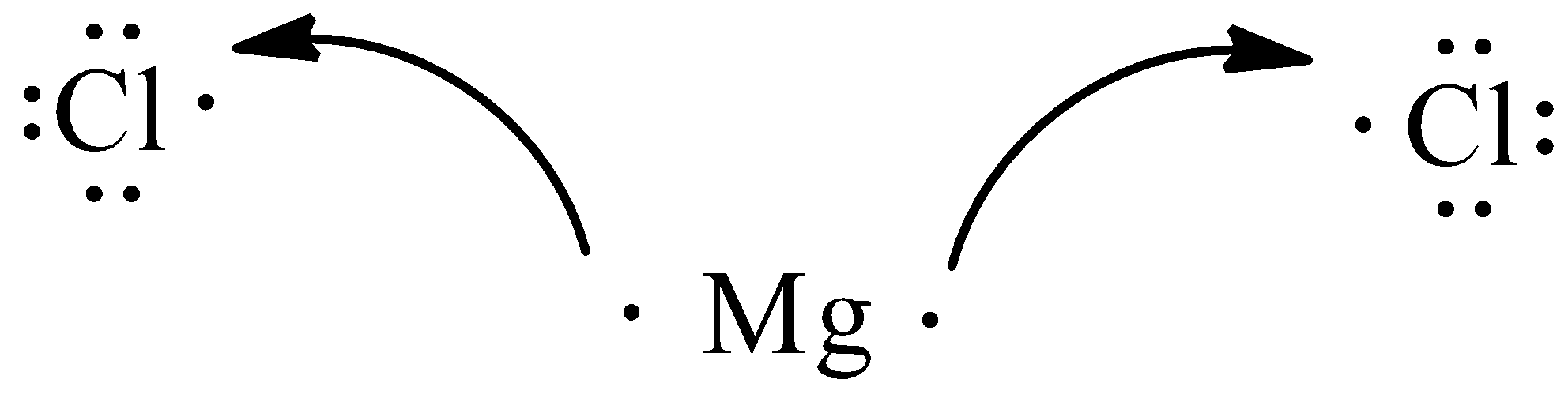
This will form $MgC{{l}_{2}}$.
There are two ions involved in the formation of magnesium chloride, two electrons are removed from the magnesium ion, then the cation will be $M{{g}^{2+}}$, and one electron is gained by the chlorine, that will form $C{{l}^{-}}$ anion.
Note:
When you write the electron dot structure, all the electrons of the valence shell should be considered, valence shell is the last shell in the electronic configuration, and in both the magnesium and chlorine, the valence shell is 3.
Complete answer:
First, we have to draw the electron dot structure of magnesium and chlorine, to draw electron dot structure we have to write the electron configuration of magnesium and chlorine.
Magnesium has atomic number 12, so there are 12 electrons in magnesium atom. Its electronic configuration will be:
$1{{s}^{2}}2{{s}^{2}}2{{p}^{6}}3{{s}^{2}}$
Chlorine has atomic number 17, so there are 17 electrons in chlorine atom. Its electronic configuration will be:
$1{{s}^{2}}2{{s}^{2}}2{{p}^{6}}3{{s}^{2}}3{{p}^{5}}$
In magnesium, valence electrons are 2 and in chlorine, valence electrons are 7
The electron dot structure of magnesium is given below:
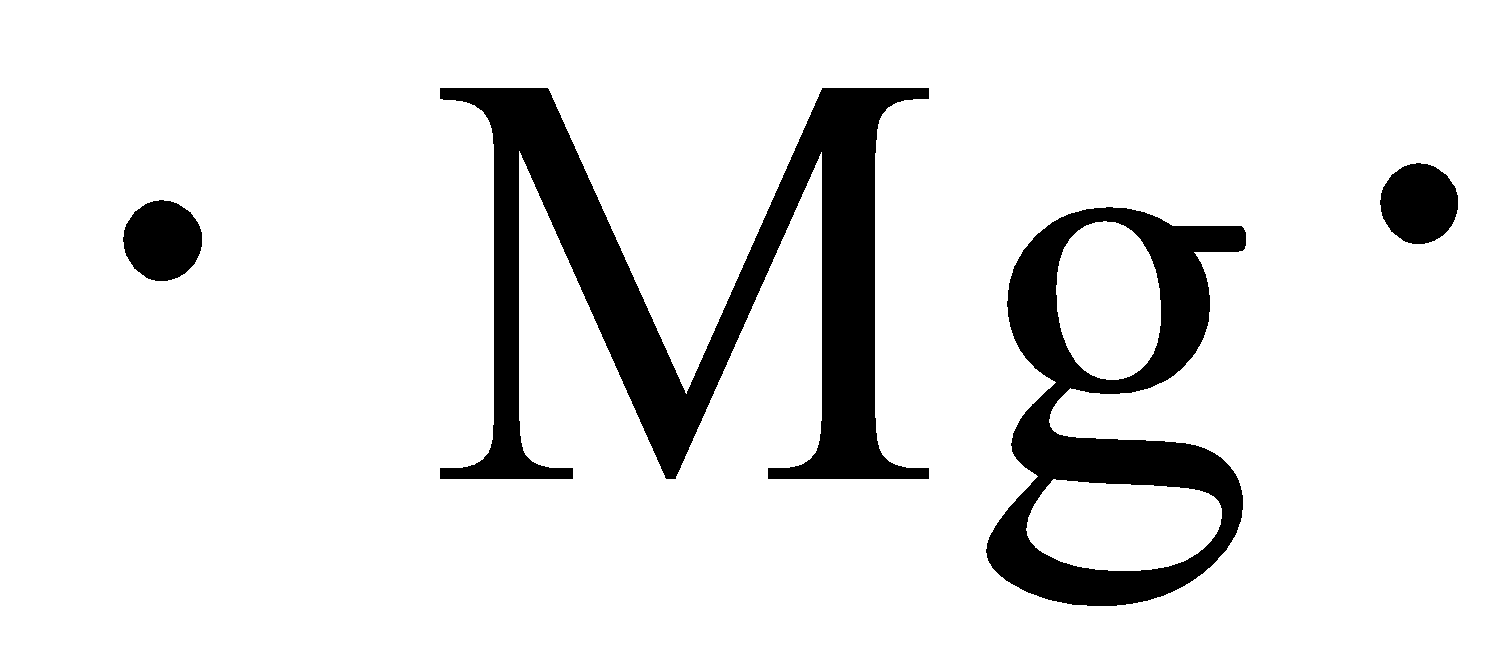
The electron dot structure of chlorine is given below:
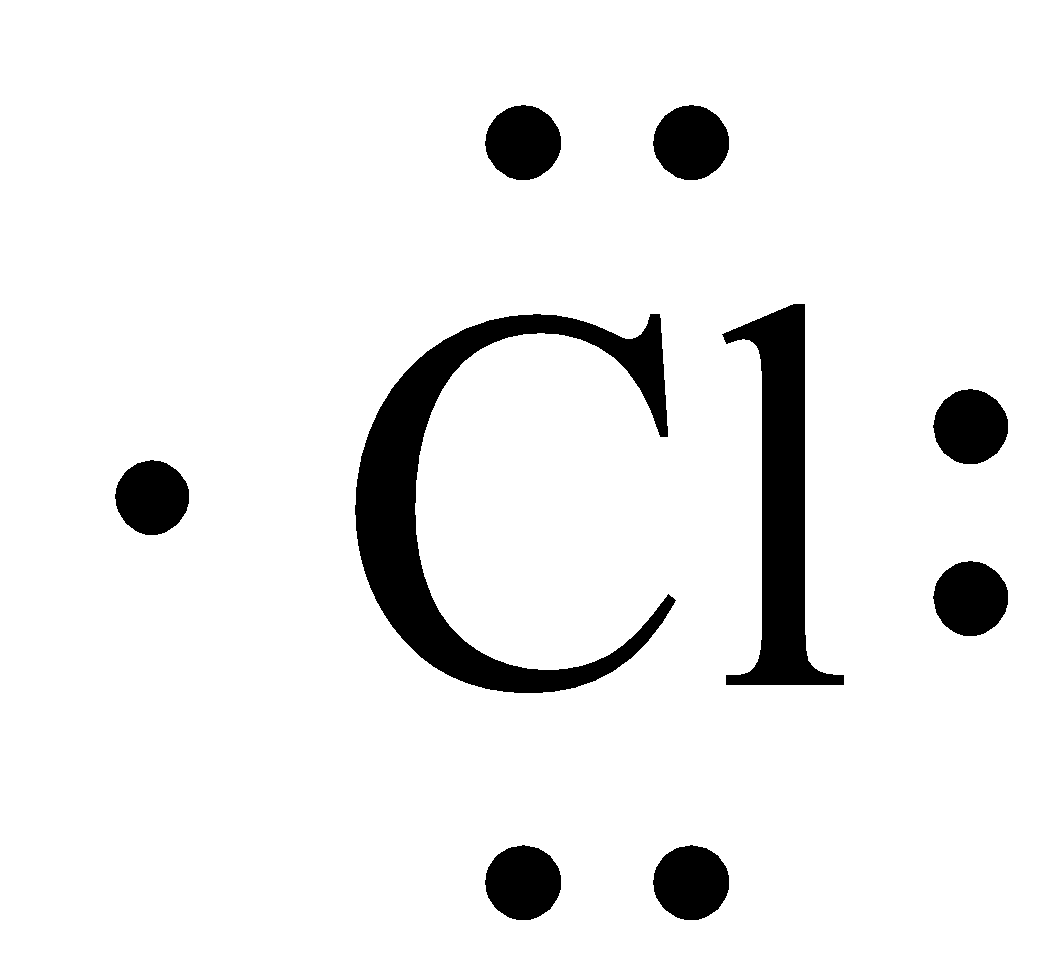
When 2 chlorine atoms and magnesium atoms combine by transfer of electrons then magnesium chloride is formed by transfer of electrons. Chlorine atom needs only one electron to complete its octet and magnesium cal removes two electrons to complete its octet. The transfer of electrons is given below:
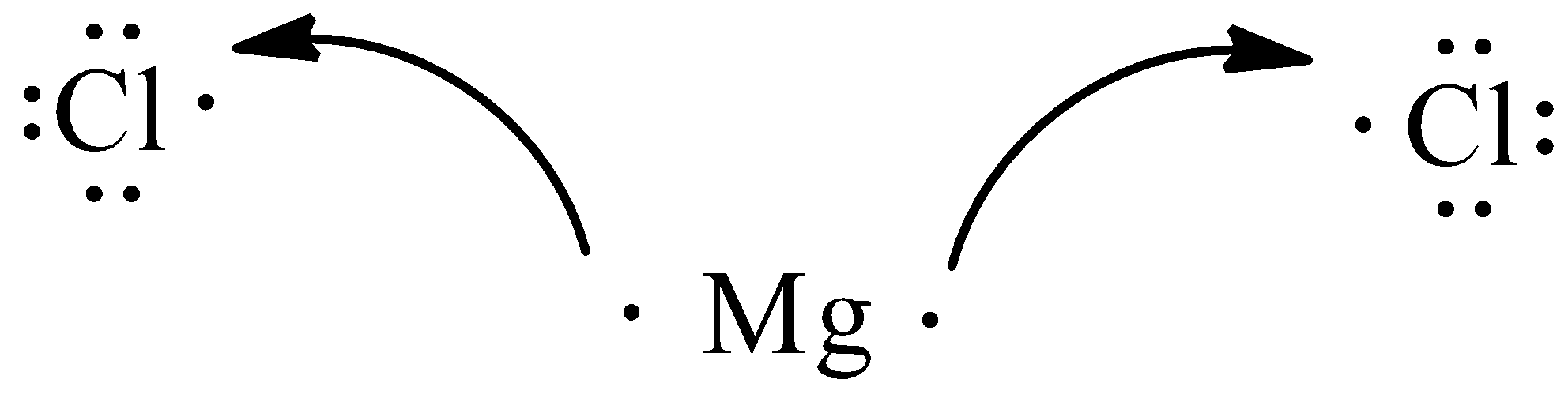
This will form $MgC{{l}_{2}}$.
There are two ions involved in the formation of magnesium chloride, two electrons are removed from the magnesium ion, then the cation will be $M{{g}^{2+}}$, and one electron is gained by the chlorine, that will form $C{{l}^{-}}$ anion.
Note:
When you write the electron dot structure, all the electrons of the valence shell should be considered, valence shell is the last shell in the electronic configuration, and in both the magnesium and chlorine, the valence shell is 3.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

Name the part of the brain responsible for the precision class 11 biology CBSE

The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to AEffect class 11 biology CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE




