
Write the chemical name and formula for Hinsberg’s reagent.
Answer
501.6k+ views
Hint: Hinsberg reagent is an alternative name for Benzene Sulfonyl Chloride. This name is given for its use in the Hinsberg test for the detection and distinction of primary, secondary, and tertiary amines in a given sample.
Complete answer:
We need to know if this reagent is an organo sulfur compound. Its chemical formula can be written as \[{C_6}{H_5}S{O_2}Cl\]. The appearance of Hinsberg reagent can be described as colorless oil that is viscous in nature and is soluble in organic solvents.
This Reagent undergoes reaction with compounds that contain $O - H$ and $N - H$ bonds that are reactive in nature. It is used in the preparation of sulfonamides (via reaction with amines) and sulfonamide esters (via reaction with alcohol).
Hinsberg’s reagent can be prepared by the chlorination of benzene sulfonic acid or the salts of benzene sulfonic acid with phosphorus oxychloride (\[POC{l_3}\]) gives the required reagent.
Another way to prepare the required Hinsberg’s Reagent is by reacting benzene with chloro sulfuric acid (chemical formula \[HS{O_3}Cl\]). Both these methods for the preparation of the required reagent are given below.
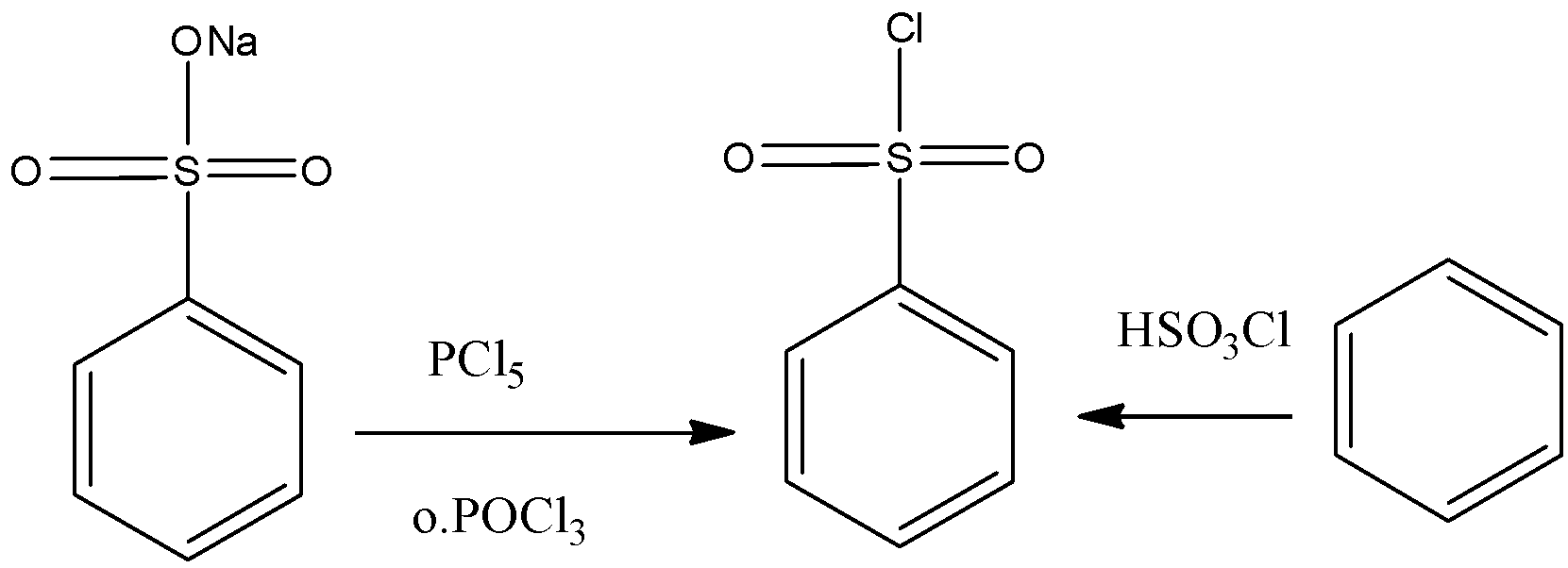
Hinsberg test is a chemical reaction that is used to distinguish between primary, secondary, and tertiary amines. The Hinsberg reagent can be used to react with primary, secondary, and tertiary amines. These differences are observed in the solubility of the sulfonamide product in alkali.
Note:
We need to know that in the Hinsberg Test, the amines act as nucleophiles and attack the electrophile (sulfonyl chloride). This leads to the displacement of the chloride and the generation of the sulfonamides. When primary and secondary amines form sulfonamides, this sulfonamide product is not soluble and precipitates from the solution as a solid.
Complete answer:
We need to know if this reagent is an organo sulfur compound. Its chemical formula can be written as \[{C_6}{H_5}S{O_2}Cl\]. The appearance of Hinsberg reagent can be described as colorless oil that is viscous in nature and is soluble in organic solvents.
This Reagent undergoes reaction with compounds that contain $O - H$ and $N - H$ bonds that are reactive in nature. It is used in the preparation of sulfonamides (via reaction with amines) and sulfonamide esters (via reaction with alcohol).
Hinsberg’s reagent can be prepared by the chlorination of benzene sulfonic acid or the salts of benzene sulfonic acid with phosphorus oxychloride (\[POC{l_3}\]) gives the required reagent.
Another way to prepare the required Hinsberg’s Reagent is by reacting benzene with chloro sulfuric acid (chemical formula \[HS{O_3}Cl\]). Both these methods for the preparation of the required reagent are given below.

Hinsberg test is a chemical reaction that is used to distinguish between primary, secondary, and tertiary amines. The Hinsberg reagent can be used to react with primary, secondary, and tertiary amines. These differences are observed in the solubility of the sulfonamide product in alkali.
Note:
We need to know that in the Hinsberg Test, the amines act as nucleophiles and attack the electrophile (sulfonyl chloride). This leads to the displacement of the chloride and the generation of the sulfonamides. When primary and secondary amines form sulfonamides, this sulfonamide product is not soluble and precipitates from the solution as a solid.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




