
Write short notes on the ornithine cycle.
Answer
596.1k+ views
Hint: A cycle of reactions that occur due to the formation of urea from ammonia to convert it into a less toxic waste for the removal outside the body.
Complete answer:
The ornithine cycle, also known as the urea cycle which converts the highly toxic ammonia to urea for the excretion. It occurs mostly in uricotelic organisms. Most aquatic organisms, or ammonotelic animals, excrete ammonia without converting it into urea. This occurs because of the amino acid catabolism which results in the formation of ammonia as a waste product.
The organisms need to remove this ammonia waste product from their body as it is highly toxic. Few organisms cannot easily remove nitrogen from ammonia, these organisms convert the ammonia into less toxic substances like urea and uric acid with the help of the ornithine cycle. This cycle occurs mainly in the liver of an organism.
The urea produced in the liver is then passed into the bloodstream from where it travels to the kidneys and gets filtered resulting in the excretion of the urine. The ornithine cycle is very significant in the case of those organisms which cannot convert ammonia into urea and this will become deadly for the organism.
The ammonia which is converted into uric acid is mostly excreted in the solid form. This cycle is generally found in birds and insects.
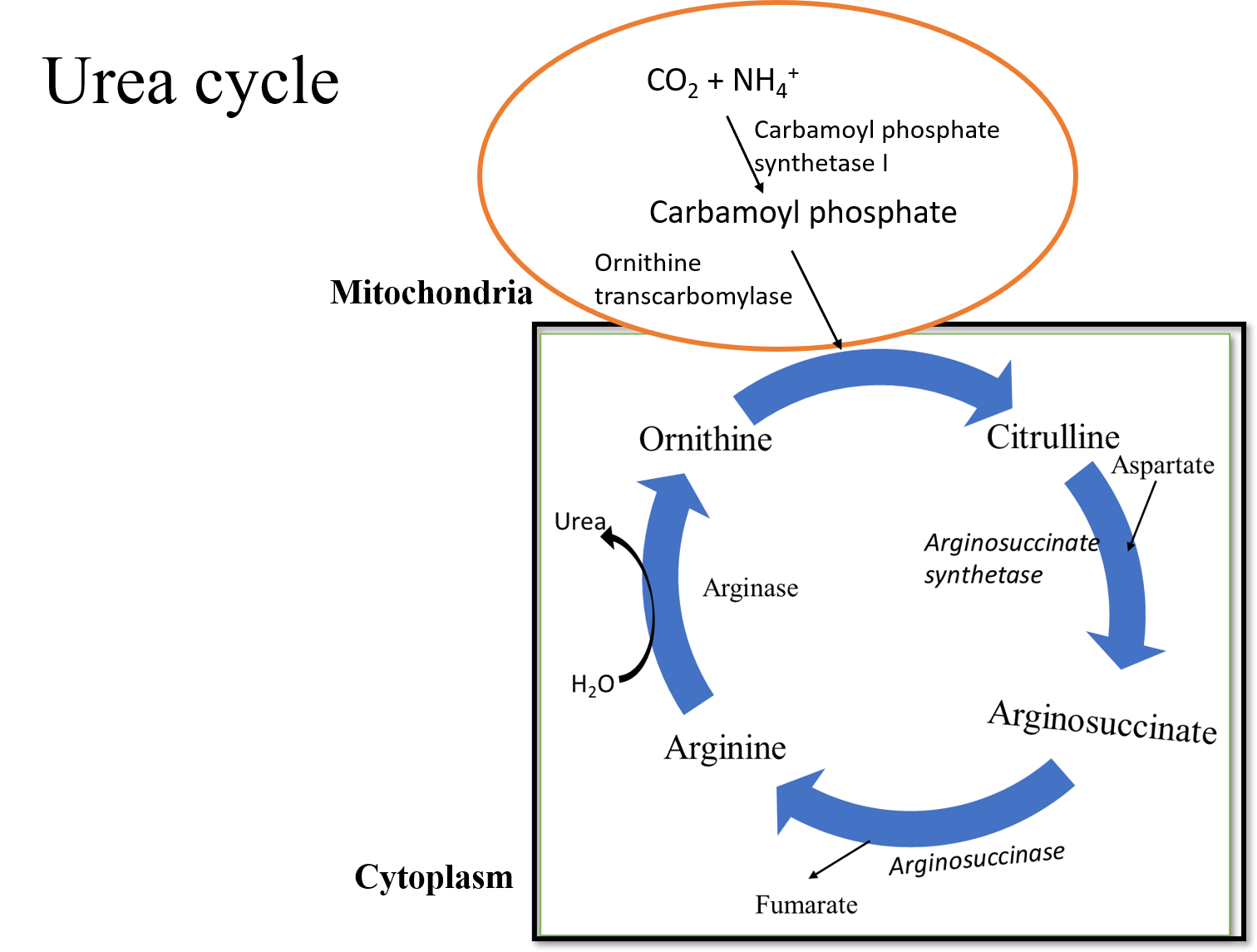
Note: During protein metabolism, excess nitrogen is eliminated from nitrogen compounds resulting in nitrogenous wastes. These nitrogenous wastes can be ammonia, urea, uric acid, and creatinine. The organisms which excrete ammonia are called ammonotelic, those organisms which excrete urea are called ureotelic, and those organisms which excrete uric acid are called uricotelic.
Complete answer:
The ornithine cycle, also known as the urea cycle which converts the highly toxic ammonia to urea for the excretion. It occurs mostly in uricotelic organisms. Most aquatic organisms, or ammonotelic animals, excrete ammonia without converting it into urea. This occurs because of the amino acid catabolism which results in the formation of ammonia as a waste product.
The organisms need to remove this ammonia waste product from their body as it is highly toxic. Few organisms cannot easily remove nitrogen from ammonia, these organisms convert the ammonia into less toxic substances like urea and uric acid with the help of the ornithine cycle. This cycle occurs mainly in the liver of an organism.
The urea produced in the liver is then passed into the bloodstream from where it travels to the kidneys and gets filtered resulting in the excretion of the urine. The ornithine cycle is very significant in the case of those organisms which cannot convert ammonia into urea and this will become deadly for the organism.
The ammonia which is converted into uric acid is mostly excreted in the solid form. This cycle is generally found in birds and insects.

Note: During protein metabolism, excess nitrogen is eliminated from nitrogen compounds resulting in nitrogenous wastes. These nitrogenous wastes can be ammonia, urea, uric acid, and creatinine. The organisms which excrete ammonia are called ammonotelic, those organisms which excrete urea are called ureotelic, and those organisms which excrete uric acid are called uricotelic.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

Name the part of the brain responsible for the precision class 11 biology CBSE

The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to AEffect class 11 biology CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE




