
Write out the electron configuration for neutral bromine. Draw the Lewis dot structure. Which depiction allows for a better understanding of electrons involved in bonding? Explain your reasoning.
Answer
486.3k+ views
Hint: Each electron is described as travelling independently in an orbital in an average field created by all other orbitals in electronic setups. Configurations are described mathematically by Slater determinants or configuration state functions. According to quantum mechanics, each electron configuration has a level of energy associated with it, and electrons can migrate from one configuration to another by emitting or absorbing a quantum of energy in the form of a photon under particular conditions.
Complete answer:
Bromine is an atomic number 35 chemical element with the symbol Br. It's the third-lightest halogen, and at room temperature, it's a seething red-brown liquid that quickly evaporates to form a similar-coloured vapour. Bromine is a highly reactive element that only occurs in nature as colourless soluble crystalline mineral halide salts, similar to table salt.
The elemental form of bromine, Br is bromine, or dibromine, $B{{r}_{2}}$ . Bromine does not occur naturally in the form of free bromine; instead, it is found in the form of mineral halide salts. Bromine is a fuming, red-brown liquid that is corrosive and poisonous, with a strong disagreeable and suffocating odour at room temperature.
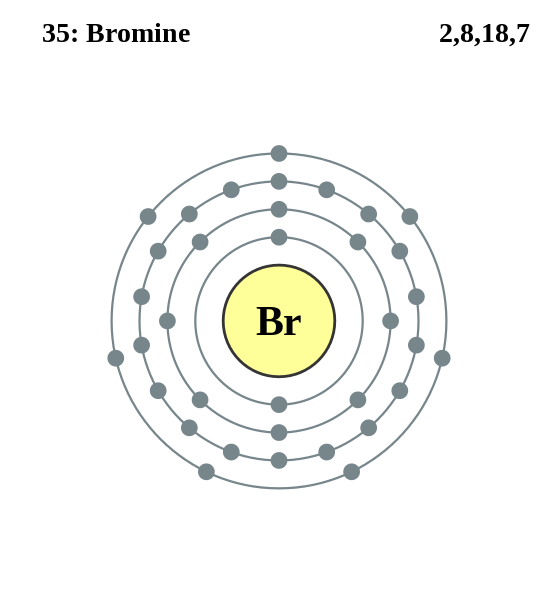
Electronic configuration = \[\text{1}{{\text{s}}^{\text{2}}}\text{ 2}{{\text{s}}^{\text{2}}}\text{ 2}{{\text{p}}^{\text{6}}}\text{ 3}{{\text{s}}^{\text{2}}}\text{ 3}{{\text{p}}^{\text{6}}}\text{ 4}{{\text{s}}^{\text{2}}}\text{ 3}{{\text{d}}^{\text{10}}}\text{ 4}{{\text{p}}^{\text{5}}}\]
\[:\underset{\ \centerdot \text{ }\centerdot }{\overset{\text{ }\centerdot \text{ }\centerdot }{\mathop{Br}}}\,\cdot \text{ }+\text{ }:\underset{\ \centerdot \text{ }\centerdot }{\overset{\text{ }\centerdot \text{ }\centerdot }{\mathop{Br}}}\,\cdot \text{ }\to \text{ }:\underset{\ \centerdot \text{ }\centerdot }{\overset{\text{ }\centerdot \text{ }\centerdot }{\mathop{Br}}}\,-\underset{\ \centerdot \text{ }\centerdot }{\overset{\text{ }\centerdot \text{ }\centerdot }{\mathop{Br}}}\,:\]
The Lewis dot structure helps in better understanding.
Lewis structures are diagrams that depict the bonding between atoms in a molecule, as well as any lone pairs of electrons present. Any covalently bound molecule, as well as coordination compounds, can be represented by a Lewis structure. Gilbert N. Lewis introduced the Lewis structure in his 1916 article The Atom and the Molecule, and it was named after him. Lewis structures add lines between atoms to represent shared pairs in a chemical bond, extending the concept of the electron dot diagram.
Note:
It is a liquid at ordinary temperatures and pressures; the only other element that is liquid at comparable temperatures and pressures is mercury. Organobromine compounds quickly disintegrate at high temperatures to generate free bromine atoms, halting free radical chemical chain reactions. Organobromine compounds are effective as fire retardants because of this function, and more than half of the bromine produced each year is used for this reason. The same feature causes ozone depletion by dissociating volatile organobromine molecules in the atmosphere and releasing free bromine atoms.
Complete answer:
Bromine is an atomic number 35 chemical element with the symbol Br. It's the third-lightest halogen, and at room temperature, it's a seething red-brown liquid that quickly evaporates to form a similar-coloured vapour. Bromine is a highly reactive element that only occurs in nature as colourless soluble crystalline mineral halide salts, similar to table salt.
The elemental form of bromine, Br is bromine, or dibromine, $B{{r}_{2}}$ . Bromine does not occur naturally in the form of free bromine; instead, it is found in the form of mineral halide salts. Bromine is a fuming, red-brown liquid that is corrosive and poisonous, with a strong disagreeable and suffocating odour at room temperature.
Electronic configuration = \[\text{1}{{\text{s}}^{\text{2}}}\text{ 2}{{\text{s}}^{\text{2}}}\text{ 2}{{\text{p}}^{\text{6}}}\text{ 3}{{\text{s}}^{\text{2}}}\text{ 3}{{\text{p}}^{\text{6}}}\text{ 4}{{\text{s}}^{\text{2}}}\text{ 3}{{\text{d}}^{\text{10}}}\text{ 4}{{\text{p}}^{\text{5}}}\]

\[:\underset{\ \centerdot \text{ }\centerdot }{\overset{\text{ }\centerdot \text{ }\centerdot }{\mathop{Br}}}\,\cdot \text{ }+\text{ }:\underset{\ \centerdot \text{ }\centerdot }{\overset{\text{ }\centerdot \text{ }\centerdot }{\mathop{Br}}}\,\cdot \text{ }\to \text{ }:\underset{\ \centerdot \text{ }\centerdot }{\overset{\text{ }\centerdot \text{ }\centerdot }{\mathop{Br}}}\,-\underset{\ \centerdot \text{ }\centerdot }{\overset{\text{ }\centerdot \text{ }\centerdot }{\mathop{Br}}}\,:\]
The Lewis dot structure helps in better understanding.
Lewis structures are diagrams that depict the bonding between atoms in a molecule, as well as any lone pairs of electrons present. Any covalently bound molecule, as well as coordination compounds, can be represented by a Lewis structure. Gilbert N. Lewis introduced the Lewis structure in his 1916 article The Atom and the Molecule, and it was named after him. Lewis structures add lines between atoms to represent shared pairs in a chemical bond, extending the concept of the electron dot diagram.
Note:
It is a liquid at ordinary temperatures and pressures; the only other element that is liquid at comparable temperatures and pressures is mercury. Organobromine compounds quickly disintegrate at high temperatures to generate free bromine atoms, halting free radical chemical chain reactions. Organobromine compounds are effective as fire retardants because of this function, and more than half of the bromine produced each year is used for this reason. The same feature causes ozone depletion by dissociating volatile organobromine molecules in the atmosphere and releasing free bromine atoms.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

Name the part of the brain responsible for the precision class 11 biology CBSE

The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to AEffect class 11 biology CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE




