
Write down the equation of the line AB through (3, 2), parallel to the line $ 3x - 2y + 5 = 0 $ . AB meets x-axis at A and y-axis at B. Calculate the area of the triangle OAB when O is the origin.
Answer
590.1k+ views
Hint: Parallel lines will have the same slope. So, find the slope of the given equation (linear) from the question by converting the equation into slope-intercept form. The resulting slope is the slope for the required equation too. Substitute the slope value and coordinates (3, 2) in the point-slope form to get the new line equation. Convert the obtained line equation to x-intercept and y-intercept format (intercept form) and we will get the x and y coordinates which is the base and the height of the triangle OAB. Find the area of the triangle using formula by substituting its base and height.
Complete step-by-step answer:
We are given that the line AB is parallel to the line $ 3x - 2y + 5 = 0 $ and line AB passes through the point (3, 2). AB meets the x-axis at A and y-axis at B which means the y-coordinate of point A is zero and x-coordinate of point B is zero.
A= (x, 0); B= (0, y)
Convert the equation $ 3x - 2y + 5 = 0 $ into slope -intercept form $ y = mx + c $
$
3x - 2y + 5 = 0 \\
3x + 5 = 2y \\
2y = 3x + 5 \\
y = \dfrac{{3x + 5}}{2} \\
y = \dfrac{{3x}}{2} + \dfrac{5}{2} \\
y = \dfrac{3}{2}x + \dfrac{5}{2} \\
$
Comparing the above obtained equation with $ y = mx + c $ , we get $ m = \dfrac{3}{2},c = \dfrac{5}{2} $
Therefore, the slope of the required equation is $ \dfrac{3}{2} $ .
Substitute the slope and the point (3, 2) in the point-slope form of an equation $ y - {y_1} = m\left( {x - {x_1}} \right) $ to get the desired equation.
$
m = \dfrac{3}{2},\left( {{x_1},{y_1}} \right) = \left( {3,2} \right) \\
\to y - {y_1} = m\left( {x - {x_1}} \right) \\
\to y - 2 = \dfrac{3}{2}\left( {x - 3} \right) \\
\to 2\left( {y - 2} \right) = 3\left( {x - 3} \right) \\
\to 2y - 4 = 3x - 9 \\
\to 3x - 9 - 2y + 4 = 0 \\
\to 3x - 2y - 5 = 0 \\
$
Therefore, the new line equation if $ 3x - 2y - 5 = 0 $
Convert the above equation into intercept form which is $ \dfrac{x}{a} + \dfrac{y}{b} = 1 $
$ 3x - 2y = 5 $
Divide both sides by 5
$
\dfrac{{3x - 2y}}{5} = \dfrac{5}{5} \\
\dfrac{{3x}}{5} - \dfrac{{2y}}{5} = 1 \\
\dfrac{x}{{\left( {\dfrac{5}{3}} \right)}} - \dfrac{y}{{\left( {\dfrac{5}{2}} \right)}} = 1 \\
\dfrac{x}{{\left( {\dfrac{5}{3}} \right)}} + \dfrac{y}{{\left( { - \dfrac{5}{2}} \right)}} = 1 \\
\\
$
By comparing the above equation with $ \dfrac{x}{a} + \dfrac{y}{b} = 1 $
We get $ a = \dfrac{5}{3},b = - \dfrac{5}{2} $
Which means the x-coordinate of point A, y-coordinate of point B is $ \dfrac{5}{3}, - \dfrac{5}{2} $ respectively.
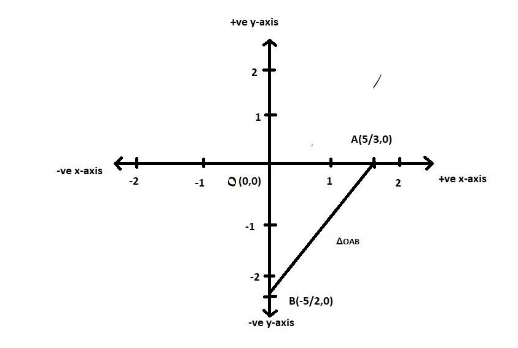
From the above diagram, we can see the triangle OAB with base OA and height OB
$ OA = \dfrac{5}{3},OB = - \dfrac{5}{2} $
Area of the triangle is $ \dfrac{1}{2} \times b \times h $
$
b = \dfrac{5}{3},h = - \dfrac{5}{2} \\
= \dfrac{1}{2} \times \dfrac{5}{3} \times \left| {\dfrac{{ - 5}}{2}} \right| \\
= \dfrac{{25}}{{12}}sq.units \\
$
As the area cannot be negative considered all the negative values as positive
Therefore, the area of triangle OAB where O is the origin is $ \dfrac{{25}}{{12}}sq.units $
Note: Do not confuse the different forms of line equations. Other types of line equations are Standard form, Two points form, Vertical form, Horizontal form etc.
Slope-intercept form of a linear equation $ y = mx + c $ where c is the y-intercept and ‘m’ is the slope.
Point-slope form of an equation is $ y - {y_1} = m\left( {x - {x_1}} \right) $
Intercept form of an equation is $ \dfrac{x}{a} + \dfrac{y}{b} = 1 $ where ‘a’ is the x-intercept and ‘b’ is the y-intercept.
Area of a triangle when base ’b’ and height ‘h’ is given is $ \dfrac{1}{2} \times b \times h $
Complete step-by-step answer:
We are given that the line AB is parallel to the line $ 3x - 2y + 5 = 0 $ and line AB passes through the point (3, 2). AB meets the x-axis at A and y-axis at B which means the y-coordinate of point A is zero and x-coordinate of point B is zero.
A= (x, 0); B= (0, y)
Convert the equation $ 3x - 2y + 5 = 0 $ into slope -intercept form $ y = mx + c $
$
3x - 2y + 5 = 0 \\
3x + 5 = 2y \\
2y = 3x + 5 \\
y = \dfrac{{3x + 5}}{2} \\
y = \dfrac{{3x}}{2} + \dfrac{5}{2} \\
y = \dfrac{3}{2}x + \dfrac{5}{2} \\
$
Comparing the above obtained equation with $ y = mx + c $ , we get $ m = \dfrac{3}{2},c = \dfrac{5}{2} $
Therefore, the slope of the required equation is $ \dfrac{3}{2} $ .
Substitute the slope and the point (3, 2) in the point-slope form of an equation $ y - {y_1} = m\left( {x - {x_1}} \right) $ to get the desired equation.
$
m = \dfrac{3}{2},\left( {{x_1},{y_1}} \right) = \left( {3,2} \right) \\
\to y - {y_1} = m\left( {x - {x_1}} \right) \\
\to y - 2 = \dfrac{3}{2}\left( {x - 3} \right) \\
\to 2\left( {y - 2} \right) = 3\left( {x - 3} \right) \\
\to 2y - 4 = 3x - 9 \\
\to 3x - 9 - 2y + 4 = 0 \\
\to 3x - 2y - 5 = 0 \\
$
Therefore, the new line equation if $ 3x - 2y - 5 = 0 $
Convert the above equation into intercept form which is $ \dfrac{x}{a} + \dfrac{y}{b} = 1 $
$ 3x - 2y = 5 $
Divide both sides by 5
$
\dfrac{{3x - 2y}}{5} = \dfrac{5}{5} \\
\dfrac{{3x}}{5} - \dfrac{{2y}}{5} = 1 \\
\dfrac{x}{{\left( {\dfrac{5}{3}} \right)}} - \dfrac{y}{{\left( {\dfrac{5}{2}} \right)}} = 1 \\
\dfrac{x}{{\left( {\dfrac{5}{3}} \right)}} + \dfrac{y}{{\left( { - \dfrac{5}{2}} \right)}} = 1 \\
\\
$
By comparing the above equation with $ \dfrac{x}{a} + \dfrac{y}{b} = 1 $
We get $ a = \dfrac{5}{3},b = - \dfrac{5}{2} $
Which means the x-coordinate of point A, y-coordinate of point B is $ \dfrac{5}{3}, - \dfrac{5}{2} $ respectively.

From the above diagram, we can see the triangle OAB with base OA and height OB
$ OA = \dfrac{5}{3},OB = - \dfrac{5}{2} $
Area of the triangle is $ \dfrac{1}{2} \times b \times h $
$
b = \dfrac{5}{3},h = - \dfrac{5}{2} \\
= \dfrac{1}{2} \times \dfrac{5}{3} \times \left| {\dfrac{{ - 5}}{2}} \right| \\
= \dfrac{{25}}{{12}}sq.units \\
$
As the area cannot be negative considered all the negative values as positive
Therefore, the area of triangle OAB where O is the origin is $ \dfrac{{25}}{{12}}sq.units $
Note: Do not confuse the different forms of line equations. Other types of line equations are Standard form, Two points form, Vertical form, Horizontal form etc.
Slope-intercept form of a linear equation $ y = mx + c $ where c is the y-intercept and ‘m’ is the slope.
Point-slope form of an equation is $ y - {y_1} = m\left( {x - {x_1}} \right) $
Intercept form of an equation is $ \dfrac{x}{a} + \dfrac{y}{b} = 1 $ where ‘a’ is the x-intercept and ‘b’ is the y-intercept.
Area of a triangle when base ’b’ and height ‘h’ is given is $ \dfrac{1}{2} \times b \times h $
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

What organs are located on the left side of your body class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

How do I convert ms to kmh Give an example class 11 physics CBSE




