
Write about the Carbylamine reaction.
Answer
594.9k+ views
Hint: The Carbylamine reaction is used to help distinguish primary amines from secondary and tertiary amines. It involves formation of carbene intermediate.
Complete answer:
Let us dive straight into what the carbylamine reaction is, does and its significance in the field of Organic Chemistry.
In general, the carbylamine reaction can be written as:
\[R-N{{H}_{2}}+CHC{{l}_{3}}+3KOH\to \underset{\text{Carbylamine}}{\mathop{R-NC}}\,+3KCl+3{{H}_{2}}O\]
- We can see that Chloroform, Potassium hydroxide and primary amine react to give carbylamine as a main product alongside salt and water. This reaction is also known as Hofmann isocyanide synthesis as carbylamine is also called isocyanide.
- The intermediate dichlorocarbene is involved in this reaction.
- In organic qualitative analysis, the carbylamine reaction is also called Hofmann’s isocyanide test. In this test, the test substance is heated with chloroform and alcoholic potassium hydroxide. So, if primary amine is present, it will form isocyanide and this can be observed by its foul smell.
- Let’s understand the mechanism and role of the intermediate in this reaction.
- In this reaction, the initial step of mechanism involves addition of an amine to the intermediate created from the dehydrohalogenation of chloroform. This intermediate is called dichlorocarbene.
- The first step is the dehydrohalogenation (removal of hydrogen halide from a given substrate) of chloroform to give dichlorocarbene intermediate. This dichlorocarbene intermediate is very reactive.
- Then, nitrogen of primary amine attacks the electrophilic carbon of dichlorocarbene to form a doubly charged intermediate. The elimination of the hydrochloric acid leads to the formation of isonitrile.
Formation of Dichlorocarbene:
\[CHC{{l}_{3}}\xrightarrow{KOH}\text{ }\underset{\text{Dichlorocarbene}}{\mathop{:CC{{l}_{2}}}}\,+HCl\]
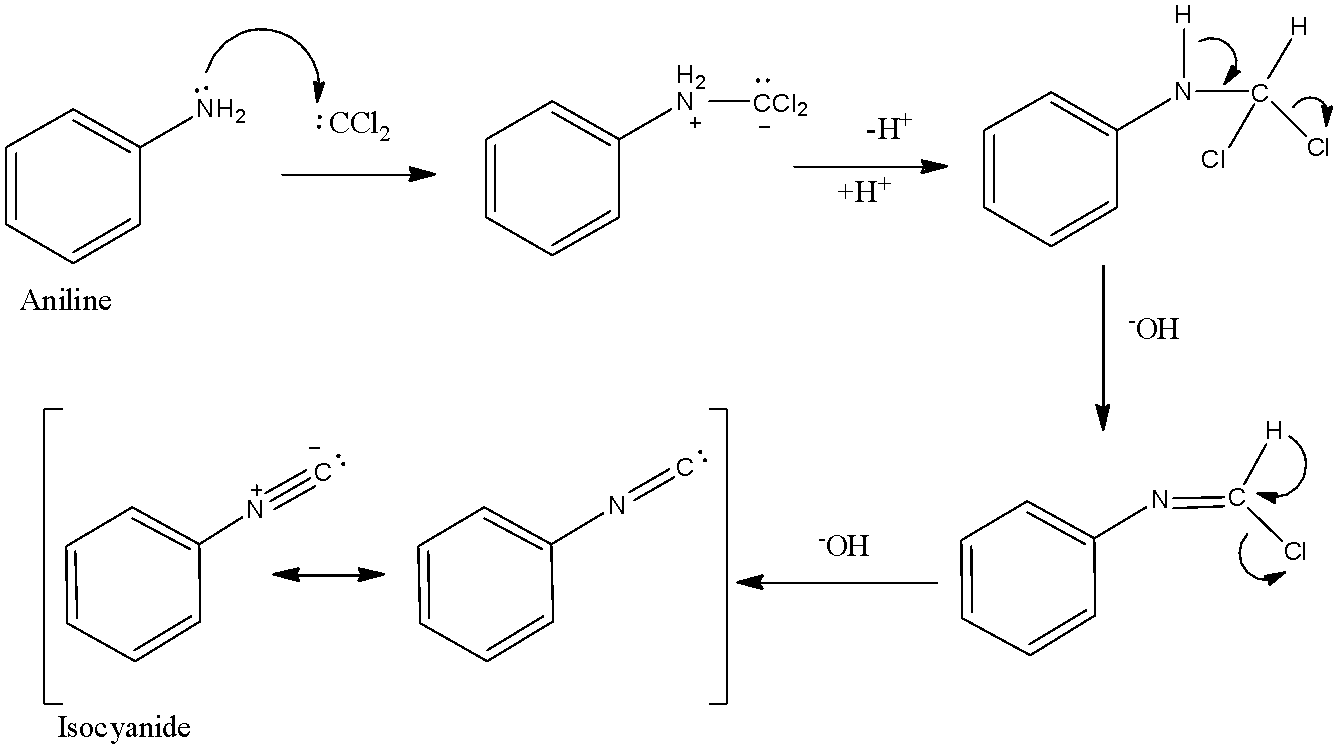
Note: Remember that carbylamine reaction cannot be used to synthesize isocyanides from secondary or tertiary amines because they have two or three alkyl groups on nitrogen atoms of amine and so that it cannot form a triple bond with carbon atom to form isocyanide. Note that chloroform is used here not only as a solvent but also as a reagent.
Complete answer:
Let us dive straight into what the carbylamine reaction is, does and its significance in the field of Organic Chemistry.
In general, the carbylamine reaction can be written as:
\[R-N{{H}_{2}}+CHC{{l}_{3}}+3KOH\to \underset{\text{Carbylamine}}{\mathop{R-NC}}\,+3KCl+3{{H}_{2}}O\]
- We can see that Chloroform, Potassium hydroxide and primary amine react to give carbylamine as a main product alongside salt and water. This reaction is also known as Hofmann isocyanide synthesis as carbylamine is also called isocyanide.
- The intermediate dichlorocarbene is involved in this reaction.
- In organic qualitative analysis, the carbylamine reaction is also called Hofmann’s isocyanide test. In this test, the test substance is heated with chloroform and alcoholic potassium hydroxide. So, if primary amine is present, it will form isocyanide and this can be observed by its foul smell.
- Let’s understand the mechanism and role of the intermediate in this reaction.
- In this reaction, the initial step of mechanism involves addition of an amine to the intermediate created from the dehydrohalogenation of chloroform. This intermediate is called dichlorocarbene.
- The first step is the dehydrohalogenation (removal of hydrogen halide from a given substrate) of chloroform to give dichlorocarbene intermediate. This dichlorocarbene intermediate is very reactive.
- Then, nitrogen of primary amine attacks the electrophilic carbon of dichlorocarbene to form a doubly charged intermediate. The elimination of the hydrochloric acid leads to the formation of isonitrile.
Formation of Dichlorocarbene:
\[CHC{{l}_{3}}\xrightarrow{KOH}\text{ }\underset{\text{Dichlorocarbene}}{\mathop{:CC{{l}_{2}}}}\,+HCl\]

Note: Remember that carbylamine reaction cannot be used to synthesize isocyanides from secondary or tertiary amines because they have two or three alkyl groups on nitrogen atoms of amine and so that it cannot form a triple bond with carbon atom to form isocyanide. Note that chloroform is used here not only as a solvent but also as a reagent.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

What organs are located on the left side of your body class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

How do I convert ms to kmh Give an example class 11 physics CBSE




