
Write a short note on the nervous system of cockroaches.
Answer
512.4k+ views
Hint: The Cockroach Nervous System can be split into three parts:
-The Nervous Central System,
-The Nervous Peripheral System,
-Nervous system, visceral, or sympathetic.
Complete answer:
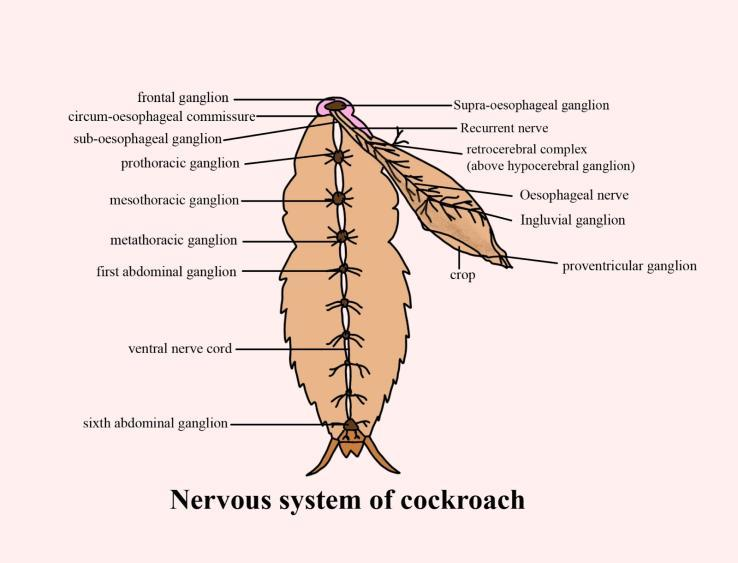
The cockroach nervous system consists of a series of fused, segmentally arranged ganglia, connected on the ventral side by paired longitudinal connections. In the thorax lie three ganglions, and in the abdomen six. The cockroach's nervous system is distributed across the body. The head retains a bit of a nervous system while the rest is distributed along the portion of its body ventral (belly-side).
If a cockroach's head is cut off it will continue to exist for as long as one week. The brain is represented in the head area by the supra-oesophageal ganglion that supplies nerves to the antennas and compound eyes. The sense organs in cockroach are antennas, pupils, maxillary palps, labial palps, anal cert.', etc. The compound eyes are located on the head's dorsal surface. About 2000 hexagonal ommatidia (sing.: ommatidium) are composed of each eye. A cockroach may obtain multiple photographs of an object with the help of several ommatidia. This form of vision is known as a vision mosaic with more sensitivity, but at night it is normal to have less resolution (hence called nocturnal vision).
Additional information:
The central nervous system consists of the brain or supra-oesophageal ganglion, suboesophageal ganglion, the head nerve cord and circum oesophageal connections, and the thorax and abdomen of a double ganglionated ventral nerve cord. A joint of large, intimately applied ganglia in the head is the brain or supra-oesophageal ganglia. The fusion of three pairs of ganglia produces it. It represents the brain and is primarily concerned with sensory functions.
The peripheral nervous system is made up of nerves that start from the central nervous system's ganglia and supply various organs in the periphery. The peripheral nervous system is composed of nerves originating from the nerve ring and ventral nerve cord to internalize various areas of the body. A pair of optic and antennary nerves emerge from the brain that correspondingly supplies the eyes and antennas. The supra-oesophageal ganglion originates from three pairs of nerves: optic, antennary and labor frontal nerves. The suboesophageal ganglia provide the mandibles, maxillae, and labium with paired nerves.
Any ganglia and their connectives constitute the autonomic or stomatogastric or sympathetic or visceral cockroach nervous system. A small frontal ganglion in front of the brain dorsal to the pharynx, an esophageal ganglion on the dorsal side of the esophagus, and an immense visceral ganglion on the dorsal surface of the crop form the sympathetic or visceral nervous system. The frontal, occipital, visceral, or ingluvial, and pre-ventricular ganglia are included. The nerves are connected with the supra-oesophageal ganglion from these ganglia.
Note:
The cockroach nervous system consists of a series of fused, segmentally arranged ganglia, connected on the ventral side by paired longitudinal connections. In the thorax lie three ganglions, and in the abdomen six.
-The Nervous Central System,
-The Nervous Peripheral System,
-Nervous system, visceral, or sympathetic.
Complete answer:
The cockroach nervous system consists of a series of fused, segmentally arranged ganglia, connected on the ventral side by paired longitudinal connections. In the thorax lie three ganglions, and in the abdomen six. The cockroach's nervous system is distributed across the body. The head retains a bit of a nervous system while the rest is distributed along the portion of its body ventral (belly-side).
If a cockroach's head is cut off it will continue to exist for as long as one week. The brain is represented in the head area by the supra-oesophageal ganglion that supplies nerves to the antennas and compound eyes. The sense organs in cockroach are antennas, pupils, maxillary palps, labial palps, anal cert.', etc. The compound eyes are located on the head's dorsal surface. About 2000 hexagonal ommatidia (sing.: ommatidium) are composed of each eye. A cockroach may obtain multiple photographs of an object with the help of several ommatidia. This form of vision is known as a vision mosaic with more sensitivity, but at night it is normal to have less resolution (hence called nocturnal vision).
Additional information:
The central nervous system consists of the brain or supra-oesophageal ganglion, suboesophageal ganglion, the head nerve cord and circum oesophageal connections, and the thorax and abdomen of a double ganglionated ventral nerve cord. A joint of large, intimately applied ganglia in the head is the brain or supra-oesophageal ganglia. The fusion of three pairs of ganglia produces it. It represents the brain and is primarily concerned with sensory functions.
The peripheral nervous system is made up of nerves that start from the central nervous system's ganglia and supply various organs in the periphery. The peripheral nervous system is composed of nerves originating from the nerve ring and ventral nerve cord to internalize various areas of the body. A pair of optic and antennary nerves emerge from the brain that correspondingly supplies the eyes and antennas. The supra-oesophageal ganglion originates from three pairs of nerves: optic, antennary and labor frontal nerves. The suboesophageal ganglia provide the mandibles, maxillae, and labium with paired nerves.
Any ganglia and their connectives constitute the autonomic or stomatogastric or sympathetic or visceral cockroach nervous system. A small frontal ganglion in front of the brain dorsal to the pharynx, an esophageal ganglion on the dorsal side of the esophagus, and an immense visceral ganglion on the dorsal surface of the crop form the sympathetic or visceral nervous system. The frontal, occipital, visceral, or ingluvial, and pre-ventricular ganglia are included. The nerves are connected with the supra-oesophageal ganglion from these ganglia.
Note:
The cockroach nervous system consists of a series of fused, segmentally arranged ganglia, connected on the ventral side by paired longitudinal connections. In the thorax lie three ganglions, and in the abdomen six.

Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Name the part of the brain responsible for the precision class 11 biology CBSE

The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to AEffect class 11 biology CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

State and prove Bernoullis theorem class 11 physics CBSE

Actinoid contraction is more than lanthanoid contraction class 11 chemistry CBSE

Which out of the following hydrocarbons undergo addition class 11 chemistry CBSE




