
Wolff-kishner reduction cannot be used in which of the following?
A.
B.
C.
D.




Answer
569.4k+ views
Hint: The reduction of aldehyde and ketones by alkaline hydrazine solution is called Wolff-kishner reduction reaction. In this reaction aldehyde and ketone functional groups are reduced to alkane functional groups.
Complete Step by step answer: In Wolff-kishner reduction reaction aldehyde and ketone are reduced to alkane in alkaline hydrazine solution.
The mechanism of the general reaction is as follows:
Step1: Nucleophilic attack of hydrazine to the electrophilic carbonyl group and conversion of aldehyde or ketone to hydrazone.
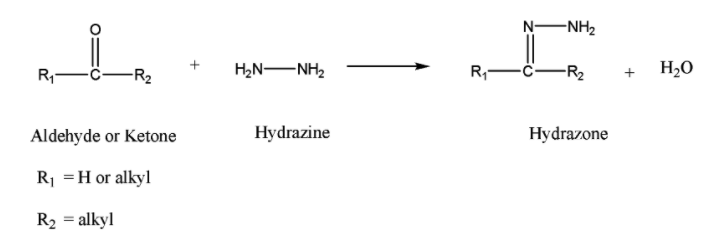
Step2: Deprotonation of terminal nitrogen by the base.
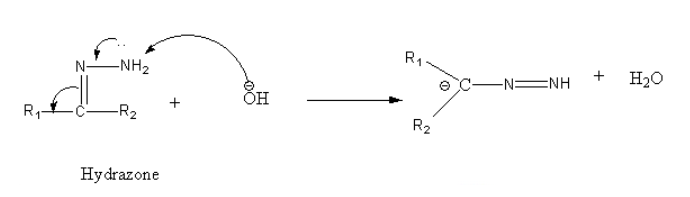
Step3: Protonation of carbon by a water molecule.
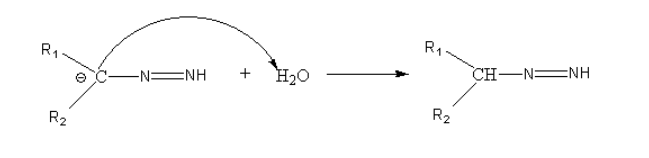
Step 4: Again there is deprotonation of terminal nitrogen and carbanion and nitrogen gas formed.
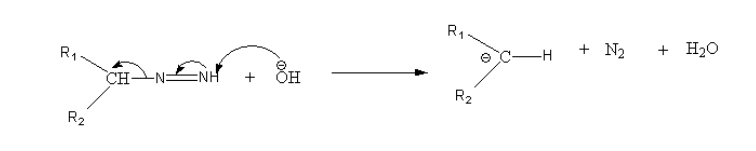
Step5: Again there is protonation of carbon by a water molecule.
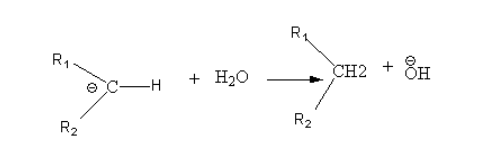
In this reaction the first step is the nucleophilic attack of hydrazine to electrophilic carbonyl group so in the case of reactants containing more than one carbonyl group reaction favour the reduction of the more electrophilic carbonyl group.
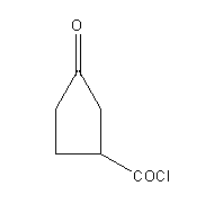
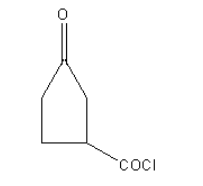
In the case of following organic compounds given in option A as carbonyl of an acyl chloride is more electropositive due to electron-withdrawing effect of chloride group than ketonic carbonyl so Wolff-kishner reduction cannot be used. Also, the ketone group is sterically hindered by the acyl chloride group. Reactant A will not be reduced to an alkane.
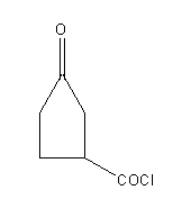
So, option (A) is the correct answer.
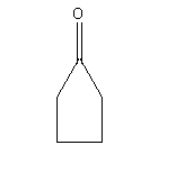
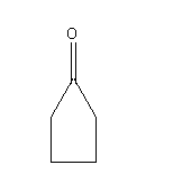
Wolff-kishner reduction can be used for the compound given in option B as it contains only ketonic carbonyl groups.
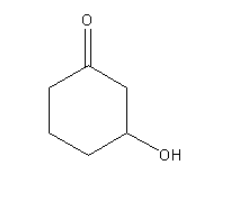
Wolff-kishner reduction can be used for the compound given in option C as it contains only ketonic carbonyl group. The Hydroxyl group will not affect the reduction.

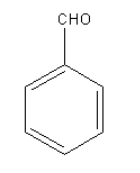
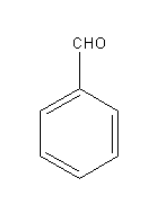
Wolff-kishner reduction can be used for the compound given in option D as it contains only the aldehydic carbonyl group.
Thus, the correct option is (A)
Note: Wolff-kishner reduction cannot be used for sterically hindered aldehyde and ketone. For Wolff-kishner reduction reaction medium should be basic. The presence of different carbonyl function groups other than aldehyde and ketone results in a different product.
Complete Step by step answer: In Wolff-kishner reduction reaction aldehyde and ketone are reduced to alkane in alkaline hydrazine solution.
The mechanism of the general reaction is as follows:
Step1: Nucleophilic attack of hydrazine to the electrophilic carbonyl group and conversion of aldehyde or ketone to hydrazone.

Step2: Deprotonation of terminal nitrogen by the base.

Step3: Protonation of carbon by a water molecule.

Step 4: Again there is deprotonation of terminal nitrogen and carbanion and nitrogen gas formed.

Step5: Again there is protonation of carbon by a water molecule.

In this reaction the first step is the nucleophilic attack of hydrazine to electrophilic carbonyl group so in the case of reactants containing more than one carbonyl group reaction favour the reduction of the more electrophilic carbonyl group.
In the case of following organic compounds given in option A as carbonyl of an acyl chloride is more electropositive due to electron-withdrawing effect of chloride group than ketonic carbonyl so Wolff-kishner reduction cannot be used. Also, the ketone group is sterically hindered by the acyl chloride group. Reactant A will not be reduced to an alkane.

So, option (A) is the correct answer.
Wolff-kishner reduction can be used for the compound given in option B as it contains only ketonic carbonyl groups.

Wolff-kishner reduction can be used for the compound given in option C as it contains only ketonic carbonyl group. The Hydroxyl group will not affect the reduction.

Wolff-kishner reduction can be used for the compound given in option D as it contains only the aldehydic carbonyl group.

Thus, the correct option is (A)

Note: Wolff-kishner reduction cannot be used for sterically hindered aldehyde and ketone. For Wolff-kishner reduction reaction medium should be basic. The presence of different carbonyl function groups other than aldehyde and ketone results in a different product.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




