
With what speed can a body be thrown upwards so that the distance traversed in \[{5^{th}}\] second and \[{6^{th}}\] seconds are equal?
A. \[5.84\,m{s^{ - 1}}\]
B. \[49\,m{s^{ - 1}}\]
C. \[\sqrt {98}\,m{s^{ - 1}}\]
D. \[98\,m{s^{ - 1}}\]
Answer
502.5k+ views
Hint:in this question the condition that distance traversed in \[{5^{th}}\] second and \[{6^{th}}\] seconds are equal only conceivable if the body decelerates for 4 to 5 seconds and then accelerates for 5 to 6 seconds. This state is suitable for projectile motion if the body moves upward in 4 to 5 seconds and downward in 5 to 6 seconds. After understanding this concept in detail we will apply the first equation of motion and come to an answer.
Formula used:
\[v = u + at\]
Where $v$- final velocity, $u$- initial velocity, $a$- acceleration and $t$-time.
Complete step by step answer:
Initially the ball is thrown with a certain speed. We are supposed to find this speed.
The condition that distance traversed in \[{5^{th}}\] second and \[{6^{th}}\] seconds are equal only when the body is at highest point, and it reaches there at \[{5^{th}}\] second.Here time of flight is equal to time of descent. Hence the body is at its highest point at \[{5^{th}}\] second.
The body when thrown up slowly decelerates when it moves upwards and becomes 0 at the top most point. It again accelerates from that point and falls downwards. The same condition has to be applied here. From \[{4^{th}}\] to \[{5^{th}}\] second the body decelerates at \[{5^{th}}\] second its speed becomes ‘0’ and again from \[{5^{th}}\] second to \[{6^{th}}\] second the body accelerates.
Hence the time required by the body upwards (during \[{4^{th}}\] to \[{5^{th}}\] second) is equal to the time required by it to move downwards (from \[{5^{th}}\] second to \[{6^{th}}\] second),which has to be 5seconds.Look at the diagram to get a better idea:
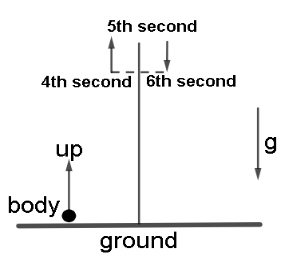
Hence we will apply first equation of motion:
\[v = u + at\]
We know that at the highest point of a projectile the velocity is zero. Hence
\[0 = u + at\]
Also a will be equal to acceleration due to gravity ‘g’. (it will be –g because the body is thrown upwards).
\[0 = u - gt\]
\[\Rightarrow u = gt\]
\[\Rightarrow u = 9.8 \times 5\]
\[\therefore u = 49\,m{s^{ - 1}}\]
Hence the correct answer is option B.
Note:Students make a very common mistake in solving distance covered in \[{n^{th}}\]second problems, they tend to apply the formula \[s = u + \dfrac{1}{2}\left( {2n - 1} \right)\]. This formula is correct but this definitely cannot be used to solve this problem, because if $u$ equates distances. All variables get canceled out. Also acceleration for a body moving upwards has to be negative.
Formula used:
\[v = u + at\]
Where $v$- final velocity, $u$- initial velocity, $a$- acceleration and $t$-time.
Complete step by step answer:
Initially the ball is thrown with a certain speed. We are supposed to find this speed.
The condition that distance traversed in \[{5^{th}}\] second and \[{6^{th}}\] seconds are equal only when the body is at highest point, and it reaches there at \[{5^{th}}\] second.Here time of flight is equal to time of descent. Hence the body is at its highest point at \[{5^{th}}\] second.
The body when thrown up slowly decelerates when it moves upwards and becomes 0 at the top most point. It again accelerates from that point and falls downwards. The same condition has to be applied here. From \[{4^{th}}\] to \[{5^{th}}\] second the body decelerates at \[{5^{th}}\] second its speed becomes ‘0’ and again from \[{5^{th}}\] second to \[{6^{th}}\] second the body accelerates.
Hence the time required by the body upwards (during \[{4^{th}}\] to \[{5^{th}}\] second) is equal to the time required by it to move downwards (from \[{5^{th}}\] second to \[{6^{th}}\] second),which has to be 5seconds.Look at the diagram to get a better idea:

Hence we will apply first equation of motion:
\[v = u + at\]
We know that at the highest point of a projectile the velocity is zero. Hence
\[0 = u + at\]
Also a will be equal to acceleration due to gravity ‘g’. (it will be –g because the body is thrown upwards).
\[0 = u - gt\]
\[\Rightarrow u = gt\]
\[\Rightarrow u = 9.8 \times 5\]
\[\therefore u = 49\,m{s^{ - 1}}\]
Hence the correct answer is option B.
Note:Students make a very common mistake in solving distance covered in \[{n^{th}}\]second problems, they tend to apply the formula \[s = u + \dfrac{1}{2}\left( {2n - 1} \right)\]. This formula is correct but this definitely cannot be used to solve this problem, because if $u$ equates distances. All variables get canceled out. Also acceleration for a body moving upwards has to be negative.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




