
With the help of a labelled diagram describe the structure of a bacterial cell.
Answer
588k+ views
Hint: Bacteria are a type of biological cell. They constitute a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. The length of the bacteria is a few micrometers. Bacteria have several shapes, ranging from spheres, rod, cocci and spirals. A prokaryotic cell has five essential structural components: a nucleoid, ribosomes, cell membrane, cell wall, and a surface layer.
Complete answer:
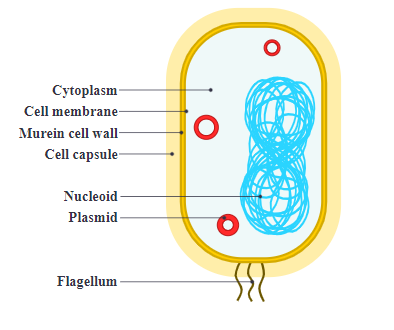
Bacteria are unicellular prokaryotic microorganisms. They do not have a nuclear membrane. The nucleus consists of double-stranded circular DNA. They possess long filamentous flagella which is used for locomotion. They also contain thin, short filaments called fimbriae or pili.
The capsule, which is the outer covering of the cell wall. It is mainly made up of polysaccharide, which is present in some bacteria. The cell wall is the rigid outer covering of the bacteria. It is made up of peptidoglycan.
It gives a particular shape to bacteria. They do not contain a nuclear membrane, a Golgi complex, cytoskeleton. They contain cytoplasmic membrane, mesosomes, ribosomes, and cytoplasmic inclusions.
Based on their features and characteristics, Bacteria can be classified into various categories. The bacteria are classified mainly based on the:
- Shape
- Composition of the cell wall
- Mode of respiration
- Mode of nutrition
Additional information:
Bacteria are also very versatile organisms, surviving in extremely inhospitable conditions, and hence, such organisms are called extremophiles. The further categories based on types of environments they inhabit, namely, Thermophiles, Acidophiles, Alkaliphiles, Osmophiles, Barophiles, Cryophiles.
Note: Bacteria follow an asexual mode of reproduction. It is called binary fission. A single bacterium divides into two daughter cells. The beginning of the fission is marked by the replication of DNA within the parent bacterium. Eventually, the cell elongates to form two daughter cells. The daughter cells are identical to the parent cell as well as to each other.
Complete answer:
Bacteria are unicellular prokaryotic microorganisms. They do not have a nuclear membrane. The nucleus consists of double-stranded circular DNA. They possess long filamentous flagella which is used for locomotion. They also contain thin, short filaments called fimbriae or pili.
The capsule, which is the outer covering of the cell wall. It is mainly made up of polysaccharide, which is present in some bacteria. The cell wall is the rigid outer covering of the bacteria. It is made up of peptidoglycan.
It gives a particular shape to bacteria. They do not contain a nuclear membrane, a Golgi complex, cytoskeleton. They contain cytoplasmic membrane, mesosomes, ribosomes, and cytoplasmic inclusions.
Based on their features and characteristics, Bacteria can be classified into various categories. The bacteria are classified mainly based on the:
- Shape
- Composition of the cell wall
- Mode of respiration
- Mode of nutrition

Additional information:
Bacteria are also very versatile organisms, surviving in extremely inhospitable conditions, and hence, such organisms are called extremophiles. The further categories based on types of environments they inhabit, namely, Thermophiles, Acidophiles, Alkaliphiles, Osmophiles, Barophiles, Cryophiles.
Note: Bacteria follow an asexual mode of reproduction. It is called binary fission. A single bacterium divides into two daughter cells. The beginning of the fission is marked by the replication of DNA within the parent bacterium. Eventually, the cell elongates to form two daughter cells. The daughter cells are identical to the parent cell as well as to each other.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




