
Why is a crystal anisotropic?
Answer
515.1k+ views
Hint: Physical properties like refractive index or resistance are sensitive to the arrangement of particles inside a crystal. It is the size, position of a particle and spaces to show mobility inside the crystal that directly affects these properties.
Complete answer:
Crystalline solids can be identified by the perfectly ordered arrangement of their constituent particles that keeps repeating itself for long distances (known as long range order). This fixed and ordered arrangement gives rise to a lot of other properties that are characteristic to the crystalline solids only.
Properties like a fixed geometrical shape, sharp melting points and definite heat of fusion are a direct consequence of the intermolecular or interionic arrangement of crystalline solids.
One such property is the ability to be anisotropic in nature. Anisotropic solids tend to give different values of physical quantities like refractive index or electrical resistance when measured along different directions of the same crystal.
The reason for showing anisotropic behavior shown by crystalline solids lies in their long range order. Due to a rigid arrangement of constituent particles in crystalline solids, particles tend to occupy fixed positions and are not subject to any movement or disorder. Therefore one observes a unique arrangement along different directions in the same crystal. These different arrangements are responsible for showing variable results while calculating many physical properties.
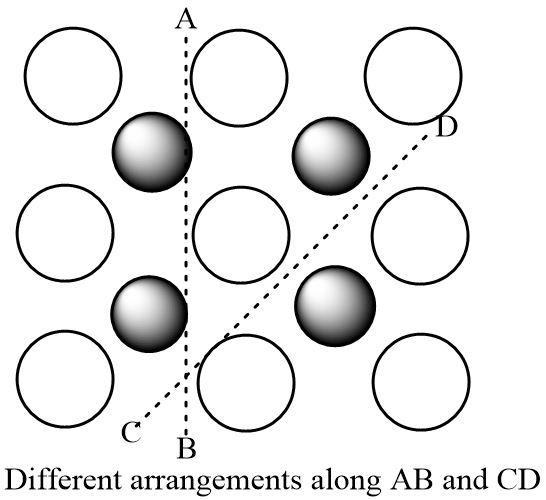
On the contrary, amorphous solids with a randomized arrangement of particles are isotropic as one observes nearly the arrangement (irregular) in all directions.
Thus a crystal is amorphous due to its long range order.
Note:
Even though amorphous solids are isotropic and give the same value of certain physical properties when measured in different directions, that does not make them capable of showing sharp melting points or having a definite heat of fusion.
Complete answer:
Crystalline solids can be identified by the perfectly ordered arrangement of their constituent particles that keeps repeating itself for long distances (known as long range order). This fixed and ordered arrangement gives rise to a lot of other properties that are characteristic to the crystalline solids only.
Properties like a fixed geometrical shape, sharp melting points and definite heat of fusion are a direct consequence of the intermolecular or interionic arrangement of crystalline solids.
One such property is the ability to be anisotropic in nature. Anisotropic solids tend to give different values of physical quantities like refractive index or electrical resistance when measured along different directions of the same crystal.
The reason for showing anisotropic behavior shown by crystalline solids lies in their long range order. Due to a rigid arrangement of constituent particles in crystalline solids, particles tend to occupy fixed positions and are not subject to any movement or disorder. Therefore one observes a unique arrangement along different directions in the same crystal. These different arrangements are responsible for showing variable results while calculating many physical properties.

On the contrary, amorphous solids with a randomized arrangement of particles are isotropic as one observes nearly the arrangement (irregular) in all directions.
Thus a crystal is amorphous due to its long range order.
Note:
Even though amorphous solids are isotropic and give the same value of certain physical properties when measured in different directions, that does not make them capable of showing sharp melting points or having a definite heat of fusion.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Giving reasons state the signs positive or negative class 12 physics CBSE

Explain esterification reaction with the help of a class 12 chemistry CBSE

What is defined as a solenoid Depict a diagram with class 12 physics CBSE




