
Which type of isomerism is shown by alkanes?
A.Chain isomerism
B.Position isomerism
C.Metamerism
D.Functional group isomerism
Answer
561.6k+ views
Note:Alkanes are the simplest family of hydrocarbons - compounds containing carbon and hydrogen only. Alkanes only contain carbon-hydrogen bonds and carbon-carbon single bonds. All of the alkanes which contain four or more carbon atoms show structural isomerism, which means that there are two or more different structural formulae that we can draw for each molecular formula and chain isomerism.
Complete answer:
Alkanes are the organic compounds which consist entirely of single-bonded carbon(C) and hydrogen (H) atoms and lack any other functional groups. Alkanes have the general formula CnH2n+2 and they can be subdivided into the following three groups - the linear straight-chain alkanes, the branched alkanes, and the cycloalkanes. Alkanes are also saturated hydrocarbons. And, the cycloalkanes are cyclic hydrocarbons, which means that the carbons of the molecule are arranged in the form of a ring. Cycloalkanes are also saturated, which means that all of the carbons atoms which make up the ring are singly bonded to other atoms and there are no double or triple bonds.
Alkanes are the simplest family of hydrocarbons - compounds containing carbon and hydrogen only. Alkanes only contain carbon-hydrogen bonds and carbon-carbon single bonds.
Some examples of alkanes are methane, ethane, propane etc.
Alkanes showed chain isomerism. These isomers arise because of the possibility of branching in carbon chains.
For example - there are two isomers of butane, C4H10. In one of them, the carbon atoms lie in a straight chain and in the other, the chain is in branched form.
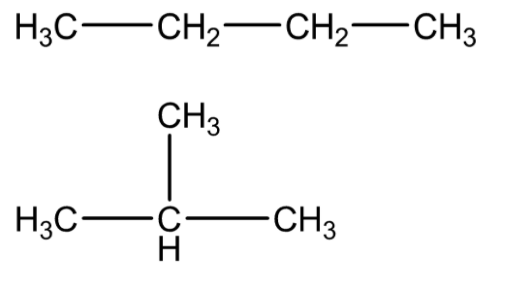
Therefore, the correct answer is option (A).
Hint:
We should be careful not to draw the false isomers which are just twisted versions of the original molecule. For example, the structure which is shown below is just the straight chain version of butane rotated about the central carbon-carbon bond.
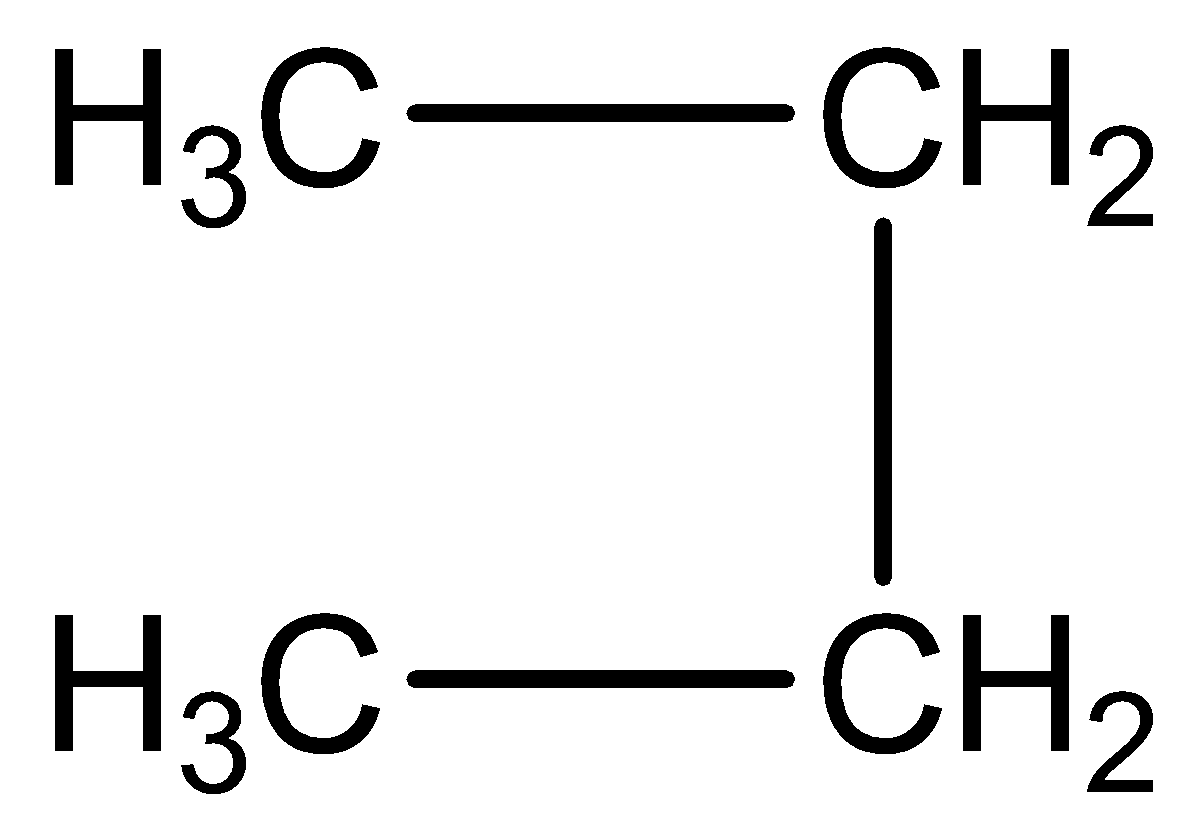
Complete answer:
Alkanes are the organic compounds which consist entirely of single-bonded carbon(C) and hydrogen (H) atoms and lack any other functional groups. Alkanes have the general formula CnH2n+2 and they can be subdivided into the following three groups - the linear straight-chain alkanes, the branched alkanes, and the cycloalkanes. Alkanes are also saturated hydrocarbons. And, the cycloalkanes are cyclic hydrocarbons, which means that the carbons of the molecule are arranged in the form of a ring. Cycloalkanes are also saturated, which means that all of the carbons atoms which make up the ring are singly bonded to other atoms and there are no double or triple bonds.
Alkanes are the simplest family of hydrocarbons - compounds containing carbon and hydrogen only. Alkanes only contain carbon-hydrogen bonds and carbon-carbon single bonds.
Some examples of alkanes are methane, ethane, propane etc.
Alkanes showed chain isomerism. These isomers arise because of the possibility of branching in carbon chains.
For example - there are two isomers of butane, C4H10. In one of them, the carbon atoms lie in a straight chain and in the other, the chain is in branched form.

Therefore, the correct answer is option (A).
Hint:
We should be careful not to draw the false isomers which are just twisted versions of the original molecule. For example, the structure which is shown below is just the straight chain version of butane rotated about the central carbon-carbon bond.

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




