
Which structure of the mouth contains intrinsic and extrinsic muscles and what are their functions?
Answer
516.6k+ views
Hint: The tongue is a fleshy, moveable, muscular organ that is linked to the floor of the mouth in most vertebrates and serves as the primary organ of taste, a tool for chewing and swallowing, and an important organ of speech in humans.
Complete answer:
The tongue is necessary for chewing and swallowing food as well as speaking. Sweet, sour, bitter, and salty are the four basic tastes. When you experience glutamate, you get a fifth taste called umami. Many nerves in the tongue assist detect and convey taste information to the brain.
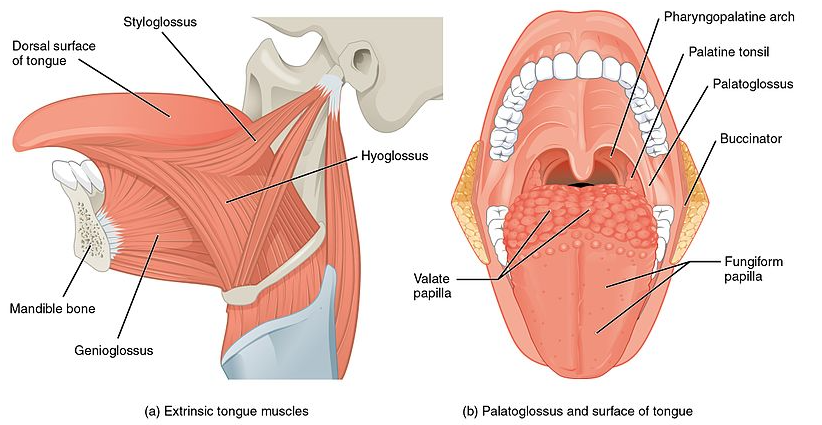
Intrinsic and extrinsic muscles are found on the tongue, which is a component of the mouth.The tongue can alter shape thanks to the four paired intrinsic tongue muscles. Just below the superior surface mucosa, the superior longitudinal muscles run down the tongue. These muscles dorsiflex the tongue's tip and shorten it.
The intrinsic tongue muscles are those that are uniquely found in the tongue. Outside of the tongue, these muscles do not originate or intrude. Because the intrinsic muscles are located inside the tongue, they work to change the shape of the tongue.
Extrinsic muscles are responsible for changing the position of the tongue, allowing for protrusion, retraction, and side-to-side movement. The extrinsic tongue muscles help the tongue move around in the mouth and are essential for swallowing. All of these muscles have their origins outside the tongue and insert into it at different locations.
Note: The tongue is a flexible articulator that helps us make speech. A specific region of the tongue produces several consonant sounds by restricting the flow of air coming up from the trachea at a certain location and in a specific manner.
Complete answer:
The tongue is necessary for chewing and swallowing food as well as speaking. Sweet, sour, bitter, and salty are the four basic tastes. When you experience glutamate, you get a fifth taste called umami. Many nerves in the tongue assist detect and convey taste information to the brain.
Intrinsic and extrinsic muscles are found on the tongue, which is a component of the mouth.The tongue can alter shape thanks to the four paired intrinsic tongue muscles. Just below the superior surface mucosa, the superior longitudinal muscles run down the tongue. These muscles dorsiflex the tongue's tip and shorten it.
The intrinsic tongue muscles are those that are uniquely found in the tongue. Outside of the tongue, these muscles do not originate or intrude. Because the intrinsic muscles are located inside the tongue, they work to change the shape of the tongue.
Extrinsic muscles are responsible for changing the position of the tongue, allowing for protrusion, retraction, and side-to-side movement. The extrinsic tongue muscles help the tongue move around in the mouth and are essential for swallowing. All of these muscles have their origins outside the tongue and insert into it at different locations.

Note: The tongue is a flexible articulator that helps us make speech. A specific region of the tongue produces several consonant sounds by restricting the flow of air coming up from the trachea at a certain location and in a specific manner.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

The largest wind power cluster is located in the state class 11 social science CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

State and prove Bernoullis theorem class 11 physics CBSE

What steps did the French revolutionaries take to create class 11 social science CBSE

Which among the following are examples of coming together class 11 social science CBSE




