
Which part of the soap \[\left( {RCO{O^ - }} \right)\] dissolves grease and forms micelle?
A. \[R\] part (called tail of the anion)
B. \[CO{O^ - }\] part (called head of the anion)
C. both A and B
D. none of these
Answer
592.2k+ views
Hint:
As we know that, soap and detergents help in removing dirt. The soap molecule consists of two parts. The hydrophobic end and hydrophilic end. Whenever soap is mixed with water, the hydrophobic ends of the soap molecule get attached to the dirt on all sides.
Complete step by step solution
Soap and detergents both have the same impact on grease. Their non-polar tails bind to the non-polar grease forming a micelle with an exposed polar head. This micelle of the polar surface is easily mixed with water and can remove the grease from the cloth.
Micelles are molecular compounds that are hydrophilic, mixed with water and hydrophobic, not mixed with water. In general case, micelles are formed when there is an ideal temperature in the medium which is called Kraft temperature.
You see, dirt usually is a form of oil or some non-polar compounds, So the hydrophobic end is non-polar. Micelles have a polar “head” and a “tail” of non-polar nature attached to a particular globule of a substance that is in a medium in which it is not soluble.
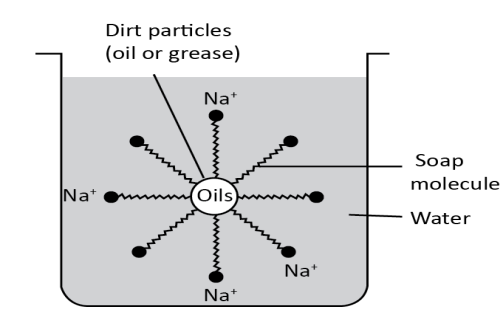
In these micelles, spherical surface is negatively charged by the carbohydrate group, with the hydrocarbon chains within the sphere. Soap micelles repel each other and stay dispersed in water because they are negatively charged. We know that grease and oil have non-polar properties and they are also insoluble in water. The non-polar hydrocarbon component of the micelles breaks up the non-polar oil molecules as soap and oils are combined with non-polar molecules in the center, a different form of micelle then forms.
Therefore, the correct answer is A.
Note:
When water is mixed with soap, then micelle forms. Because of the presence of soap molecules in the form of hydrocarbon chains, their ends are negative which is hydrophilic that’s why they are soluble in water.
As we know that, soap and detergents help in removing dirt. The soap molecule consists of two parts. The hydrophobic end and hydrophilic end. Whenever soap is mixed with water, the hydrophobic ends of the soap molecule get attached to the dirt on all sides.
Complete step by step solution
Soap and detergents both have the same impact on grease. Their non-polar tails bind to the non-polar grease forming a micelle with an exposed polar head. This micelle of the polar surface is easily mixed with water and can remove the grease from the cloth.
Micelles are molecular compounds that are hydrophilic, mixed with water and hydrophobic, not mixed with water. In general case, micelles are formed when there is an ideal temperature in the medium which is called Kraft temperature.
You see, dirt usually is a form of oil or some non-polar compounds, So the hydrophobic end is non-polar. Micelles have a polar “head” and a “tail” of non-polar nature attached to a particular globule of a substance that is in a medium in which it is not soluble.

In these micelles, spherical surface is negatively charged by the carbohydrate group, with the hydrocarbon chains within the sphere. Soap micelles repel each other and stay dispersed in water because they are negatively charged. We know that grease and oil have non-polar properties and they are also insoluble in water. The non-polar hydrocarbon component of the micelles breaks up the non-polar oil molecules as soap and oils are combined with non-polar molecules in the center, a different form of micelle then forms.
Therefore, the correct answer is A.
Note:
When water is mixed with soap, then micelle forms. Because of the presence of soap molecules in the form of hydrocarbon chains, their ends are negative which is hydrophilic that’s why they are soluble in water.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers

Coming together federation is practiced in A India class 12 social science CBSE

How was the Civil Disobedience Movement different from class 12 social science CBSE




