
Which one of the following will be reactive for Perkin Condensation?
A.
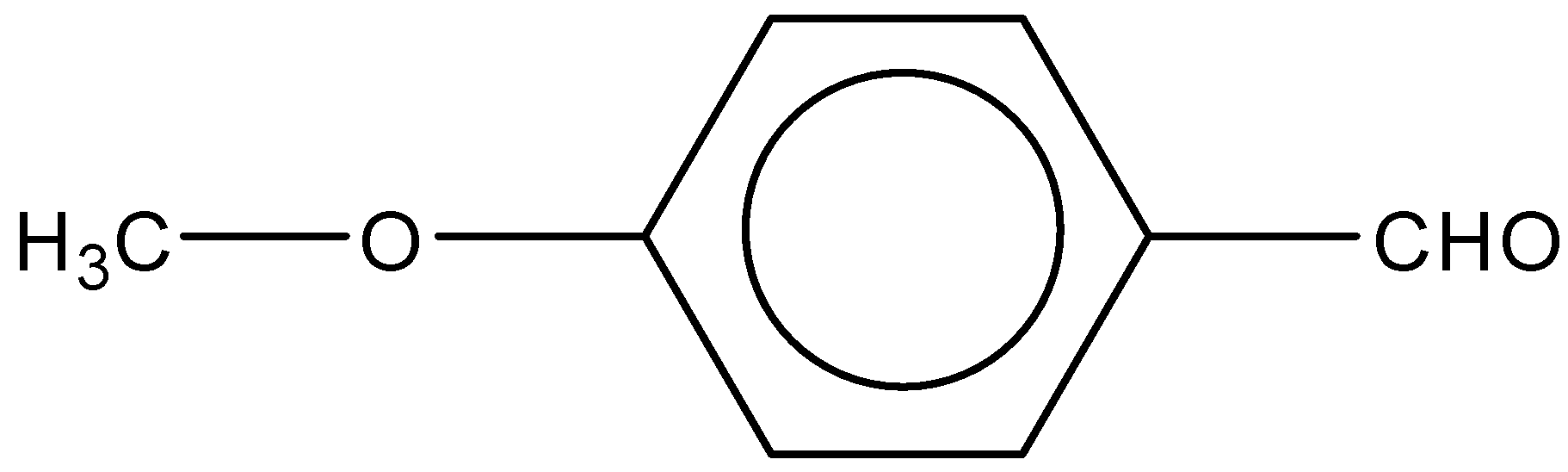
B.
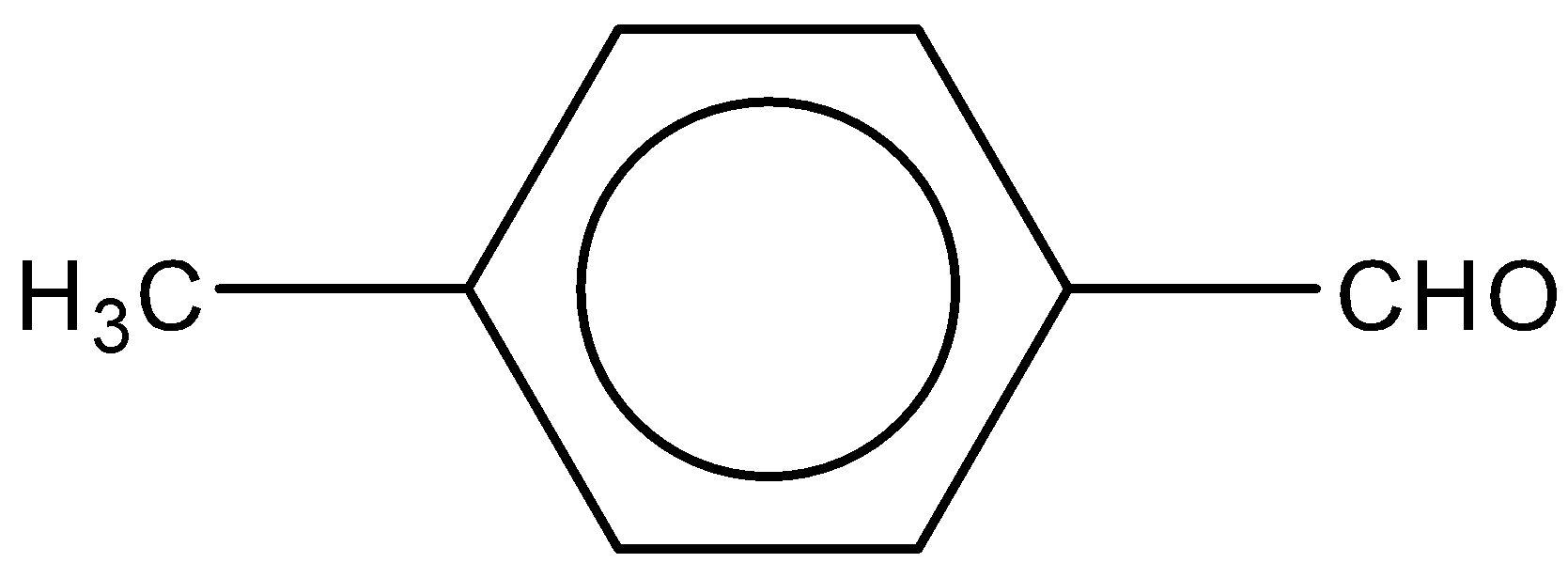
C.
D.
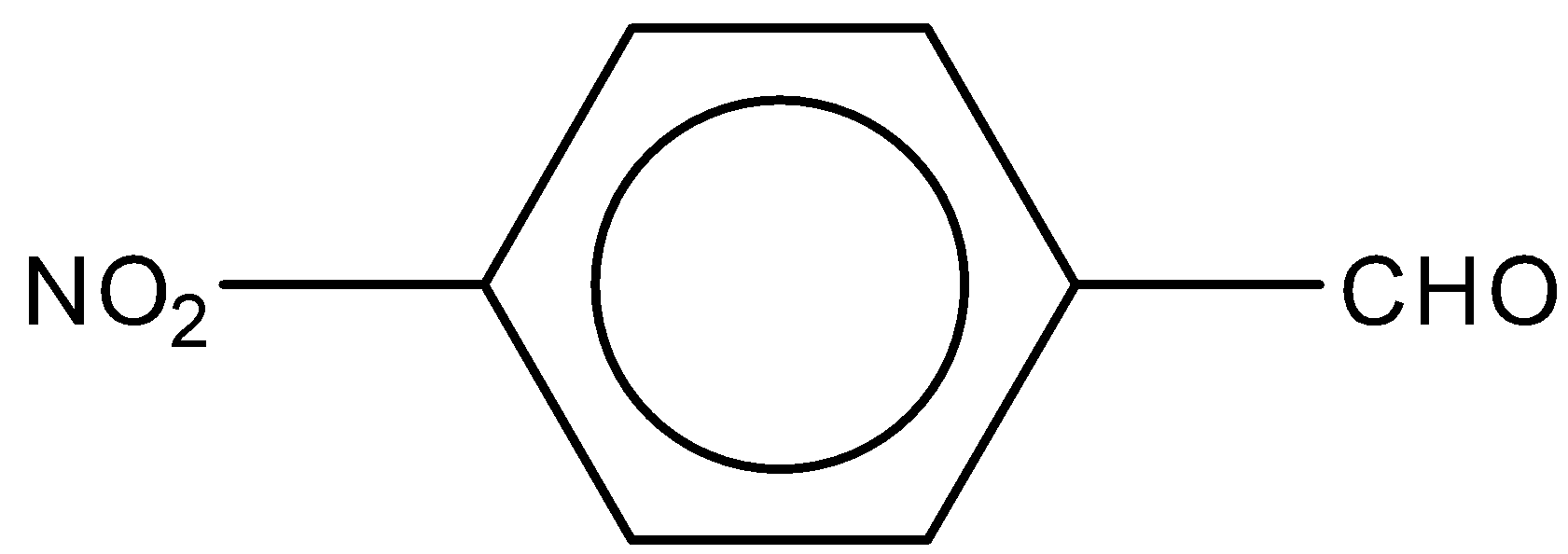
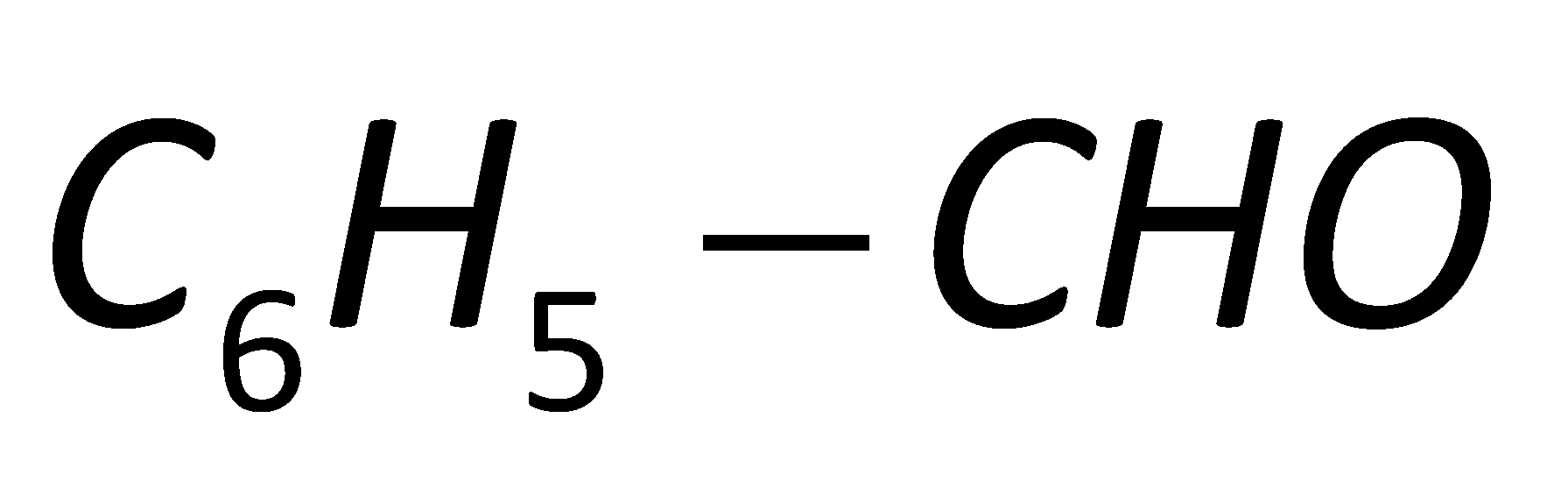



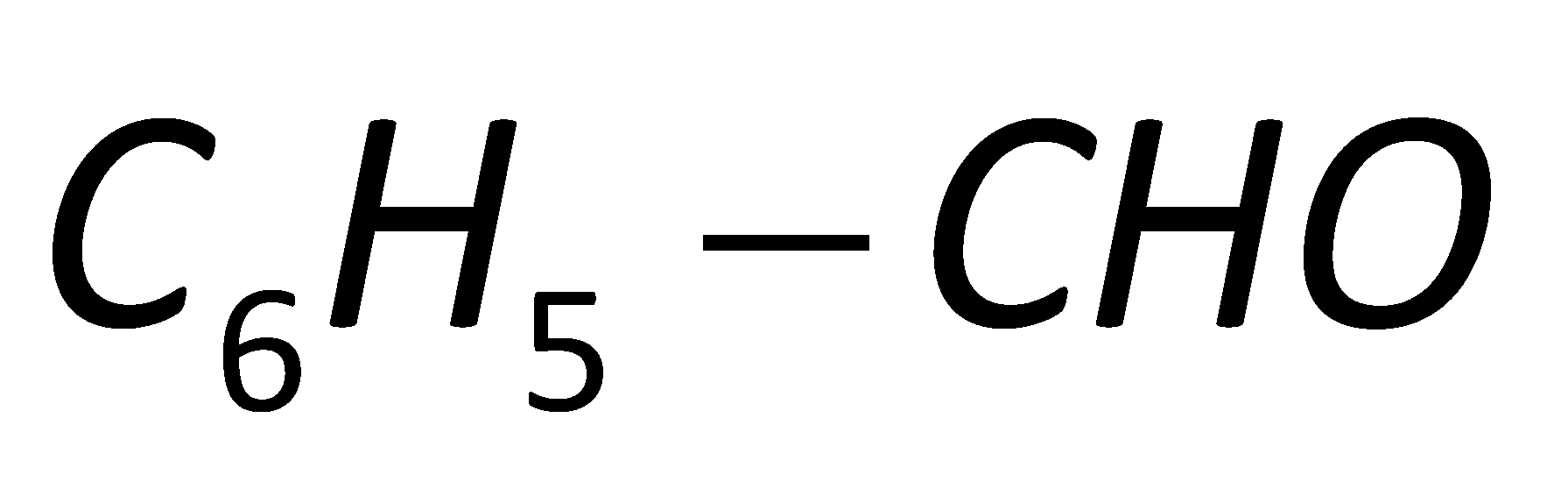
Answer
571.2k+ views
Hint: Perkin condensation involves the reaction of aromatic aldehyde, aliphatic acid anhydride, and alkali salt and the product attained are the derivatives of cinnamic acid. The reactivity towards Perkin condensation depends upon the electron donating or electron withdrawing group attached to the benzene ring.
Complete step by step answer:
Now, let us discuss Perkin condensation in detail.
As mentioned, the reactants involved are aromatic aldehyde, aliphatic acid anhydride, and an alkali salt. The general reaction can be represented as follows:
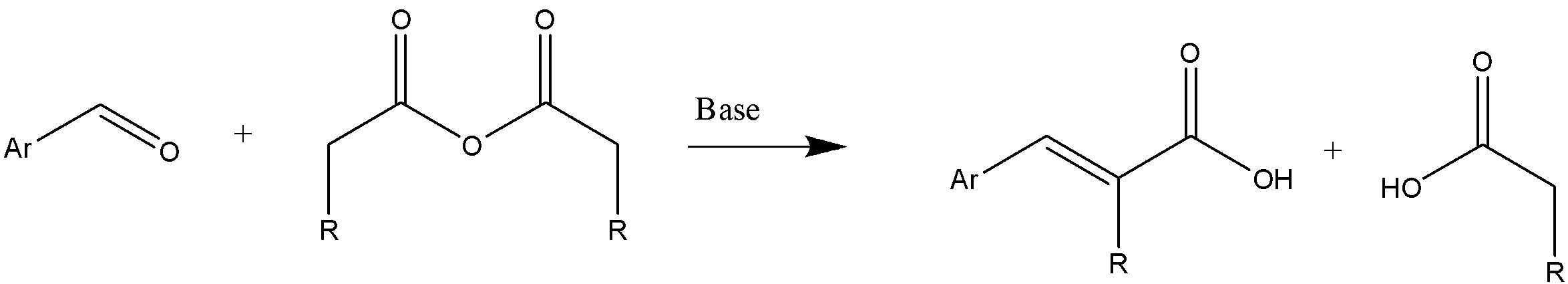
Here, in the general reaction we can see that alkali salt behaves as a base catalyst. The necessary condition for Perkin condensation is the presence of minimum 2 $\alpha $ hydrogen in a molecule.
As we know that the reactivity towards Perkin condensation depends upon the nature of the group attached to it. If the electron withdrawing group is attached to the ring it will lead to increase in reactivity and the electron releasing (donating) groups will lead to the decrease in the reactivity.
Now, if we look at the given options, in the A and B option, $OC{H_3}\;and\;C{H_3}$ groups are attached to the benzene ring. Both the groups are electron donating groups in nature. $OC{H_3}$ is more electron donating than $C{H_3}$ as lone pairs are present on the oxygen atom in $OC{H_3}$. So, we can say that these two will decrease the reactivity towards Perkin condensation.
In the third option C, the nitro group ($N{O_2}$) is attached to the benzene ring. $N{O_2}$ group acts as an electron withdrawing group in nature. During the reaction it increases the charge on the carbonyl group. Therefore, we can say it increases the reactivity towards Perkin condensation.
In the fourth option D, no group is attached to the benzaldehyde. Thus, it will not show any effect towards the Perkin condensation.
So, the correct answer is Option C.
Note: In the question we came across a factor that $OC{H_3}$is more electron donating group than $C{H_3}$ because $C{H_3}$ group shows hyperconjugation and $ + I$ effect whereas $OC{H_3}$ shows $ + M$ effect. Thus, in aromatic electrophilic substitution reaction $OC{H_3}$ group will be more effective towards the formation of ortho and para substituents.
Complete step by step answer:
Now, let us discuss Perkin condensation in detail.
As mentioned, the reactants involved are aromatic aldehyde, aliphatic acid anhydride, and an alkali salt. The general reaction can be represented as follows:

Here, in the general reaction we can see that alkali salt behaves as a base catalyst. The necessary condition for Perkin condensation is the presence of minimum 2 $\alpha $ hydrogen in a molecule.
As we know that the reactivity towards Perkin condensation depends upon the nature of the group attached to it. If the electron withdrawing group is attached to the ring it will lead to increase in reactivity and the electron releasing (donating) groups will lead to the decrease in the reactivity.
Now, if we look at the given options, in the A and B option, $OC{H_3}\;and\;C{H_3}$ groups are attached to the benzene ring. Both the groups are electron donating groups in nature. $OC{H_3}$ is more electron donating than $C{H_3}$ as lone pairs are present on the oxygen atom in $OC{H_3}$. So, we can say that these two will decrease the reactivity towards Perkin condensation.
In the third option C, the nitro group ($N{O_2}$) is attached to the benzene ring. $N{O_2}$ group acts as an electron withdrawing group in nature. During the reaction it increases the charge on the carbonyl group. Therefore, we can say it increases the reactivity towards Perkin condensation.
In the fourth option D, no group is attached to the benzaldehyde. Thus, it will not show any effect towards the Perkin condensation.
So, the correct answer is Option C.
Note: In the question we came across a factor that $OC{H_3}$is more electron donating group than $C{H_3}$ because $C{H_3}$ group shows hyperconjugation and $ + I$ effect whereas $OC{H_3}$ shows $ + M$ effect. Thus, in aromatic electrophilic substitution reaction $OC{H_3}$ group will be more effective towards the formation of ortho and para substituents.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Giving reasons state the signs positive or negative class 12 physics CBSE

Explain esterification reaction with the help of a class 12 chemistry CBSE

What is defined as a solenoid Depict a diagram with class 12 physics CBSE




