
Which one of the following is the simplest amino acid?
A. Alanine
B. Asparagine
C. Glycine
D. Tyrosine
Answer
573.3k+ views
Hint: Organic compounds consisting of both amino groups and an acid group is known as Amino Acids. The amino acids are the building blocks for proteins. Each protein is made up of a specific chain of Amino acids. There are twenty essential amino acids. The amino acids have an additional alkyl group which is specific to each amino acid, the amino acids in which the alkyl group is constituted of just simple atoms is known as simple amino acids.
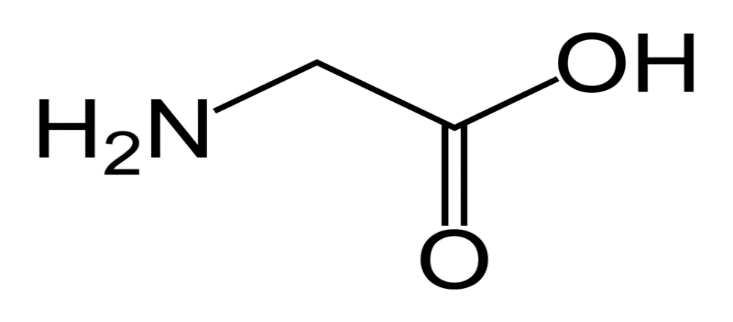
Step by step answer: Glycine is the simplest amino acid since the only atom present in the side chain is a hydrogen atom. It is an important component in the formation of the alpha-helical structure in the secondary structure of the protein. It is present in abundance in the collagen. It also functions as a neurotransmitter, having an inhibitory activity.
i. Alanine has a methyl group as the side chain. It is involved in protein biosynthesis. It is a non-essential amino acid present in humans.
ii. Asparagine is an amino acid falling into the non-essential type in humans. The side chain present in this is a more complex carboxamide group. It is termed as non-essential in humans since human bodies can produce asparagine. Asparagine helps in the development of the brain. It is also involved in the biosynthesis of Ammonia.
iii. Tyrosine is an aromatic amino acid. Consisting of Phenol as the side chain. Tyrosine functions as a starting material for different amino acid synthesis.
Hence, the correct answer is option C.
Note: The constituent amino acids in a protein molecule is connected by a peptide bond. It is a covalent type of bond existing in between the carbon atom of one amino acid and the nitrogen atom of the neighbouring one. This chain continues till the length of the protein molecule.
Step by step answer: Glycine is the simplest amino acid since the only atom present in the side chain is a hydrogen atom. It is an important component in the formation of the alpha-helical structure in the secondary structure of the protein. It is present in abundance in the collagen. It also functions as a neurotransmitter, having an inhibitory activity.

i. Alanine has a methyl group as the side chain. It is involved in protein biosynthesis. It is a non-essential amino acid present in humans.
ii. Asparagine is an amino acid falling into the non-essential type in humans. The side chain present in this is a more complex carboxamide group. It is termed as non-essential in humans since human bodies can produce asparagine. Asparagine helps in the development of the brain. It is also involved in the biosynthesis of Ammonia.
iii. Tyrosine is an aromatic amino acid. Consisting of Phenol as the side chain. Tyrosine functions as a starting material for different amino acid synthesis.
Hence, the correct answer is option C.
Note: The constituent amino acids in a protein molecule is connected by a peptide bond. It is a covalent type of bond existing in between the carbon atom of one amino acid and the nitrogen atom of the neighbouring one. This chain continues till the length of the protein molecule.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




