
Which one of the following human organs is often called the ‘graveyard’ of RBCs?
A. Kidney
B. Spleen
C. Liver
D. Gallbladder
Answer
577.5k+ views
Hint: The RBCs have a very short life span. They undergo haemolysis after some days. This happens in an organ that acts as a blood filter and comprises immune cells of the blood. Also, this organ acts as a large lymph node.
Complete step by step answer: The Red blood cells or RBCs are the hemoglobin carrying cells that are disc-shaped. They circulate throughout the body providing oxygen to various other cells. The RBCs lack major cellular organelles like the endoplasmic reticulum, mitochondria, nucleus, etc. Thus, they do not have any of their energy sources to sustain a longer life span. Therefore, they survive just for around 120 days.
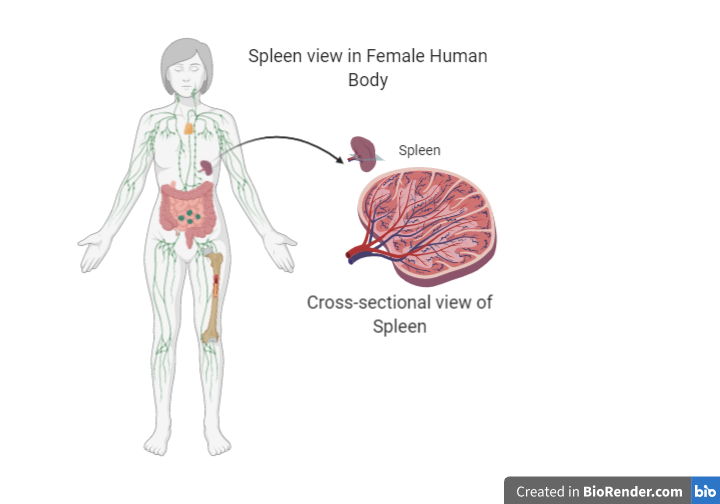
When they are about to die they attract auto-antibodies. Auto-antibodies are immune components that act against the body’s cells. Once the auto-antibodies attach to RBCs they initiate a cascade effect. The macrophage cells of the immune system attach to suicidal RBCs. After this, the macrophages lyse the RBCs in the liver and spleen. This is known as haemolysis. The product of hemolysis is a large waste of red blood cell debris. This needs to be removed from the body’s circulation to prevent any blockage. The spleen is the main organ that removes the dead red blood cells from the bloodstream.
Hence, it is called the ‘Graveyard’ of RBCs. So, the right answer is option B.
Note: The spleen acts as a synthesis organ for RBCs in the fetal stage. It acts as the center of production of all types of blood cells during fetal life. Also, in the adult stage, the spleen functions to provide an active immune response in case of infections. It filters the blood from cellular debris and foreign particles including pathogenic microbes.
Complete step by step answer: The Red blood cells or RBCs are the hemoglobin carrying cells that are disc-shaped. They circulate throughout the body providing oxygen to various other cells. The RBCs lack major cellular organelles like the endoplasmic reticulum, mitochondria, nucleus, etc. Thus, they do not have any of their energy sources to sustain a longer life span. Therefore, they survive just for around 120 days.

When they are about to die they attract auto-antibodies. Auto-antibodies are immune components that act against the body’s cells. Once the auto-antibodies attach to RBCs they initiate a cascade effect. The macrophage cells of the immune system attach to suicidal RBCs. After this, the macrophages lyse the RBCs in the liver and spleen. This is known as haemolysis. The product of hemolysis is a large waste of red blood cell debris. This needs to be removed from the body’s circulation to prevent any blockage. The spleen is the main organ that removes the dead red blood cells from the bloodstream.
Hence, it is called the ‘Graveyard’ of RBCs. So, the right answer is option B.
Note: The spleen acts as a synthesis organ for RBCs in the fetal stage. It acts as the center of production of all types of blood cells during fetal life. Also, in the adult stage, the spleen functions to provide an active immune response in case of infections. It filters the blood from cellular debris and foreign particles including pathogenic microbes.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




