
Which one of the following graphs between molar conductivity $\left( {{\Lambda }_{m}} \right)$ versus $\sqrt{C}$ is correct?
[A]
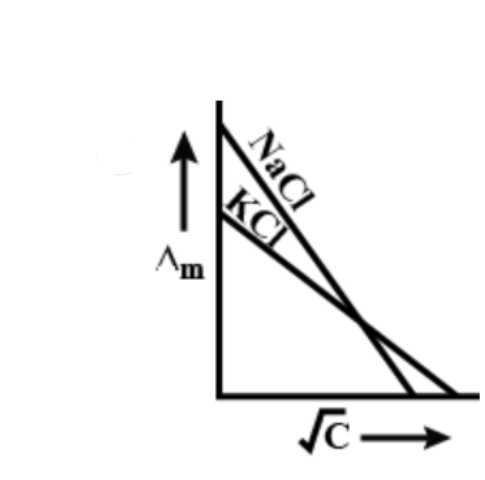 [B]
[B]
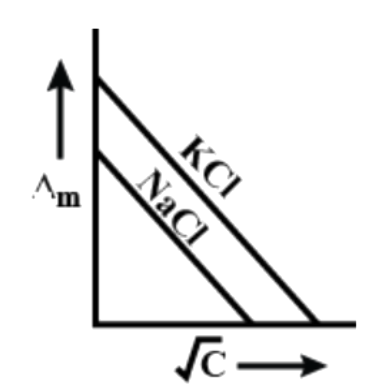
[C]
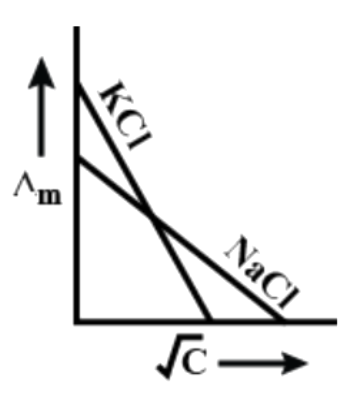 [D]
[D]
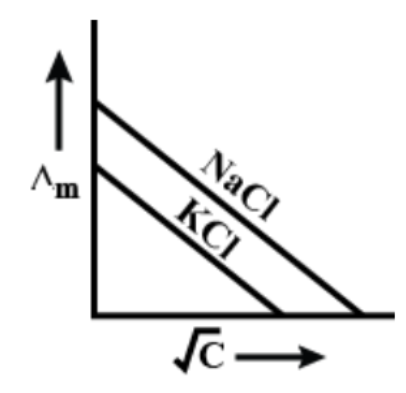




Answer
578.1k+ views
Hint:.To solve this firstly think of the factors that affect the molar conductivity of the solution. Remember the factor of hydration and how it affects the conductance of the smaller ion thus increasing the conductance of the ion with a larger radius.
Complete step by step answer:
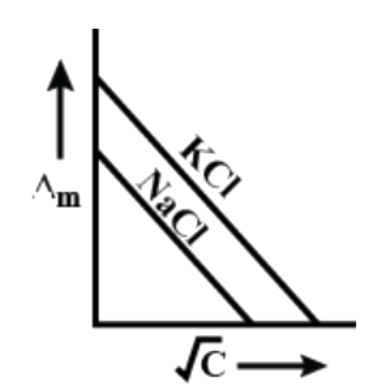
From the given graphs we can understand that here we have two electrolytes namely NaCl and KCl. To answer this, firstly let us discuss molar conductance.
At a given constant temperature, the conductivity of solutions containing different electrolytes differs due to the concentration of the ions and difference in charge and size of the electrolytes when they dissociate into ions. Therefore, we needed to use the molar conductivity of each ion which is given as-
\[{{\lambda }_{m}}=\dfrac{k}{c}\]
Where, ${{\lambda }_{m}}$ is the molar conductance.
K is the specific conductivity and
C is the concentration of the solution.
Here, both the electrolytes i.e. NaCl and KCl are strong electrolytes but their conductivity will not be the same. So, firstly let us identify which one of them will have higher conductivity and from there we can try to find out the correct graph.
As we have already mentioned above that conductivity depends upon the charge and size of the electrolytes. Here, in both the electrolytes the charge of the cations will be +1 and that on anions will be -1. So, we cannot compare the two on the basis of charge so now we have to consider their size.
We know both sodium and potassium are in the same group but potassium has a larger atomic radius. So, when they dissociate in water, sodium cation will be more hydrated due to its smaller size compared to potassium ions. So, this will block the movement of sodium and thus lower its movement. This makes KCl the electrolyte with higher conductance.
Now if we talk about the graphs, both KCl and NaCl will be linear with KCl having a larger intercept.
So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Note: For weak electrolytes as they are not completely dissociated in the solution, the more dilute the solute is higher is the molar conductivity but the stronger electrolytes are not strongly dependent on the concentration of the solution because they will dissociate easily irrespective of the concentration of the solution. Therefore, there is a regular increase in molar conductivity on dilution for strong electrolytes.
Complete step by step answer:
From the given graphs we can understand that here we have two electrolytes namely NaCl and KCl. To answer this, firstly let us discuss molar conductance.
At a given constant temperature, the conductivity of solutions containing different electrolytes differs due to the concentration of the ions and difference in charge and size of the electrolytes when they dissociate into ions. Therefore, we needed to use the molar conductivity of each ion which is given as-
\[{{\lambda }_{m}}=\dfrac{k}{c}\]
Where, ${{\lambda }_{m}}$ is the molar conductance.
K is the specific conductivity and
C is the concentration of the solution.
Here, both the electrolytes i.e. NaCl and KCl are strong electrolytes but their conductivity will not be the same. So, firstly let us identify which one of them will have higher conductivity and from there we can try to find out the correct graph.
As we have already mentioned above that conductivity depends upon the charge and size of the electrolytes. Here, in both the electrolytes the charge of the cations will be +1 and that on anions will be -1. So, we cannot compare the two on the basis of charge so now we have to consider their size.
We know both sodium and potassium are in the same group but potassium has a larger atomic radius. So, when they dissociate in water, sodium cation will be more hydrated due to its smaller size compared to potassium ions. So, this will block the movement of sodium and thus lower its movement. This makes KCl the electrolyte with higher conductance.
Now if we talk about the graphs, both KCl and NaCl will be linear with KCl having a larger intercept.
So, the correct answer is “Option B”.

Note: For weak electrolytes as they are not completely dissociated in the solution, the more dilute the solute is higher is the molar conductivity but the stronger electrolytes are not strongly dependent on the concentration of the solution because they will dissociate easily irrespective of the concentration of the solution. Therefore, there is a regular increase in molar conductivity on dilution for strong electrolytes.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




