
Which one is the product of aerobic respiration?
A. Malic acid
B. Ethyl alcohol
C. Lactic acid
D. Pyruvic acid
Answer
601.5k+ views
Hint: Aerobic respiration generally involves the citric acid cycle. The end product of aerobic respiration is carbon dioxide and water. Aerobic respiration takes place in the powerhouse of the cell (mitochondria) and produces many by-products.
Complete answer:
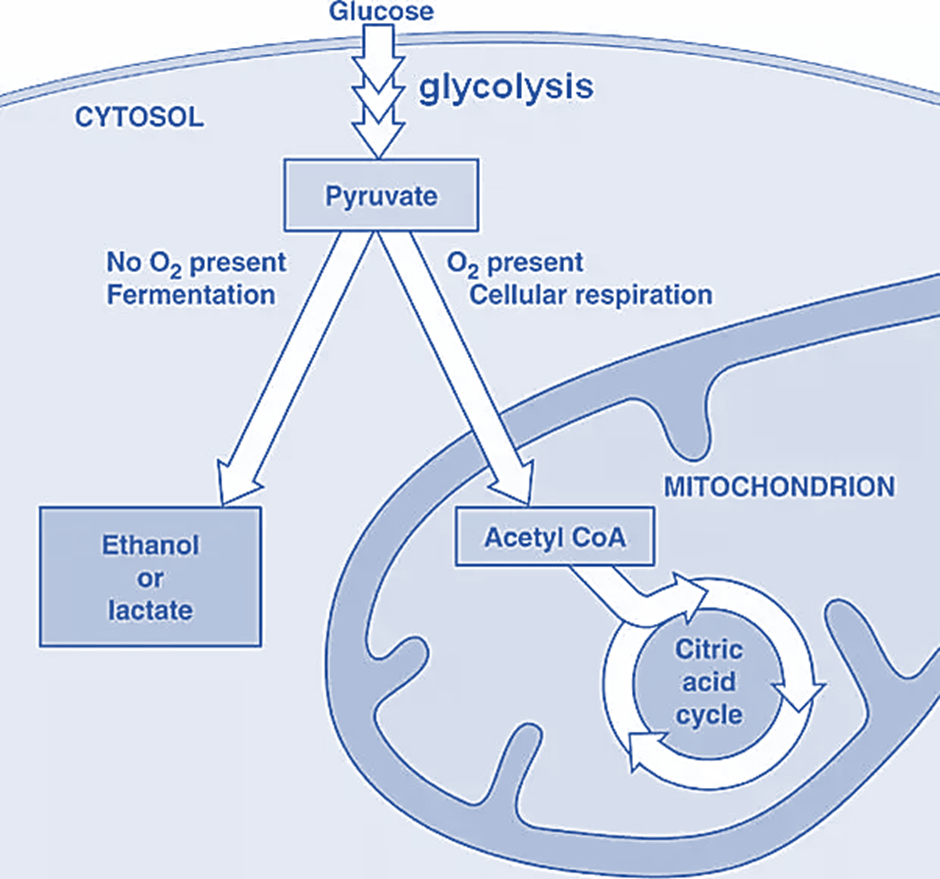
-Glucose is taken up from the cell environment by the cell for their energy needs. The glucose is then broken down into 3-carbon pyruvic acid in the cell cytoplasm by a process of Glycolysis. The end product of glycolysis can then enter either an aerobic cycle inside the mitochondria or remain in the cytoplasm to undergo anaerobic respiration.
-The aerobic cycle is the process of aerobic respiration where the 3 carbon pyruvic acid enters mitochondria and is broken down into 2 carbon acetic acid. This acetic acid is then combined with coenzyme A to form Acetyl – CoA complex which enters the citric acid cycle.
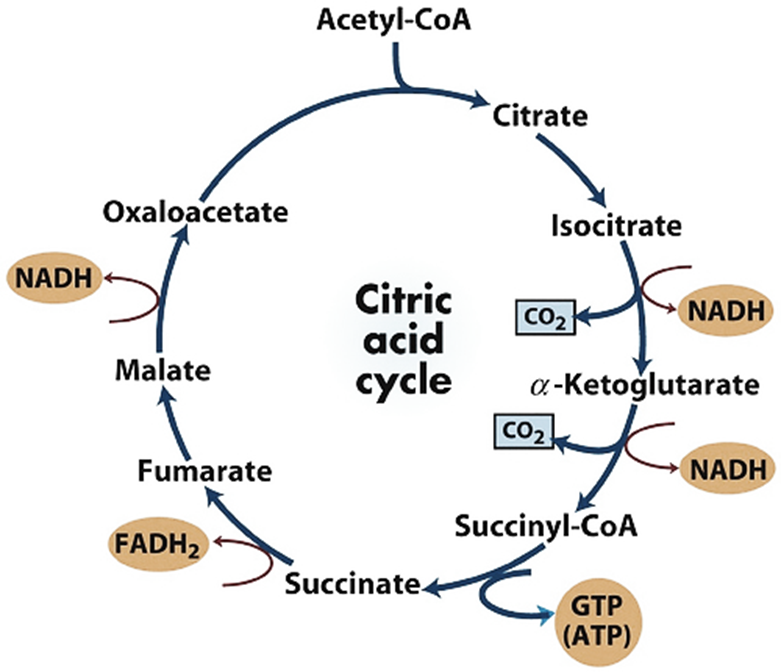
-Some of the products of aerobic respiration include acetic acid, acetyl CoA, Citric acid, ketoglutaric acid, Succinic acid, fumaric acid, Oxaloacetic acid, and malic acid (see figure 2).
Figure 1: Fate of glucose in the cell
Additional information:
A citric acid cycle is also known as the Krebs cycle or Tri-carboxylic acid cycle.
Cellular respiration involves three major steps: Glycolysis, Krebs cycle, and Electron transport chain. Cellular respiration produces a net of 38 ATP molecules.
Oxaloacetate, malate, and pyruvate are also involved in the C4 pathway of plants.
Figure 2: Citric acid cycle
Note: Pyruvic acid is a product of Glycolysis, Malic acid is a product of aerobic respiration in the Krebs cycle, and Ethyl alcohol/lactic acid are the products of anaerobic respiration. Pyruvate from the glycolysis process enters the mitochondria only when the cell requires energy. When the pyruvate is not taken up by the mitochondria it remains in the cytoplasm where it is converted to ethanol/ethyl alcohol or lactic acid.
Complete answer:
-Glucose is taken up from the cell environment by the cell for their energy needs. The glucose is then broken down into 3-carbon pyruvic acid in the cell cytoplasm by a process of Glycolysis. The end product of glycolysis can then enter either an aerobic cycle inside the mitochondria or remain in the cytoplasm to undergo anaerobic respiration.
-The aerobic cycle is the process of aerobic respiration where the 3 carbon pyruvic acid enters mitochondria and is broken down into 2 carbon acetic acid. This acetic acid is then combined with coenzyme A to form Acetyl – CoA complex which enters the citric acid cycle.
-Some of the products of aerobic respiration include acetic acid, acetyl CoA, Citric acid, ketoglutaric acid, Succinic acid, fumaric acid, Oxaloacetic acid, and malic acid (see figure 2).
Figure 1: Fate of glucose in the cell

Additional information:
A citric acid cycle is also known as the Krebs cycle or Tri-carboxylic acid cycle.
Cellular respiration involves three major steps: Glycolysis, Krebs cycle, and Electron transport chain. Cellular respiration produces a net of 38 ATP molecules.
Oxaloacetate, malate, and pyruvate are also involved in the C4 pathway of plants.
Figure 2: Citric acid cycle

Note: Pyruvic acid is a product of Glycolysis, Malic acid is a product of aerobic respiration in the Krebs cycle, and Ethyl alcohol/lactic acid are the products of anaerobic respiration. Pyruvate from the glycolysis process enters the mitochondria only when the cell requires energy. When the pyruvate is not taken up by the mitochondria it remains in the cytoplasm where it is converted to ethanol/ethyl alcohol or lactic acid.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

Name the part of the brain responsible for the precision class 11 biology CBSE

The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to AEffect class 11 biology CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE




