
Which of these is a type of protein secondary structure?
(a) α-helix
(b) β-pleated
(c)Collagen helix
(d)All of the above
Answer
599.1k+ views
Hint: The three-dimensional form of protein segments is known as protein secondary structure and it acts as an intermediate spontaneous form before the protein turns into a tertiary structure.
Complete answer:
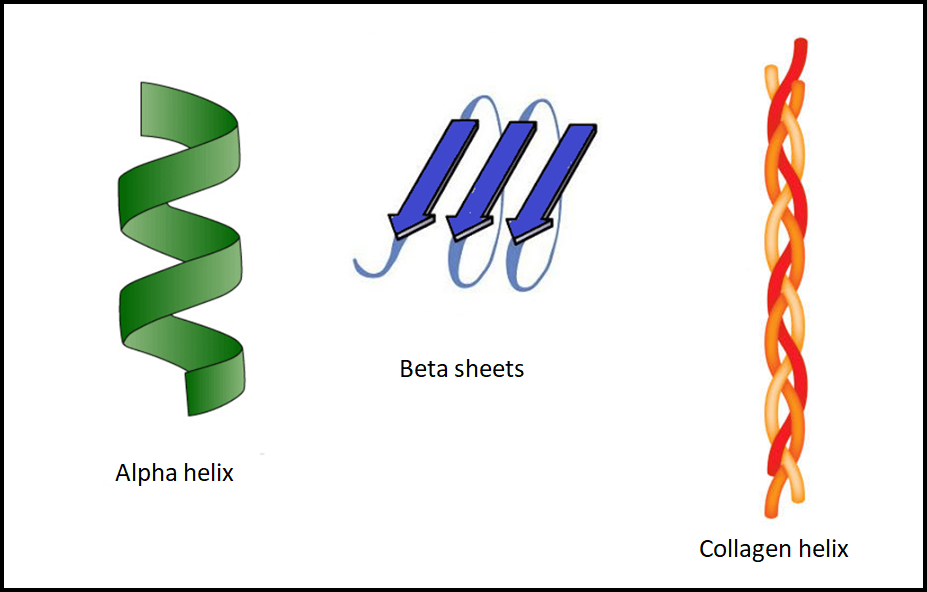
Two common protein secondary structures are alpha helix and beta sheets. Even the collagen helix is a secondary structure. `The secondary structure has regions of stabilized hydrogen bonds between atoms in the polypeptide backbone.
The alpha helix being one of the secondary structure proteins is formed within a polypeptide chain because of the emergence of hydrogen bonds between backbone amide and carbonyl groups. This right hand- helix is formed by the N-H group being the backbone of hydrogen bonds and the C=O group of another amino acid situated three or four residues earlier along the protein sequence. It has 3.6 amino acid residues per turn; this means that an alpha-helix of 10 turns has 36 amino acids.
The beta-sheet has beta strands connected parallel or antiparallel polypeptide chains linked together by H- bonds and forms a general twisted pleated sheet. The successive side chains point straight up, then down and again up, this continues. The beta-strand has 3 to 10 amino acids with a polypeptide chain along the backbone in an extended conformation.
Collagen or type-2 helix is a fibrous protein and consists of the triple helix that is made of repeating glycine-X and glycine-Y amino acid sequence. X and Y are usually proline or hydroxyproline. It is more stretched or elongated compared to the alpha-helix and is a left-handed helix.
So, the correct answer is ‘All of the above’.
Note: Fibrous proteins like collagens are polypeptide chains that are stretched and fibrous in nature. They may even have a sheet-like structure. These sheets are mechanically strong and insoluble in water. They are structural proteins and provide strength and support to the cells and tissue. Other examples of fibrous proteins are keratins, myosins, and elastins.
Complete answer:
Two common protein secondary structures are alpha helix and beta sheets. Even the collagen helix is a secondary structure. `The secondary structure has regions of stabilized hydrogen bonds between atoms in the polypeptide backbone.
The alpha helix being one of the secondary structure proteins is formed within a polypeptide chain because of the emergence of hydrogen bonds between backbone amide and carbonyl groups. This right hand- helix is formed by the N-H group being the backbone of hydrogen bonds and the C=O group of another amino acid situated three or four residues earlier along the protein sequence. It has 3.6 amino acid residues per turn; this means that an alpha-helix of 10 turns has 36 amino acids.
The beta-sheet has beta strands connected parallel or antiparallel polypeptide chains linked together by H- bonds and forms a general twisted pleated sheet. The successive side chains point straight up, then down and again up, this continues. The beta-strand has 3 to 10 amino acids with a polypeptide chain along the backbone in an extended conformation.
Collagen or type-2 helix is a fibrous protein and consists of the triple helix that is made of repeating glycine-X and glycine-Y amino acid sequence. X and Y are usually proline or hydroxyproline. It is more stretched or elongated compared to the alpha-helix and is a left-handed helix.
So, the correct answer is ‘All of the above’.
Note: Fibrous proteins like collagens are polypeptide chains that are stretched and fibrous in nature. They may even have a sheet-like structure. These sheets are mechanically strong and insoluble in water. They are structural proteins and provide strength and support to the cells and tissue. Other examples of fibrous proteins are keratins, myosins, and elastins.

Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

State and prove Bernoullis theorem class 11 physics CBSE

Actinoid contraction is more than lanthanoid contraction class 11 chemistry CBSE

The transition element that has lowest enthalpy of class 11 chemistry CBSE

Can anyone list 10 advantages and disadvantages of friction

State the laws of reflection of light




