
Which of the following will provide the most efficient overlap?
(A) $ s - s $ overlap
(B) $ s - p $ overlap
(C) $ s{p^2} - s{p^2} $ overlap
(D) $ sp - sp $ overlap
Answer
515.4k+ views
Hint: Let us first get some idea about the Atomic orbital. An atomic orbital is a mathematical feature in atomic theory and quantum mechanics that describes the position and wave-like behaviour of an electron in an atom. This function can be used to determine the likelihood of having any atom's electron in any given area around the nucleus.
Complete answer:
An orbital overlap is the accumulation of orbitals on neighbouring atoms in the same regions of space in chemical bonds. Bond formation can be caused by orbital overlap. Since the carbon hybrid orbitals overlap more with the hydrogen orbitals, they can form stronger C–H bonds.
Types of overlapping:
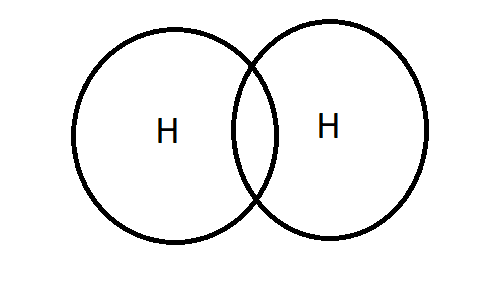
S-S overlapping is the overlapping of the s-s orbitals of two identical or dissimilar atoms, which results in a single covalent bond.
S-P Overlapping: S-P Overlapping is the overlapping of s- and p-orbitals. The overlapping of three nitrogen orbitals ( $ {p_x},{\text{ }}{p_y},{\text{ }}and{\text{ }}{p_z} $ ) with three orbitals of three hydrogen atoms produces $ N{H_3} $ .
$ \begin{gathered}
_7N = 1{s^2}2{s^2}2p_x^12p_y^12p_z^1 \\
1H = 1{s^1} \\
\end{gathered} $
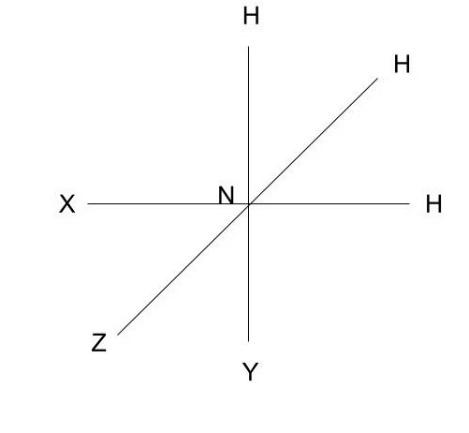
Only when hydrogen electrons approach at right angles to each other in the direction of the X, Y, and Z axes can a strong bond be formed.
P-P overlapping: The overlapping of the atoms' p-orbitals causes p-p overlapping. It is generated by the overlapping of the $ 3{p_z} $ orbitals of two chlorine atoms in the case of the chlorine molecule.
Since these orbitals have a more directional character, the strength of bonds created by overlap of $ sp3 - sp3 $ bonds is greater.
As a result, (s-s) is the correct answer. So the correct option is (A).
Note:
When orbitals have the same energy, they are said to be degenerate. Since the electron spends more time away from the nucleus of the atom as the orbital becomes larger or the shape becomes more complex, the energy of the orbital is affected by both its size and shape.
Complete answer:
An orbital overlap is the accumulation of orbitals on neighbouring atoms in the same regions of space in chemical bonds. Bond formation can be caused by orbital overlap. Since the carbon hybrid orbitals overlap more with the hydrogen orbitals, they can form stronger C–H bonds.
Types of overlapping:
S-S overlapping is the overlapping of the s-s orbitals of two identical or dissimilar atoms, which results in a single covalent bond.

S-P Overlapping: S-P Overlapping is the overlapping of s- and p-orbitals. The overlapping of three nitrogen orbitals ( $ {p_x},{\text{ }}{p_y},{\text{ }}and{\text{ }}{p_z} $ ) with three orbitals of three hydrogen atoms produces $ N{H_3} $ .
$ \begin{gathered}
_7N = 1{s^2}2{s^2}2p_x^12p_y^12p_z^1 \\
1H = 1{s^1} \\
\end{gathered} $

Only when hydrogen electrons approach at right angles to each other in the direction of the X, Y, and Z axes can a strong bond be formed.
P-P overlapping: The overlapping of the atoms' p-orbitals causes p-p overlapping. It is generated by the overlapping of the $ 3{p_z} $ orbitals of two chlorine atoms in the case of the chlorine molecule.
Since these orbitals have a more directional character, the strength of bonds created by overlap of $ sp3 - sp3 $ bonds is greater.
As a result, (s-s) is the correct answer. So the correct option is (A).
Note:
When orbitals have the same energy, they are said to be degenerate. Since the electron spends more time away from the nucleus of the atom as the orbital becomes larger or the shape becomes more complex, the energy of the orbital is affected by both its size and shape.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




