
Which of the following will be compound P?
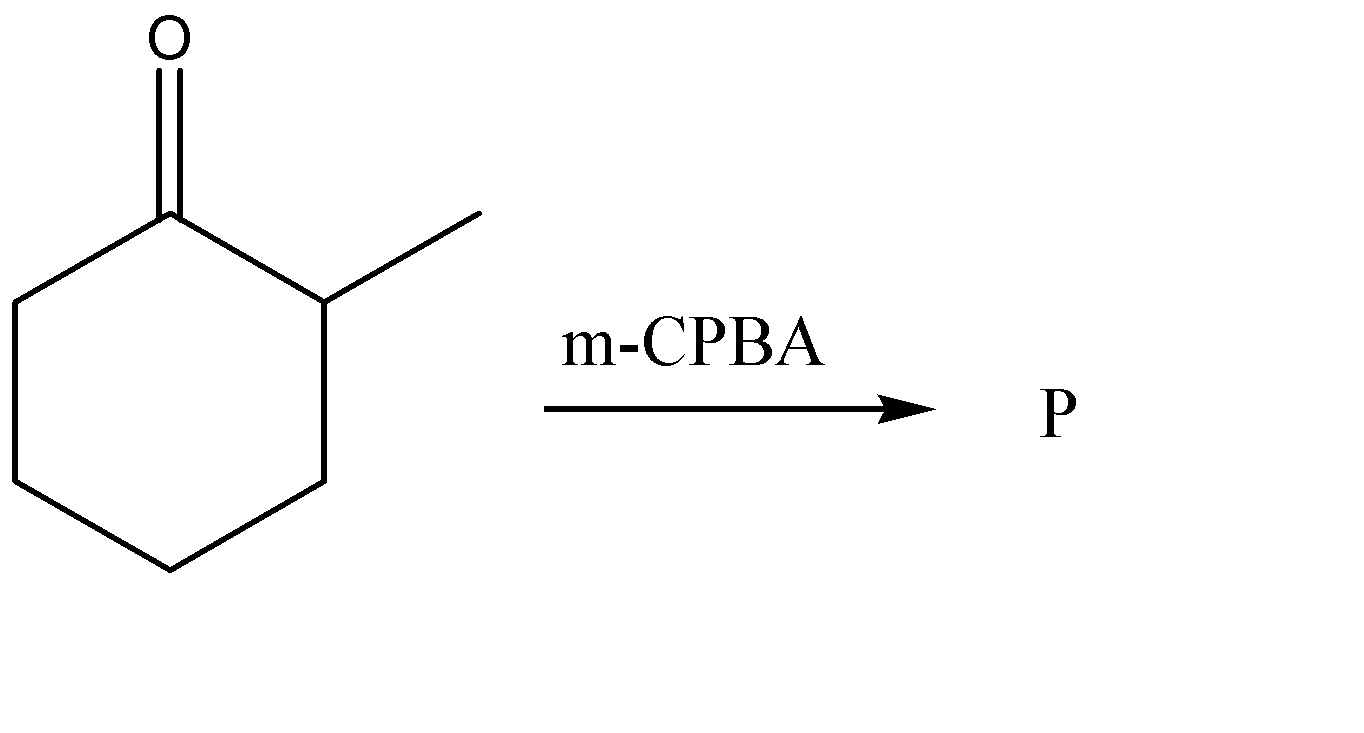
A.
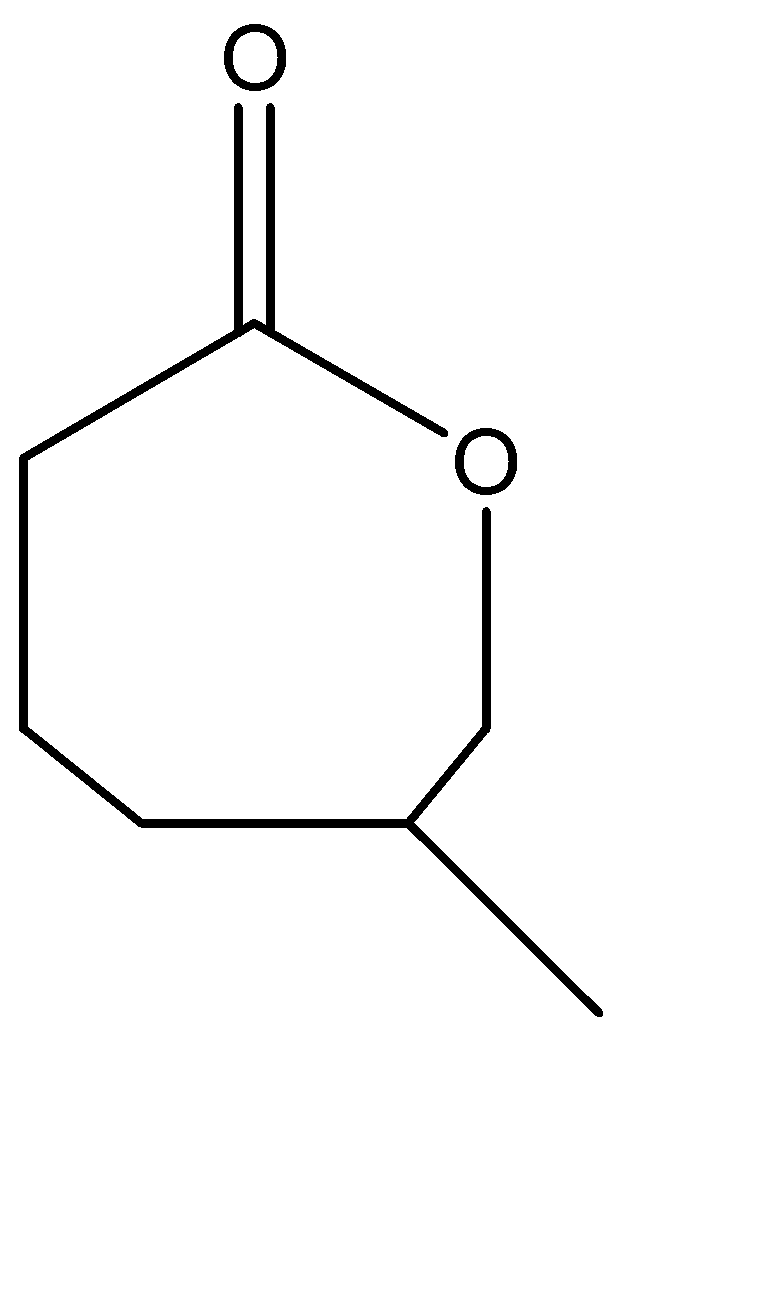
B.
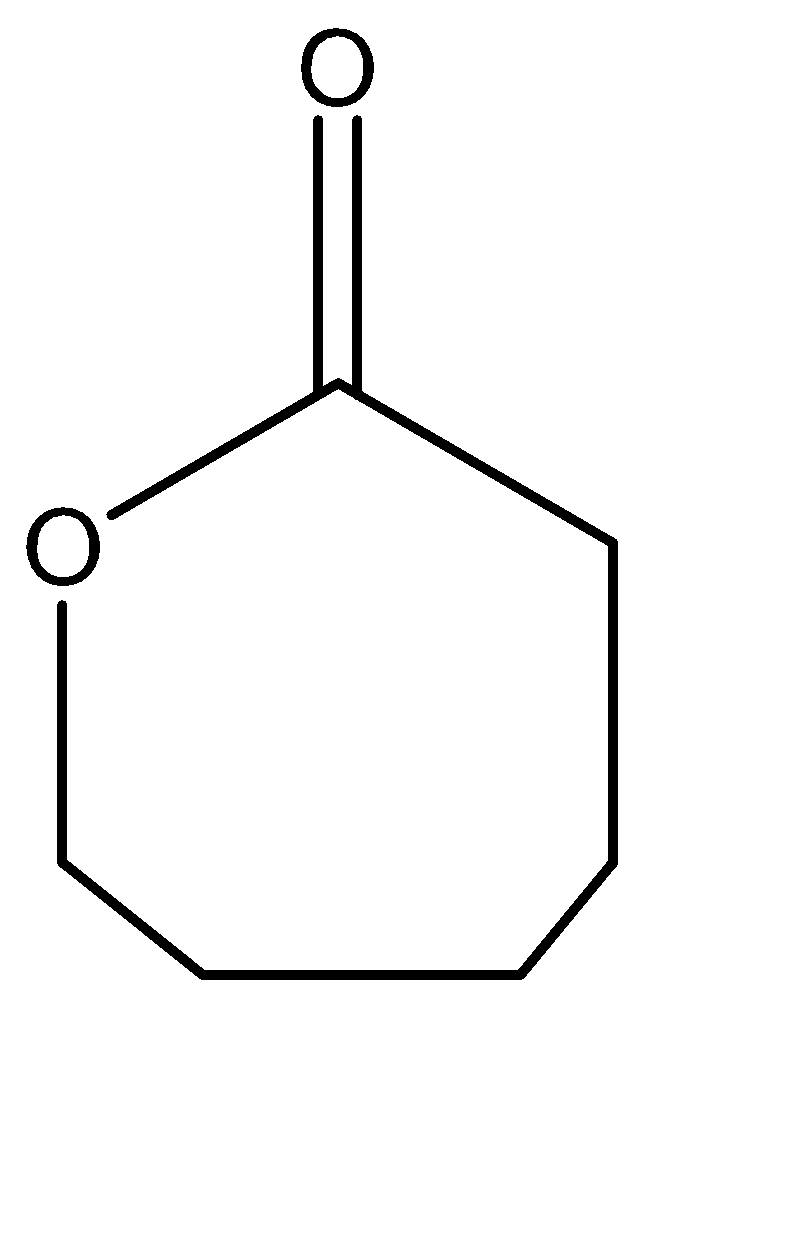
C.
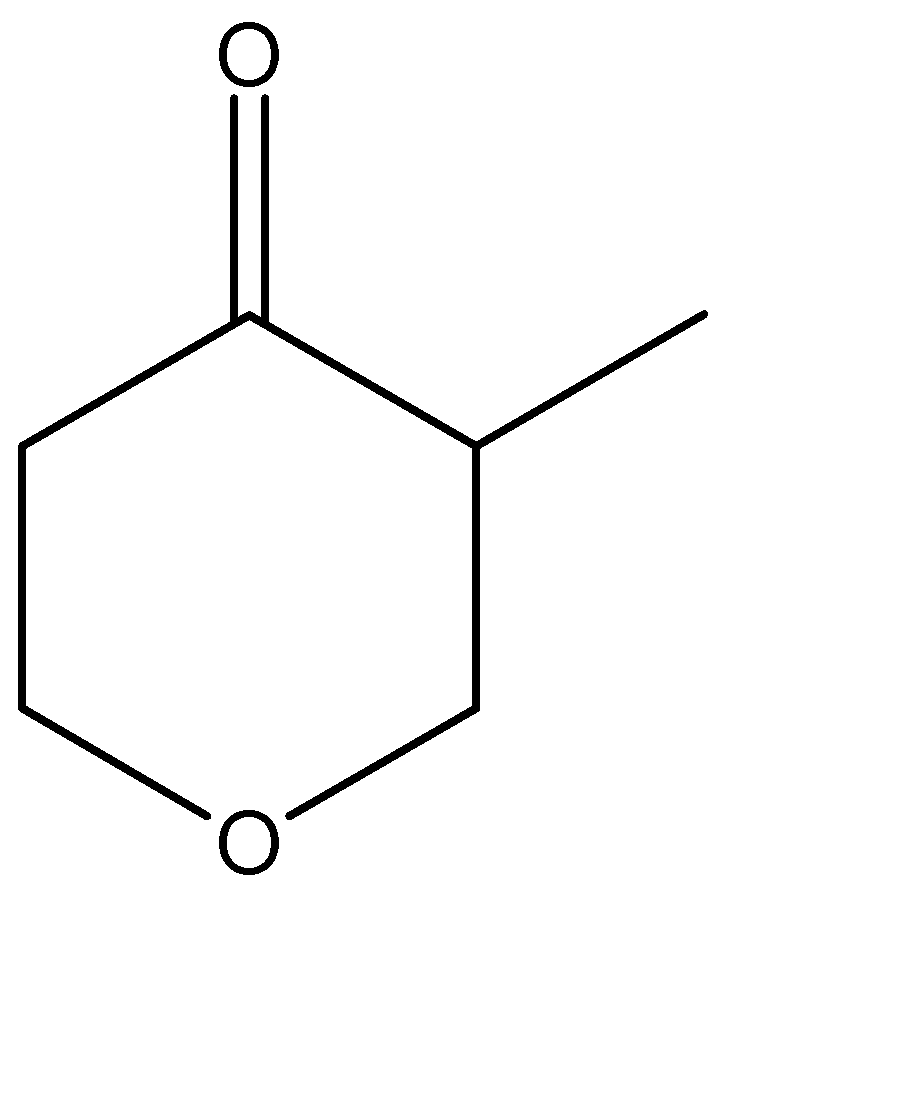
D.
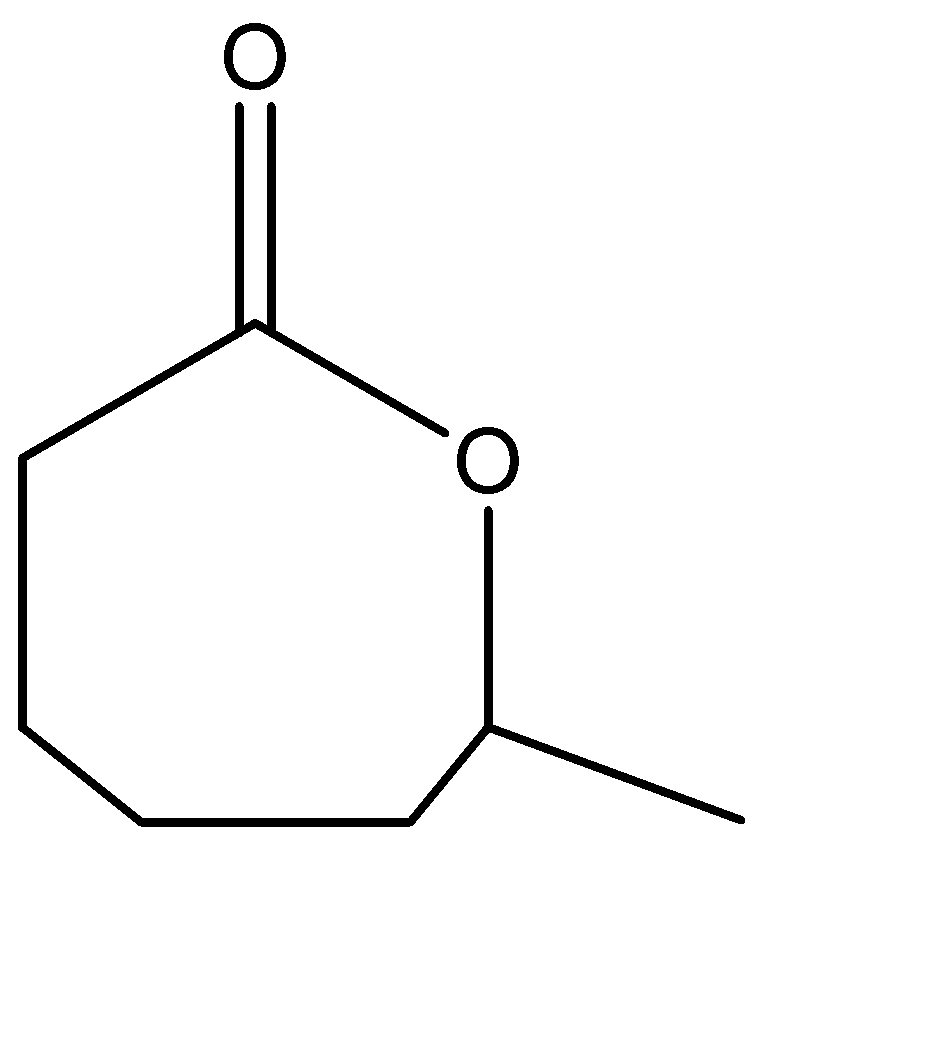





Answer
571.8k+ views
Hint: The compound given to us 2 – methyl cyclohexanone. This compound is a saturated cyclic hydrocarbon compound which has a methyl group at position 02 carbon and has a carbonyl group at its position 01 carbon atom.
Complete step by step answer:
Before we move forward with the solution of the given question, let us first understand some important basic concepts.
Now, the oxygen atom present in the carbonyl group has a lone pair of electrons. This lone pair of electrons can be donated by the oxygen atom and hence it can exhibit nucleophilic nature.
Now, the other compound given to us is meta – chloro pyroxenoid acid. The structure of this compound can be explained as a benzene ring which has a per oxo group attached at one of the carbon atoms. And on the meta position with respect to this per oxo group, we would have a chlorine atom present. The molecular structure of this compound can be given as follows:
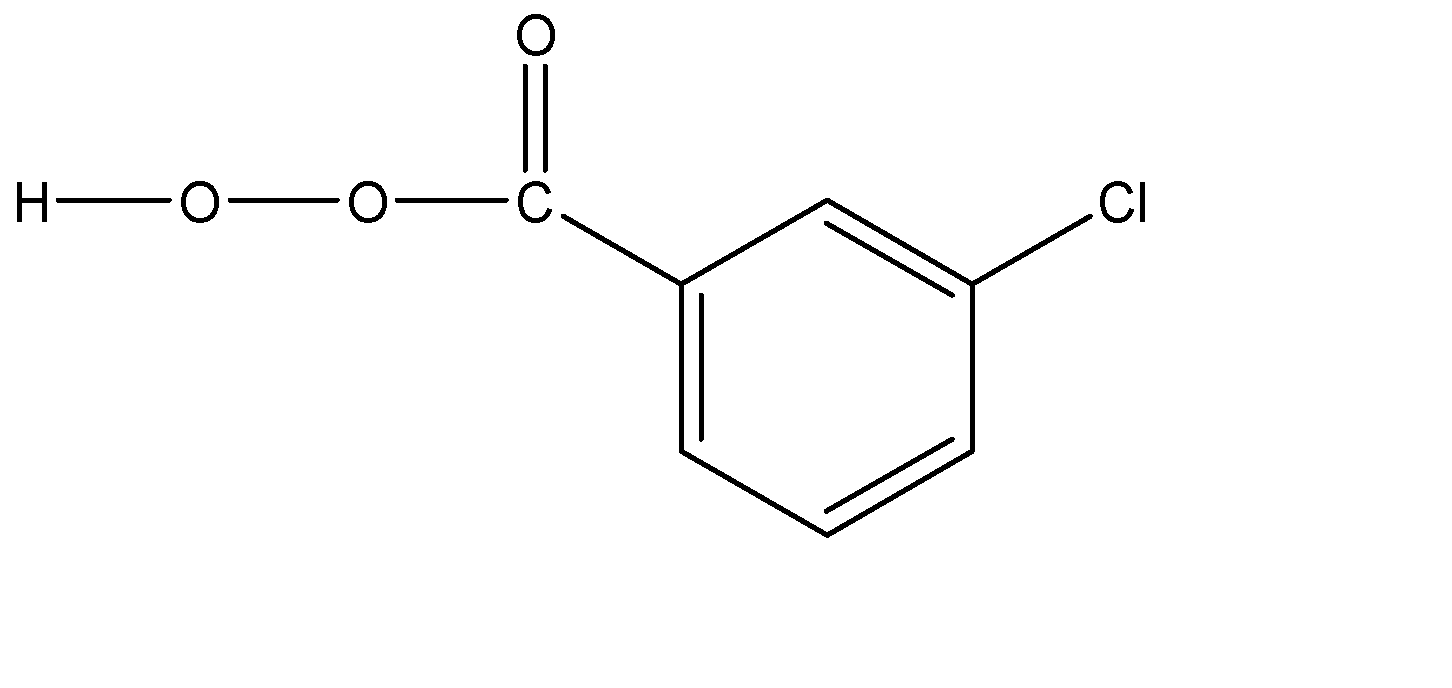
The terminal oxygen atom has a lone pair of electrons, because of which it can show a nucleophilic nature, while the hydrogen atom attached to it can show electrophilic nature.
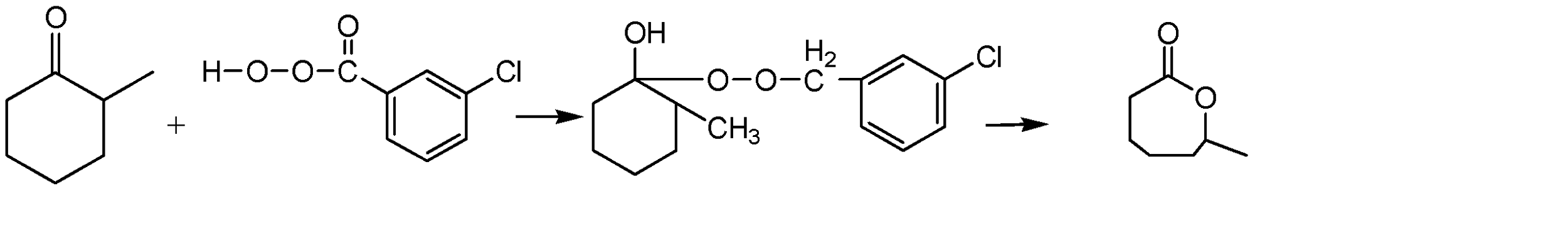
The reaction between these two compounds would result in the hydrogen atom on the terminal oxygen to get attached to the oxygen atom of 2 – methyl cyclohexanone. The lone pair of electrons from the terminal oxygen would also be transferred to the oxygen bonded carbon atom in 2 – methyl cyclohexanone, which would form a bond. This would result in the formation of an intermediate compound. To stabilise this intermediate, we would need to break the oxygen – oxygen bond and cause a ring expansion. The entire chemical reaction can be given as:
Hence, Option C is the correct option
Note: m-CPBA is a peracid derived from meta-chlorobenzoic acid. An oxidant converts an alkene to an epoxide, and a thioether to a sulfoxide, and then to a sulfone.
Complete step by step answer:
Before we move forward with the solution of the given question, let us first understand some important basic concepts.
Now, the oxygen atom present in the carbonyl group has a lone pair of electrons. This lone pair of electrons can be donated by the oxygen atom and hence it can exhibit nucleophilic nature.
Now, the other compound given to us is meta – chloro pyroxenoid acid. The structure of this compound can be explained as a benzene ring which has a per oxo group attached at one of the carbon atoms. And on the meta position with respect to this per oxo group, we would have a chlorine atom present. The molecular structure of this compound can be given as follows:

The terminal oxygen atom has a lone pair of electrons, because of which it can show a nucleophilic nature, while the hydrogen atom attached to it can show electrophilic nature.
The reaction between these two compounds would result in the hydrogen atom on the terminal oxygen to get attached to the oxygen atom of 2 – methyl cyclohexanone. The lone pair of electrons from the terminal oxygen would also be transferred to the oxygen bonded carbon atom in 2 – methyl cyclohexanone, which would form a bond. This would result in the formation of an intermediate compound. To stabilise this intermediate, we would need to break the oxygen – oxygen bond and cause a ring expansion. The entire chemical reaction can be given as:

Hence, Option C is the correct option
Note: m-CPBA is a peracid derived from meta-chlorobenzoic acid. An oxidant converts an alkene to an epoxide, and a thioether to a sulfoxide, and then to a sulfone.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Accountancy: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

10 examples of friction in our daily life




