
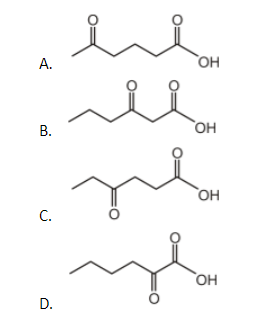
Which of the following undergoes decarboxylation upon heating?

Answer
569.1k+ views
Hint: The carbon – carbon bonds are stable and they don’t break easily. But there are few exceptions, and one of them is decarboxylation upon heating. It is a chemical reaction that removes a carboxyl group and releases carbon dioxide. Generally decarboxylation reaction refers to a reaction of carboxylic acid.
Complete Step by step answer:
The term decarboxylation itself tells its meaning, it means removal of the carboxyl group. And in that place comes hydrogen.
$ RCOOH \to R - H + C{O_2} $
It is one of the oldest known organic reactions.
Decarboxylations of alkanoic acids are slow, therefore simple fatty acid or simple carboxylic acid do not decarboxylate readily. Overall the decarboxylation upon heating occurs in a carboxylic acid if it will form a stable carbanion intermediate in the mechanism. If the carbanion is stable then the decarboxylation occurs easily.
Decarboxylation of beta- keto acids, alpha –phenyl, alpha- nitro and alpha- amino acids occurs readily because the carbanion formed will get stabilized by the resonance. When a carbonyl group will be present two carbons over, an enol can be formed, which will be stabilized by resonance, in the case of beta- keto acids.
Here in the above question, all the options are keto acid. But the beta-acid is where the acid is two carbons away from the keto group. So when we look at them, option A is delta- keto acid, option C is gamma- keto acid, option D is alpha keto acid. But option B is beta-keto acid.
Therefore the correct option will be B.
Note: In biochemistry, decarboxylation is a very important reaction. They are generally classified according to the cofactors that catalyze the transformations. Biotin- coupled processes affect the decarboxylation of malonyl-CoA to acetyl- CoA. Thiamine helps in decarboxylation of alpha- keto acids including pyruvate.
Complete Step by step answer:
The term decarboxylation itself tells its meaning, it means removal of the carboxyl group. And in that place comes hydrogen.
$ RCOOH \to R - H + C{O_2} $
It is one of the oldest known organic reactions.
Decarboxylations of alkanoic acids are slow, therefore simple fatty acid or simple carboxylic acid do not decarboxylate readily. Overall the decarboxylation upon heating occurs in a carboxylic acid if it will form a stable carbanion intermediate in the mechanism. If the carbanion is stable then the decarboxylation occurs easily.
Decarboxylation of beta- keto acids, alpha –phenyl, alpha- nitro and alpha- amino acids occurs readily because the carbanion formed will get stabilized by the resonance. When a carbonyl group will be present two carbons over, an enol can be formed, which will be stabilized by resonance, in the case of beta- keto acids.
Here in the above question, all the options are keto acid. But the beta-acid is where the acid is two carbons away from the keto group. So when we look at them, option A is delta- keto acid, option C is gamma- keto acid, option D is alpha keto acid. But option B is beta-keto acid.
Therefore the correct option will be B.
Note: In biochemistry, decarboxylation is a very important reaction. They are generally classified according to the cofactors that catalyze the transformations. Biotin- coupled processes affect the decarboxylation of malonyl-CoA to acetyl- CoA. Thiamine helps in decarboxylation of alpha- keto acids including pyruvate.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




