
Which of the following statements regarding 1,3-dimethyl cyclobutane is correct?
A) Both cis and trans forms are optically active.
B) Both cis and trans forms are optically inactive.
C) The cis form is optically active, while the trans form is optically inactive.
D) The trans form is optically active, while the cis form is optically inactive.
Answer
481.5k+ views
Hint: We know that an optically active compound rotates the plane of polarized light towards either left or right. For a compound to be optically active there should be a chiral carbon atom present. 1,3-dimethyl cyclobutane is a closed ring saturated hydrocarbon.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
To find if both the isomers of the compound are optically active or optically inactive, we need to discuss the rules for optical activity.
The very basic rule for a compound to be optically active is to have a chiral carbon atom, i.e. at least one carbon should have 4 different groups attached to it.
Also, for a compound to be optically inactive, it should have a plane of symmetry or centre of symmetry or an axis of symmetry.
Now, let’s have a look at the cis form of 1,3-dimethyl cyclobutane.
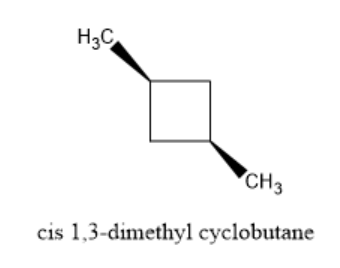
In the figure above, both the methyl groups are present on the same side of the compound. You can observe that there is a plane of symmetry in the cis isomer of 1,3-dimethyl cyclobutane. So, this cis form is optically inactive.
Similarly, observe the trans form of 1,3-dimethyl cyclobutane given below,
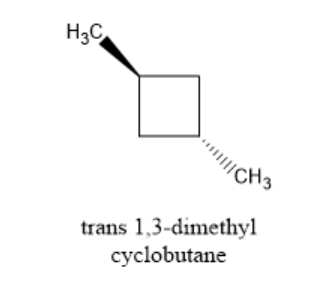
In the figure above, both the methyl groups are present on the opposite side of each other in the compound. You can observe that there is a plane of symmetry as well as the centre of symmetry in the trans isomer of 1,3-dimethyl cyclobutane. Thus, this trans form is optically inactive.
Therefore, both the trans and cis forms of the compound 1,3-dimethyl cyclobutane are optically inactive.
Final answer: The correct answer is Option B- Both cis and trans forms are optically inactive.
Note:
To find the plane of symmetry in a compound, draw a diagonal line passing through the compound. If the groups fall on the opposite side of the diagonal, so there is a plane of symmetry. If both the groups are equidistant from the centre of the compound, we can say there is a centre of symmetry.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
To find if both the isomers of the compound are optically active or optically inactive, we need to discuss the rules for optical activity.
The very basic rule for a compound to be optically active is to have a chiral carbon atom, i.e. at least one carbon should have 4 different groups attached to it.
Also, for a compound to be optically inactive, it should have a plane of symmetry or centre of symmetry or an axis of symmetry.
Now, let’s have a look at the cis form of 1,3-dimethyl cyclobutane.

In the figure above, both the methyl groups are present on the same side of the compound. You can observe that there is a plane of symmetry in the cis isomer of 1,3-dimethyl cyclobutane. So, this cis form is optically inactive.
Similarly, observe the trans form of 1,3-dimethyl cyclobutane given below,

In the figure above, both the methyl groups are present on the opposite side of each other in the compound. You can observe that there is a plane of symmetry as well as the centre of symmetry in the trans isomer of 1,3-dimethyl cyclobutane. Thus, this trans form is optically inactive.
Therefore, both the trans and cis forms of the compound 1,3-dimethyl cyclobutane are optically inactive.
Final answer: The correct answer is Option B- Both cis and trans forms are optically inactive.
Note:
To find the plane of symmetry in a compound, draw a diagonal line passing through the compound. If the groups fall on the opposite side of the diagonal, so there is a plane of symmetry. If both the groups are equidistant from the centre of the compound, we can say there is a centre of symmetry.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




