
Which of the following statements is correct for \[{\text{NO}}_3^ - \] ion?
(A) Sum of all formal charges is +1.
(B) Formal charge on one of the oxygen atoms is -2.
(C) Formal charge on nitrogen atoms is +1.
(D) Average formal charge on oxygen atom is \[ - \dfrac{2}{3}\]
Answer
584.4k+ views
Hint: \[{\text{NO}}_3^ - \] ion is nitrate ion. It is obtained when nitric acid ionizes and loses a proton.
Use the following expression to calculate the formal charge on each atom
\[\left( {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}}
{{\text{Formal charge}}} \\
{{\text{on an atom}}}
\end{array}} \right) = \left( {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}}
{{\text{Number of}}} \\
{{\text{valence electrons}}}
\end{array}} \right) - \left( {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}}
{{\text{Number of}}} \\
{{\text{non bonding electrons}}}
\end{array}} \right) - \left[ {\;\dfrac{{\text{1}}}{2}\left( {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}}
{{\text{Number of}}} \\
{{\text{bonding electrons}}}
\end{array}} \right)} \right]\]
Complete step by step answer:
Nitrogen atoms have 5 valence electrons. Oxygen atoms have 6 valence electrons. One oxygen atom has additional electrons due to negative charge on nitrate ions. This additional electron is transferred to oxygen when hydrogen-oxygen bond heterolytically breaks in nitric acid to provide an electron.
Draw the Lewis dot structure for nitrate ion.
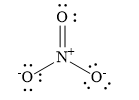
Nitrogen atoms have 5 valence electrons, 0 nonbonding electrons and 8 bonding electrons. Since nitrogen forms four bonds, it has eight electrons. Calculate the formal charge on nitrogen atom:
\[\begin{array}{l}
{\rm{Formal\;charge }} = {\rm{ 5 }} - {\rm{ 0 }} - \left[ {\dfrac{{\rm{1}}}{2}\left( {\rm{8}} \right)} \right]{\rm{ = 5 - 4 = + 1}}\\
{\rm{on\;nitrogen \;atom}}
\end{array}\]
Singly bonded atom has 6 valence electrons, 6 nonbonding electrons and 2 bonding electrons. Since oxygen forms one bond, it has two electrons. Calculate the formal charge on singly bonded atom:
\[\begin{array}{l}
{\rm{Formal\; charge }} = {\rm{ 6 }} - {\rm{ 6 }} - \left[ {\dfrac{{\rm{1}}}{2}\left( {\rm{2}} \right)} \right]{\rm{ = 0}} - {\rm{1 = }} - {\rm{1}}\\
{\rm{on \;oxygen\; atom}}
\end{array}\]
Doubly bonded atom has 6 valence electrons, 4 nonbonding electrons and 4 bonding electrons. Since oxygen forms two bonds, it has four electrons. Calculate the formal charge on doubly bonded atom:
\[\begin{array}{l}
{\rm{Formal\; charge }} = {\rm{ 6 }} - {\rm{ 4 }} - \left[ {\dfrac{{\rm{1}}}{2}\left( {\rm{4}} \right)} \right]{\rm{ = 2}} - 2{\rm{ = 0}}\\
{\rm{on\; oxygen\; atom}}
\end{array}\]
Let us consider all the options:
(A) Sum of all formal charges is -1 not +1. It is equal to the charge on the nitrate ion. So this option is not correct.
(B) Formal charge on one of the oxygen atoms is 0. For the remaining 2 oxygen atoms, the formal charge is -1 on each oxygen atom. So this option is also not correct.
(C) Formal charge on nitrogen atoms is +1. So this option is correct.
(D) Average formal charge on an oxygen atom is \[ - \dfrac{2}{3}\]. This is also correct.
There are three oxygen atoms with a total of formal charges on three oxygen atoms being \[0 - 1 - 1 = - 2\] .
Hence, the correct options are the options (C) and (D).
Note: The formal charge on an atom in a compound represents the number of electrons gained, lost or shared by that atom to form a bond. When an oxygen atom forms two covalent bonds by sharing of electrons, it has formal charge of 0. When a nitrogen atom forms three covalent bonds and one coordinate bond, it has formal charge of +1. When an oxygen atom accepts an electron, it has formal charge of -1. When an oxygen atom accepts bond pairs of electrons due to heterolytic bond cleavage, it has a formal charge of -1.
Use the following expression to calculate the formal charge on each atom
\[\left( {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}}
{{\text{Formal charge}}} \\
{{\text{on an atom}}}
\end{array}} \right) = \left( {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}}
{{\text{Number of}}} \\
{{\text{valence electrons}}}
\end{array}} \right) - \left( {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}}
{{\text{Number of}}} \\
{{\text{non bonding electrons}}}
\end{array}} \right) - \left[ {\;\dfrac{{\text{1}}}{2}\left( {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}}
{{\text{Number of}}} \\
{{\text{bonding electrons}}}
\end{array}} \right)} \right]\]
Complete step by step answer:
Nitrogen atoms have 5 valence electrons. Oxygen atoms have 6 valence electrons. One oxygen atom has additional electrons due to negative charge on nitrate ions. This additional electron is transferred to oxygen when hydrogen-oxygen bond heterolytically breaks in nitric acid to provide an electron.
Draw the Lewis dot structure for nitrate ion.

Nitrogen atoms have 5 valence electrons, 0 nonbonding electrons and 8 bonding electrons. Since nitrogen forms four bonds, it has eight electrons. Calculate the formal charge on nitrogen atom:
\[\begin{array}{l}
{\rm{Formal\;charge }} = {\rm{ 5 }} - {\rm{ 0 }} - \left[ {\dfrac{{\rm{1}}}{2}\left( {\rm{8}} \right)} \right]{\rm{ = 5 - 4 = + 1}}\\
{\rm{on\;nitrogen \;atom}}
\end{array}\]
Singly bonded atom has 6 valence electrons, 6 nonbonding electrons and 2 bonding electrons. Since oxygen forms one bond, it has two electrons. Calculate the formal charge on singly bonded atom:
\[\begin{array}{l}
{\rm{Formal\; charge }} = {\rm{ 6 }} - {\rm{ 6 }} - \left[ {\dfrac{{\rm{1}}}{2}\left( {\rm{2}} \right)} \right]{\rm{ = 0}} - {\rm{1 = }} - {\rm{1}}\\
{\rm{on \;oxygen\; atom}}
\end{array}\]
Doubly bonded atom has 6 valence electrons, 4 nonbonding electrons and 4 bonding electrons. Since oxygen forms two bonds, it has four electrons. Calculate the formal charge on doubly bonded atom:
\[\begin{array}{l}
{\rm{Formal\; charge }} = {\rm{ 6 }} - {\rm{ 4 }} - \left[ {\dfrac{{\rm{1}}}{2}\left( {\rm{4}} \right)} \right]{\rm{ = 2}} - 2{\rm{ = 0}}\\
{\rm{on\; oxygen\; atom}}
\end{array}\]
Let us consider all the options:
(A) Sum of all formal charges is -1 not +1. It is equal to the charge on the nitrate ion. So this option is not correct.
(B) Formal charge on one of the oxygen atoms is 0. For the remaining 2 oxygen atoms, the formal charge is -1 on each oxygen atom. So this option is also not correct.
(C) Formal charge on nitrogen atoms is +1. So this option is correct.
(D) Average formal charge on an oxygen atom is \[ - \dfrac{2}{3}\]. This is also correct.
There are three oxygen atoms with a total of formal charges on three oxygen atoms being \[0 - 1 - 1 = - 2\] .
Hence, the correct options are the options (C) and (D).
Note: The formal charge on an atom in a compound represents the number of electrons gained, lost or shared by that atom to form a bond. When an oxygen atom forms two covalent bonds by sharing of electrons, it has formal charge of 0. When a nitrogen atom forms three covalent bonds and one coordinate bond, it has formal charge of +1. When an oxygen atom accepts an electron, it has formal charge of -1. When an oxygen atom accepts bond pairs of electrons due to heterolytic bond cleavage, it has a formal charge of -1.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




