
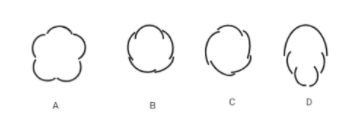
Which of the following shows the aestivation of petals in the flower of cotton?

Answer
572.7k+ views
Hint: The flowering plants (angiosperms) exhibit a variety of structure, shape, size, life span, mode of nutrition, and habitat. The flowers of these plants also show different types of arrangements (inflorescence).
Complete answer:
Flowering plants show a variation in their structure, symmetry, the arrangement of sepals, petals, and ovules, and position of the ovary with respect to all the other floral parts. The manner of arrangement of petals or sepals in the floral bud with respect to all the other floral parts of the flower is known as aestivation. There are four types of aestivation, namely, valvate, twisted, imbricate, and vexillary. When the sepals or petals do not overlap each other and just touch at the margin (as shown in option A), the aestivation is known as valvate. When the margins of the appendages overlap each other but in a random manner (not in any particular direction as shown in option B), the aestivation is known as imbricate. When the margin of one appendage overlaps that of the next and so on (as shown in option C), this type of aestivation is known as twisted. When one of the five petals is the largest and overlaps the next two lateral petals, which then overlaps the next two smallest anterior petals (as shown in option D), the aestivation is known as vexillary. The largest petal is known as the standard petal, the next two petals are called wings, and the last two smallest petals are known as the keel.
In the flower of cotton, twisted aestivation is observed.
Hence, the correct answer is option (C).
Note: Valvate aestivation is seen in the Calotropis plant, imbricate aestivation is seen in Cassia and Gulmohar, and vexillary aestivation is seen in the pea and bean flowers.
Complete answer:
Flowering plants show a variation in their structure, symmetry, the arrangement of sepals, petals, and ovules, and position of the ovary with respect to all the other floral parts. The manner of arrangement of petals or sepals in the floral bud with respect to all the other floral parts of the flower is known as aestivation. There are four types of aestivation, namely, valvate, twisted, imbricate, and vexillary. When the sepals or petals do not overlap each other and just touch at the margin (as shown in option A), the aestivation is known as valvate. When the margins of the appendages overlap each other but in a random manner (not in any particular direction as shown in option B), the aestivation is known as imbricate. When the margin of one appendage overlaps that of the next and so on (as shown in option C), this type of aestivation is known as twisted. When one of the five petals is the largest and overlaps the next two lateral petals, which then overlaps the next two smallest anterior petals (as shown in option D), the aestivation is known as vexillary. The largest petal is known as the standard petal, the next two petals are called wings, and the last two smallest petals are known as the keel.
In the flower of cotton, twisted aestivation is observed.
Hence, the correct answer is option (C).
Note: Valvate aestivation is seen in the Calotropis plant, imbricate aestivation is seen in Cassia and Gulmohar, and vexillary aestivation is seen in the pea and bean flowers.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

The largest wind power cluster is located in the state class 11 social science CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

State and prove Bernoullis theorem class 11 physics CBSE

What steps did the French revolutionaries take to create class 11 social science CBSE

Which among the following are examples of coming together class 11 social science CBSE




