
Which of the following molecules has two sigma $(\sigma )$ and two pi $(\pi )$ bonds?
(A) ${{C}_{2}}{{H}_{4}}$
(B) ${{N}_{2}}{{F}_{2}}$
(C) ${{C}_{2}}{{H}_{2}}C{{l}_{2}}$
(D) HCN
Answer
573.6k+ views
Hint: Unhybridized atomic orbitals of carbon atoms overlaps to form a bond. There are two types of bonds in organic chemistry: a sigma bond and a pi bond. The molecular skeleton is made by the sigma bond. If compounds have multiple bonds then one bond is always a sigma bond and others are considered as the pi bonds.
Complete Solution :
Organic compounds are formed by the overlapping of orbitals. This overlapping is also called bonds. Sigma bond is formed by the head to head overlap of orbitals. However, the lateral or sideways overlapping of orbitals results in pi bonds.
Sigma bond is always present in the molecule. However, if a molecule has a double bond then there is one sigma bond and one pi bond .for a triple bond, there are one sigma bond and two pi bonds.
We have been provided with four compounds${{C}_{2}}{{H}_{4}}$, ${{N}_{2}}{{F}_{2}}$, ${{C}_{2}}{{H}_{2}}C{{l}_{2}}$ and HCN.
We need to calculate the sigma and pi bonds.
So, for that:
- The first compound we have ${{C}_{2}}{{H}_{4}}$:
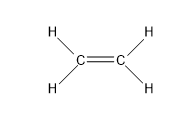
So, the sigma bonds would be 5, and pi bonds would be 1.
- The next compound is ${{N}_{2}}{{F}_{2}}$:
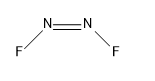
So, the sigma bonds would be 3, and pi bonds would be 1.
- The next compound is ${{C}_{2}}{{H}_{2}}C{{l}_{2}}$:
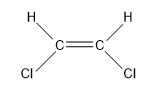
So, the sigma bonds would be 5, and pi bonds would be 1.
- The last one we have is HCN:
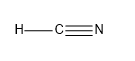
So, the sigma bonds would be 2, and pi bonds would be 2.
So, we can say that HCN has 2 sigma and 2 pi bonds.
So, the correct answer is “Option D”.
Note: Note that, sigma bond is considered the strongest type of covalent bond. This is because the sigma bond is due to the maximum extent of the overlap of orbitals. Sigma bond allows the free rotation of atoms around it. However double or the triple bond restricts the free rotation of the bond. This bond is formed by the unhybridized orbitals.
Complete Solution :
Organic compounds are formed by the overlapping of orbitals. This overlapping is also called bonds. Sigma bond is formed by the head to head overlap of orbitals. However, the lateral or sideways overlapping of orbitals results in pi bonds.
Sigma bond is always present in the molecule. However, if a molecule has a double bond then there is one sigma bond and one pi bond .for a triple bond, there are one sigma bond and two pi bonds.
We have been provided with four compounds${{C}_{2}}{{H}_{4}}$, ${{N}_{2}}{{F}_{2}}$, ${{C}_{2}}{{H}_{2}}C{{l}_{2}}$ and HCN.
We need to calculate the sigma and pi bonds.
So, for that:
- The first compound we have ${{C}_{2}}{{H}_{4}}$:

So, the sigma bonds would be 5, and pi bonds would be 1.
- The next compound is ${{N}_{2}}{{F}_{2}}$:

So, the sigma bonds would be 3, and pi bonds would be 1.
- The next compound is ${{C}_{2}}{{H}_{2}}C{{l}_{2}}$:

So, the sigma bonds would be 5, and pi bonds would be 1.
- The last one we have is HCN:
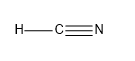
So, the sigma bonds would be 2, and pi bonds would be 2.
So, we can say that HCN has 2 sigma and 2 pi bonds.
So, the correct answer is “Option D”.
Note: Note that, sigma bond is considered the strongest type of covalent bond. This is because the sigma bond is due to the maximum extent of the overlap of orbitals. Sigma bond allows the free rotation of atoms around it. However double or the triple bond restricts the free rotation of the bond. This bond is formed by the unhybridized orbitals.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




