
Which of the following is planar?
A. \[Xe{F_2}\]
B. \[Xe{O_3}F\]
C. \[Xe{O_2}{F_2}\]
D. \[Xe{F_4}\]
Answer
568.2k+ views
Hint: The geometry of a molecule is obtained by the determination of the hybridization of the central atom. The planar geometry means all the bonded atoms to the central atom lie in one plane.
Complete step by step answer:
The given molecules are compounds of xenon atoms. Xenon is an element in the periodic table with atomic number \[54\]. Its electronic configuration is \[[Kr]4{d^{10}}5{s^2}5{p^6}\]. The outermost shell of xenon is \[5\] and it has eight electrons available to take part in chemical bonding.
Xenon also has higher \[5d\] orbitals available for bonding. The outer \[5d\] orbitals are used for making hybrid orbitals. Let us determine the hybridization and the geometry of the molecules one by one.
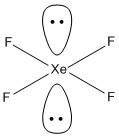
A. \[Xe{F_2}\]. The central atom is xenon and it is attached to two fluorine atoms. The number of valence electrons of xenon is \[8\] and the electrons form two fluorine atoms is\[2\]. Thus the VSEP number of \[Xe{F_2}\] is =\[\dfrac{1}{2}\left( {8 + 2} \right) = 5\] .
The VSEP number equal to \[5\] belongs to \[s{p^3}d\] hybridization. The general shape of the molecule with \[s{p^3}d\] hybridization is trigonal bipyramidal. In this compound only two bonded pairs of electrons are present and three non-bonded electron pairs are present. The two fluorine atoms occupy the axial position of the TBP structure and the three non bonded pairs occupy the equatorial positions. Thus the two fluorine atoms lie above and below the plane and the three non-bonded electrons lie in one plane. Hence the molecule attains a linear geometry and is not planar.
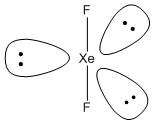
B. \[Xe{O_3}F\]. The central atom xenon is bonded to three oxygen atoms and one fluorine atom. The number of electrons from a xenon atom is \[8\] and one electron from one fluorine atom. Thus the VSEP number is
=\[\dfrac{1}{2}\left( {8 + 1} \right) = 4.5\].
The three oxygen atoms are bonded by three double bonds to the central atom. One fluorine atom is bounded by one single bond. So the molecule contains a free electron. The shape of the molecule is distorted pyramidal with the fluorine atom occupying the axial position and the three oxygen atoms occupy the equatorial position. Hence the molecule is not planar.

C. \[Xe{O_2}{F_2}\]. The central xenon atom is bonded to two oxygen atoms and two fluorine atoms. The electrons from the xenon atom are \[8\]and \[2\] electrons from two fluorine atoms. Thus the VSEP number is
=\[\dfrac{1}{2}\left( {8 + 2} \right) = 5\]
The xenon atom is \[s{p^3}d\] hybridized and the geometry is see-saw or pi shaped. The two oxygen atoms occupy the equatorial position making double bonds with the xenon atom and the two fluorine atoms occupy the axial position by making a single bond. The lone pair of electrons occupies the equatorial position. Hence the molecule is not planar.
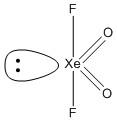
D. \[Xe{F_4}\]. The central atom xenon is bonded to four fluorine atoms. The electrons from the xenon atom are \[8\] and the electrons from four fluorine atoms are \[4\]. Thus VSEP number is
=\[\dfrac{1}{2}\left( {8 + 4} \right) = 6\] .
The VSEPR number \[6\] belongs to the \[s{p^3}{d^2}\] hybridization. The general structure of \[s{p^3}{d^2}\] hybridization is octahedral. So the four fluorine atoms bonded by a single bond occupy the equatorial position in a plane and the lone pairs occupy the axial position. The geometry of the molecule is square planar and hence the molecule is planar, i.e. option D is the correct answer.
Note:
The elements down the group use outer valence orbitals for making hybrid orbitals. In general the less electronegative atoms bonded to the central atom occupies the equatorial position and the more electronegative atoms occupies the axial position. But the case is different for \[Xe{F_4}\].
Complete step by step answer:
The given molecules are compounds of xenon atoms. Xenon is an element in the periodic table with atomic number \[54\]. Its electronic configuration is \[[Kr]4{d^{10}}5{s^2}5{p^6}\]. The outermost shell of xenon is \[5\] and it has eight electrons available to take part in chemical bonding.
Xenon also has higher \[5d\] orbitals available for bonding. The outer \[5d\] orbitals are used for making hybrid orbitals. Let us determine the hybridization and the geometry of the molecules one by one.
A. \[Xe{F_2}\]. The central atom is xenon and it is attached to two fluorine atoms. The number of valence electrons of xenon is \[8\] and the electrons form two fluorine atoms is\[2\]. Thus the VSEP number of \[Xe{F_2}\] is =\[\dfrac{1}{2}\left( {8 + 2} \right) = 5\] .
The VSEP number equal to \[5\] belongs to \[s{p^3}d\] hybridization. The general shape of the molecule with \[s{p^3}d\] hybridization is trigonal bipyramidal. In this compound only two bonded pairs of electrons are present and three non-bonded electron pairs are present. The two fluorine atoms occupy the axial position of the TBP structure and the three non bonded pairs occupy the equatorial positions. Thus the two fluorine atoms lie above and below the plane and the three non-bonded electrons lie in one plane. Hence the molecule attains a linear geometry and is not planar.

B. \[Xe{O_3}F\]. The central atom xenon is bonded to three oxygen atoms and one fluorine atom. The number of electrons from a xenon atom is \[8\] and one electron from one fluorine atom. Thus the VSEP number is
=\[\dfrac{1}{2}\left( {8 + 1} \right) = 4.5\].
The three oxygen atoms are bonded by three double bonds to the central atom. One fluorine atom is bounded by one single bond. So the molecule contains a free electron. The shape of the molecule is distorted pyramidal with the fluorine atom occupying the axial position and the three oxygen atoms occupy the equatorial position. Hence the molecule is not planar.

C. \[Xe{O_2}{F_2}\]. The central xenon atom is bonded to two oxygen atoms and two fluorine atoms. The electrons from the xenon atom are \[8\]and \[2\] electrons from two fluorine atoms. Thus the VSEP number is
=\[\dfrac{1}{2}\left( {8 + 2} \right) = 5\]
The xenon atom is \[s{p^3}d\] hybridized and the geometry is see-saw or pi shaped. The two oxygen atoms occupy the equatorial position making double bonds with the xenon atom and the two fluorine atoms occupy the axial position by making a single bond. The lone pair of electrons occupies the equatorial position. Hence the molecule is not planar.

D. \[Xe{F_4}\]. The central atom xenon is bonded to four fluorine atoms. The electrons from the xenon atom are \[8\] and the electrons from four fluorine atoms are \[4\]. Thus VSEP number is
=\[\dfrac{1}{2}\left( {8 + 4} \right) = 6\] .
The VSEPR number \[6\] belongs to the \[s{p^3}{d^2}\] hybridization. The general structure of \[s{p^3}{d^2}\] hybridization is octahedral. So the four fluorine atoms bonded by a single bond occupy the equatorial position in a plane and the lone pairs occupy the axial position. The geometry of the molecule is square planar and hence the molecule is planar, i.e. option D is the correct answer.

Note:
The elements down the group use outer valence orbitals for making hybrid orbitals. In general the less electronegative atoms bonded to the central atom occupies the equatorial position and the more electronegative atoms occupies the axial position. But the case is different for \[Xe{F_4}\].
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Giving reasons state the signs positive or negative class 12 physics CBSE

Explain esterification reaction with the help of a class 12 chemistry CBSE

What is defined as a solenoid Depict a diagram with class 12 physics CBSE




