
Which of the following is not a stage of mitosis?
A. Anaphase
B. Metaphase
C. Interphase
D. Prophase
Answer
585.6k+ views
Hint: This stage is basically the portion of the cell cycle that's not characterized by any proper observable changes under the microscope, and includes the G1, S (synthesis phase), and G2 phases. During this phase, the cell significantly increases in size (G1), replicates its DNA (S), and prepares for mitosis (G2).
Step by step answer:The cell cycle for any cell is split into two distinct phases which are namely, the interphase and M phase. The M phase is denoted for mitosis or meiosis, here the actual process of cellular division takes place. The interphase is the phase where the G1, S, and G2 phases of the cell cycle are included. During this stage, the cell grows and rests between the two consecutive following cell divisions. In the G1 phase is the first growth phase and the longest phase in which the nucleus grows in size. In the S phase or synthetic phase, DNA replication takes place and chromatin fibres are produced however the chromosome number remains the same. In the last phase of interphase which is the G2 phase, the DNA synthesis stops and RNA and protein formation occur. The mitotic division is characterized by the presence of 4 phases. During prophase of the cell cycle, the condensation of the chromatin takes place and the disappearance of the nuclear membrane follows; this is followed by metaphase where the genetic material that's the chromosomes, they're lined at the equatorial plate. After which the chromosomes are pulled at the poles of the dividing cell by the spindle fibers attached to their kinetochores which is the characteristic of anaphase. The last phase is the telophase where the nuclear membrane starts to seem again and ultimately the cytokinesis and karyokinesis take place. From prophase to telophase, these stages are part of the M phase or Mitosis phase.
Hence option C is correct.
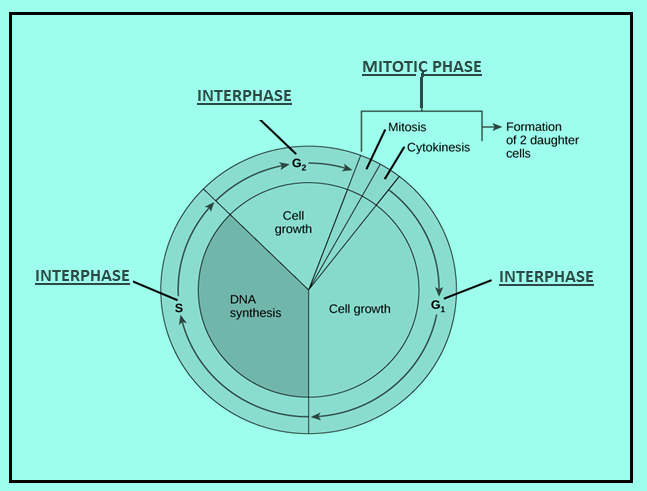
Note: During the interphase, the cell is consistently synthesizing RNA, producing protein, and growing in size. By studying molecular events in cells, scientists have determined the stages of interphase which are G1, S, and G2.
Step by step answer:The cell cycle for any cell is split into two distinct phases which are namely, the interphase and M phase. The M phase is denoted for mitosis or meiosis, here the actual process of cellular division takes place. The interphase is the phase where the G1, S, and G2 phases of the cell cycle are included. During this stage, the cell grows and rests between the two consecutive following cell divisions. In the G1 phase is the first growth phase and the longest phase in which the nucleus grows in size. In the S phase or synthetic phase, DNA replication takes place and chromatin fibres are produced however the chromosome number remains the same. In the last phase of interphase which is the G2 phase, the DNA synthesis stops and RNA and protein formation occur. The mitotic division is characterized by the presence of 4 phases. During prophase of the cell cycle, the condensation of the chromatin takes place and the disappearance of the nuclear membrane follows; this is followed by metaphase where the genetic material that's the chromosomes, they're lined at the equatorial plate. After which the chromosomes are pulled at the poles of the dividing cell by the spindle fibers attached to their kinetochores which is the characteristic of anaphase. The last phase is the telophase where the nuclear membrane starts to seem again and ultimately the cytokinesis and karyokinesis take place. From prophase to telophase, these stages are part of the M phase or Mitosis phase.
Hence option C is correct.

Note: During the interphase, the cell is consistently synthesizing RNA, producing protein, and growing in size. By studying molecular events in cells, scientists have determined the stages of interphase which are G1, S, and G2.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




