
Which of the following is a direct source of energy for muscle contraction?
(a)ATP
(b)Creatine phosphate
(c)Lactic acid
(d)Both (a) and (b)
Answer
566.7k+ views
Hint: Energy is required by the myosin filament to break the cross-bridge formation with the actin filament which is responsible for muscle contraction. The direct source of energy in muscle contraction comes from the molecule which is also known as the energy currency of the cell.
Complete answer:
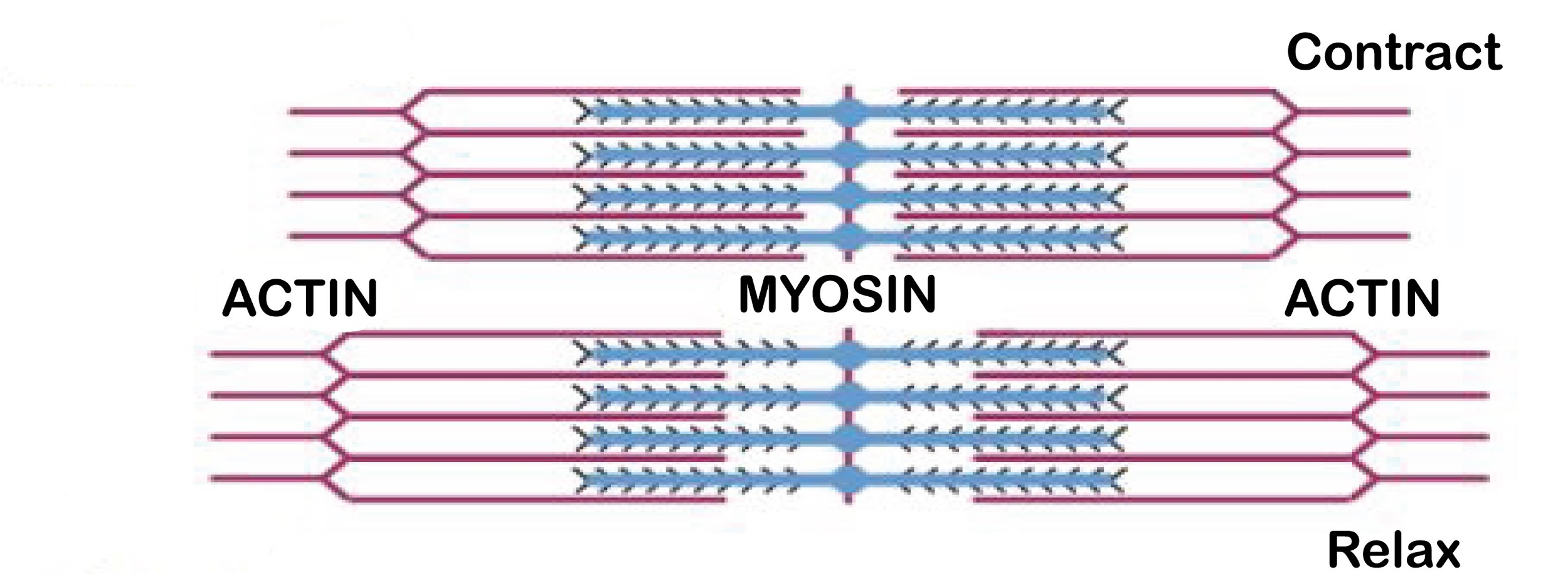
The direct source of energy for muscular contraction is ATP and creatinine. ATP binds to myosin after which it is hydrolyzed to release energy. This energy is utilized by myosin to reach its high-energy state to separate from the active site of the actin filament causing contraction. Creatine phosphate is used to regenerate ATP in the body and thus it is also a direct source of energy during muscle contraction.
Additional Information: Let us understand the cross-bridge formation in detail.
-The best explanation for the mechanism of muscle contraction is the sliding filament theory which states that contraction occurs by the sliding of thin filaments over the thick filaments.
-The muscle contraction starts with the release of ${ Ca }^{ ++ }$ ions which bind to the subunit of troponin on actin to expose the active sites for myosin.
-Myosin utilizes the energy that was released during hydrolysis of ATP and bings to the actin filament to form a cross-bridge. Then the myosin moves inwards causing the actin filaments to be pulled inwards as well.
-This causes shortening of the length of sarcomere as well as the muscle and thus is known as contraction.
-A new ATP binds to the myosin causing it to break the cross-bridge formation. Now the free myosin binds with a new actin filament to repeat the events mentioned above.
So, the correct option is ‘Both (a) and (b)’.
Note: -The initiation of muscle contraction is done by a signal that is sent from the central nervous system (CNS).
-The junction that is formed between the motor neuron and muscle fiber is known as neuromuscular junction or motor-end plate.
-Muscle cells have a red-colored pigment known as myoglobin whose function is to store oxygen.
Complete answer:
The direct source of energy for muscular contraction is ATP and creatinine. ATP binds to myosin after which it is hydrolyzed to release energy. This energy is utilized by myosin to reach its high-energy state to separate from the active site of the actin filament causing contraction. Creatine phosphate is used to regenerate ATP in the body and thus it is also a direct source of energy during muscle contraction.
Additional Information: Let us understand the cross-bridge formation in detail.
-The best explanation for the mechanism of muscle contraction is the sliding filament theory which states that contraction occurs by the sliding of thin filaments over the thick filaments.
-The muscle contraction starts with the release of ${ Ca }^{ ++ }$ ions which bind to the subunit of troponin on actin to expose the active sites for myosin.
-Myosin utilizes the energy that was released during hydrolysis of ATP and bings to the actin filament to form a cross-bridge. Then the myosin moves inwards causing the actin filaments to be pulled inwards as well.
-This causes shortening of the length of sarcomere as well as the muscle and thus is known as contraction.
-A new ATP binds to the myosin causing it to break the cross-bridge formation. Now the free myosin binds with a new actin filament to repeat the events mentioned above.
So, the correct option is ‘Both (a) and (b)’.
Note: -The initiation of muscle contraction is done by a signal that is sent from the central nervous system (CNS).
-The junction that is formed between the motor neuron and muscle fiber is known as neuromuscular junction or motor-end plate.
-Muscle cells have a red-colored pigment known as myoglobin whose function is to store oxygen.

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




