
Which of the following have both polar and nonpolar bonds?
(A) $ {C_2}{H_6} $
(B) $ N{H_4}Cl $
(C) $ HCl $
(D) $ AlC{l_3} $
Answer
478.8k+ views
Hint: Electrons are unequally shared between the atoms which form polar covalent bonds, this is because of different electronegativities of atoms. On the other hand, electrons are equally shared between the atoms then they will form nonpolar covalent bonds, this is due to the same electronegativities of atoms.
Complete answer:
To answer this question we will consider each option one by one:
$ {C_2}{H_6} $ (Ethane)
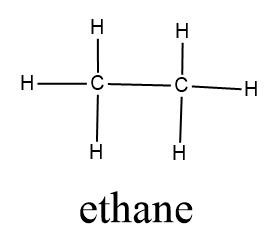
In ethane, the difference in the electronegativities of hydrogen and carbon forming bonds in this structure is remarkably less. There is zero difference in the electronegativity of the carbon atoms which are forming bonds with each other. So ethane is a nonpolar molecule.
$ N{H_4}Cl $ (Ammonium chloride)
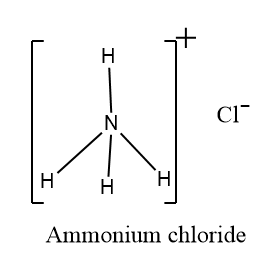
The electronegativity of nitrogen is more than hydrogen. Thus, nitrogen will have a partial negative charge as it will attract the shared pair of electrons towards itself. Hydrogen will contain a partial positive charge. Thus, $ N{H_4}Cl $ is a polar compound with a dipole moment towards nitrogen.
The ammonium chloride also have non-polar bond this is because $N{H_4}^+$ has positive charge and $ C{l^ - } $ has negative charge which shows it shares equal electrons and has the same electronegativities.
$ HCl $ (Hydrogen chloride)
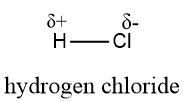
$ HCl $ is a polar compound because the chloride ion is more electronegative as compared to hydrogen ions. Thus, chloride ions carry partial negative dipoles and hydrogen carries partial positive dipoles.
$ AlC{l_3} $ (Aluminium chloride)
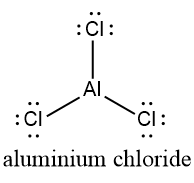
The $ AlC{l_3} $ monomer has a trigonal planar shape. The dipole moments in each bond of $ AlCl $ are aligned in a plane at an angle of $ {120^ \circ } $ and are therefore interrupted. It is therefore a non-polar molecule.
Thus, $ N{H_4}Cl $ molecule has both polar and nonpolar bonds and the option $ \left( b \right) $ is correct.
Note:
Covalent bonds which are in between two atoms where the electrons forming the bond are unequally distributed are known as polar bonds. Because of this the molecules have a slight electrical dipole moment where one end is slightly positive and the other is slightly negative.
Complete answer:
To answer this question we will consider each option one by one:
$ {C_2}{H_6} $ (Ethane)

In ethane, the difference in the electronegativities of hydrogen and carbon forming bonds in this structure is remarkably less. There is zero difference in the electronegativity of the carbon atoms which are forming bonds with each other. So ethane is a nonpolar molecule.
$ N{H_4}Cl $ (Ammonium chloride)

The electronegativity of nitrogen is more than hydrogen. Thus, nitrogen will have a partial negative charge as it will attract the shared pair of electrons towards itself. Hydrogen will contain a partial positive charge. Thus, $ N{H_4}Cl $ is a polar compound with a dipole moment towards nitrogen.
The ammonium chloride also have non-polar bond this is because $N{H_4}^+$ has positive charge and $ C{l^ - } $ has negative charge which shows it shares equal electrons and has the same electronegativities.
$ HCl $ (Hydrogen chloride)
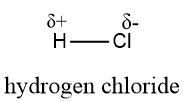
$ HCl $ is a polar compound because the chloride ion is more electronegative as compared to hydrogen ions. Thus, chloride ions carry partial negative dipoles and hydrogen carries partial positive dipoles.
$ AlC{l_3} $ (Aluminium chloride)

The $ AlC{l_3} $ monomer has a trigonal planar shape. The dipole moments in each bond of $ AlCl $ are aligned in a plane at an angle of $ {120^ \circ } $ and are therefore interrupted. It is therefore a non-polar molecule.
Thus, $ N{H_4}Cl $ molecule has both polar and nonpolar bonds and the option $ \left( b \right) $ is correct.
Note:
Covalent bonds which are in between two atoms where the electrons forming the bond are unequally distributed are known as polar bonds. Because of this the molecules have a slight electrical dipole moment where one end is slightly positive and the other is slightly negative.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




