
Which of the following has the most acidic hydrogen?
A. 3-Hexanone
B. 2,4-Hexanedione
C. 2,5-Hexanedione
D. 2,3-Hexanedione
Answer
531k+ views
Hint: Acids are those compounds which have a tendency to donate a proton i.e. hydrogen ion to any substance. Acids basically turn blue litmus paper to red and have a sour taste. The most common acid is citric acid present in lemon.
Complete answer:
Acidic hydrogen can be defined as an acid which ${{H}^{+}}$has tendency to be released ${{H}^{+}}$ion. So we can say that if any hydrogen atom is attached to another atom or group of atoms with higher electronegativity than that hydrogen atom is known as a potential acidic hydrogen atom.
Rather than this there are many other factors on which acidic hydrogen depends i.e. electromeric effect, inductive effect, resonance effect, hyperconjugation etc. Given examples can be defined on the basis of resonance effect. Whereas resonance effect is generally studied in organic chemistry which describes the change in the behavior of electrons when the elements other than that of the carbon atoms and hydrogen takes part in the formation of molecular bonds.
Resonance effects increase the strength of an acid. The most acidic hydrogen is present in option B this can be explained by the following figure
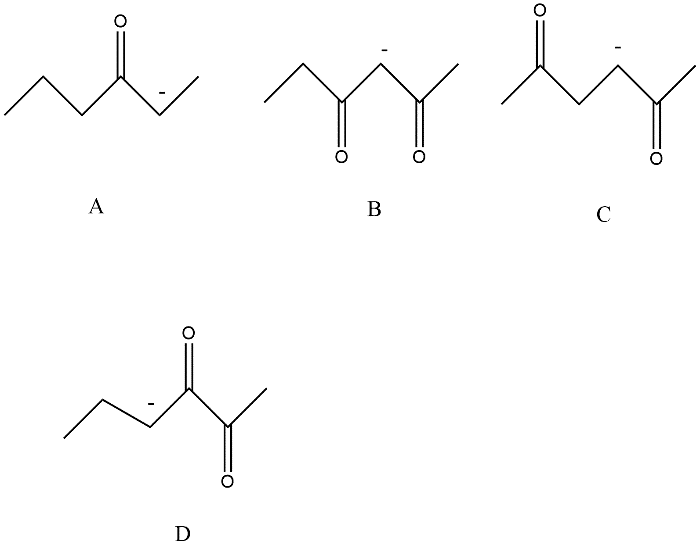
Since anion 2,4-Hexanedione option B is resonance stabilized by two carbonyl groups whereas other compounds A, C and D are in conjugation with only one carbonyl compound.
Thus we can say that option B has the most acidic hydrogen.
Note:
Resonance describes the delocalized electrons within the certain molecules where one single lewis structure does not express the bonds. An ion or molecule with these delocalized electrons can be represented by a number of structures which are called resonance structures.
Complete answer:
Acidic hydrogen can be defined as an acid which ${{H}^{+}}$has tendency to be released ${{H}^{+}}$ion. So we can say that if any hydrogen atom is attached to another atom or group of atoms with higher electronegativity than that hydrogen atom is known as a potential acidic hydrogen atom.
Rather than this there are many other factors on which acidic hydrogen depends i.e. electromeric effect, inductive effect, resonance effect, hyperconjugation etc. Given examples can be defined on the basis of resonance effect. Whereas resonance effect is generally studied in organic chemistry which describes the change in the behavior of electrons when the elements other than that of the carbon atoms and hydrogen takes part in the formation of molecular bonds.
Resonance effects increase the strength of an acid. The most acidic hydrogen is present in option B this can be explained by the following figure

Since anion 2,4-Hexanedione option B is resonance stabilized by two carbonyl groups whereas other compounds A, C and D are in conjugation with only one carbonyl compound.
Thus we can say that option B has the most acidic hydrogen.
Note:
Resonance describes the delocalized electrons within the certain molecules where one single lewis structure does not express the bonds. An ion or molecule with these delocalized electrons can be represented by a number of structures which are called resonance structures.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




