
Which of the following has the highest bond angle?
(A) ${H_2}O$
(B) ${H_2}S$
(C) $N{H_3}$
(D) $P{H_3}$
Answer
497.7k+ views
Hint: Bond angle of any chemical compound is defined as the average angle which formed between the orbitals of compound containing electron pairs surrounding the central atom of a molecule. VSEPR theory plays an important role in describing the shape and bond angle of molecules.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
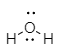
In the molecule of ${H_2}O$, an oxygen atom contains six electrons which further combine with two hydrogen atoms leaving four electrons to the central oxygen atom. These lone pair electrons at oxygen exhibit repulsion and are oriented at an angle of ${104.5^ \circ }$ to maintain the stability of the molecule.
In the molecule of ${H_2}S$, central atom sulphur has six electrons which further combine with two hydrogen atoms leaving four electrons to central sulphur atom. These lone pair electrons at sulphur exhibit repulsion but due to the lower electronegativity of sulphur atoms it exhibits less lone pair- lone pair repulsion and molecule oriented at ${92.1^ \circ }$.
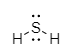
In the molecule of $N{H_3}$, the central atom of nitrogen has four electron pairs which further combine with three hydrogen atoms leaving one electron pair to the central nitrogen atom. This single lone pair of electrons in a nitrogen atom shows repulsion and pushes the bond closer and finally molecule oriented at ${107^ \circ }$.
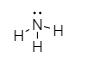
In the molecule of $P{H_3}$, the central atom of phosphorus has four electron pairs which further combine with three hydrogen atoms leaving one electron pair to the central phosphorus atom. This single lone pair of electrons in phosphorus atom shows repulsion and pushes the bond closer but due to lower electronegativity of phosphorus atom it shows lower repulsion and finally molecule oriented at ${93^ \circ }$

$ \Rightarrow $ from the above discussion we see that a molecule of $N{H_3}$ shows the maximum bond angle of ${107^ \circ }$.
Therefore, option $\left( {iii} \right)$ is the correct option.
Note:
Bond angle of compound is shown in terms of degree, minute or second. Bond angle of the compound gives a detail about the shape of the molecule along with the pattern of distribution of orbitals around the central atom.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
In the molecule of ${H_2}O$, an oxygen atom contains six electrons which further combine with two hydrogen atoms leaving four electrons to the central oxygen atom. These lone pair electrons at oxygen exhibit repulsion and are oriented at an angle of ${104.5^ \circ }$ to maintain the stability of the molecule.

In the molecule of ${H_2}S$, central atom sulphur has six electrons which further combine with two hydrogen atoms leaving four electrons to central sulphur atom. These lone pair electrons at sulphur exhibit repulsion but due to the lower electronegativity of sulphur atoms it exhibits less lone pair- lone pair repulsion and molecule oriented at ${92.1^ \circ }$.
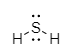
In the molecule of $N{H_3}$, the central atom of nitrogen has four electron pairs which further combine with three hydrogen atoms leaving one electron pair to the central nitrogen atom. This single lone pair of electrons in a nitrogen atom shows repulsion and pushes the bond closer and finally molecule oriented at ${107^ \circ }$.
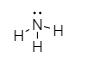
In the molecule of $P{H_3}$, the central atom of phosphorus has four electron pairs which further combine with three hydrogen atoms leaving one electron pair to the central phosphorus atom. This single lone pair of electrons in phosphorus atom shows repulsion and pushes the bond closer but due to lower electronegativity of phosphorus atom it shows lower repulsion and finally molecule oriented at ${93^ \circ }$

$ \Rightarrow $ from the above discussion we see that a molecule of $N{H_3}$ shows the maximum bond angle of ${107^ \circ }$.
Therefore, option $\left( {iii} \right)$ is the correct option.
Note:
Bond angle of compound is shown in terms of degree, minute or second. Bond angle of the compound gives a detail about the shape of the molecule along with the pattern of distribution of orbitals around the central atom.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




