
Which of the following has distorted tetrahedral shape?
(A) $Si{H_4}$
(B) $CC{l_4}$
(C) $C{H_4}$
(D) $CHC{l_3}$
Answer
574.5k+ views
Hint: A carbon atom with four bonds and bond angle of approximately ${109.5^o}$ is tetrahedral geometry. But when bond angle is different from ${109.5^o}$ i.e., less than this angle then it is called distorted tetrahedral geometry.
This is due to repulsion between the bond pair and lone pair of electron.
Complete step by step answer:
Let us discuss the geometry of each molecule one by one.
(1) $CHC{l_3}$ chloroform: The molecular shape of $CHC{l_3}$ is tetrahedral. It means that H-atoms and three Cl-atoms. The vertices of a triangular based pyramid around the central C-atom.
This is because polar covalent bonds are asymmetrically arranged around the central atom of a molecule.
The geometry of molecules is not regular because the dipole moment of $CHC{l_3}$ is not zero.
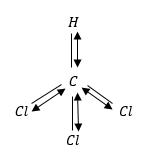
$CHC{l_3}$ has maximum dipole moment because in tetrahedral structure all Cl-atoms will be at bottom and add to individual dipoles.
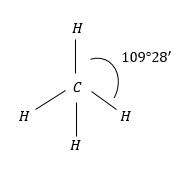
(2) $C{H_4}$: $C{H_4}$ molecules have regular tetrahedral geometry due H-atoms present and regular tetrahedron structure.
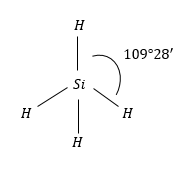
$Si{H_4}$: Molecular geometry of this molecule is also regular tetrahedral. Because it is surrounded by the same atoms i.e., H-atoms.
Therefore, the same symmetric charge distribution around $Si$atom and molecule is non-polar.
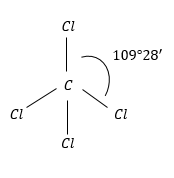
$CC{l_4}$: This has regular geometry because of the same atoms surrounding the C-atom.
Therefore, the dipole moment of the molecule is zero.
Therefore, from the above explanation the correct option is (D) $CHC{l_3}.$
Note:
Molecules show regular tetrahedral geometry when the central atom is surrounded by the same atoms. The resulting dipole moment becomes zero.
But when central atoms surrounded by different atoms [differ in their electronegativity] have dipole moment and therefore their geometry is distorted.
This is due to repulsion between the bond pair and lone pair of electron.
Complete step by step answer:
Let us discuss the geometry of each molecule one by one.
(1) $CHC{l_3}$ chloroform: The molecular shape of $CHC{l_3}$ is tetrahedral. It means that H-atoms and three Cl-atoms. The vertices of a triangular based pyramid around the central C-atom.
This is because polar covalent bonds are asymmetrically arranged around the central atom of a molecule.
The geometry of molecules is not regular because the dipole moment of $CHC{l_3}$ is not zero.

$CHC{l_3}$ has maximum dipole moment because in tetrahedral structure all Cl-atoms will be at bottom and add to individual dipoles.
(2) $C{H_4}$: $C{H_4}$ molecules have regular tetrahedral geometry due H-atoms present and regular tetrahedron structure.

$Si{H_4}$: Molecular geometry of this molecule is also regular tetrahedral. Because it is surrounded by the same atoms i.e., H-atoms.
Therefore, the same symmetric charge distribution around $Si$atom and molecule is non-polar.

$CC{l_4}$: This has regular geometry because of the same atoms surrounding the C-atom.
Therefore, the dipole moment of the molecule is zero.

Therefore, from the above explanation the correct option is (D) $CHC{l_3}.$
Note:
Molecules show regular tetrahedral geometry when the central atom is surrounded by the same atoms. The resulting dipole moment becomes zero.
But when central atoms surrounded by different atoms [differ in their electronegativity] have dipole moment and therefore their geometry is distorted.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

A solution of a substance X is used for white washing class 11 chemistry CBSE

Differentiate between calcination and roasting class 11 chemistry CBSE




