
Which of the following correctly explains a phase/event in cardiac cycle in a standard electrocardiogram?
A. QRS complex indicates atrial contraction
B. QRS complex indicates ventricular contraction
C. Time between S and T represents atrial systole
D. P-wave indicates beginning of ventricular contraction
Answer
504.3k+ views
Hint: The sequence of events, which occurs from the beginning of one heartbeat to the beginning of the next (completion of one heartbeat), is called a cardiac cycle. During a heart beat there is contraction and relaxation of the atria and ventricles. The contraction phase is called the systole and the relaxation phase is called diastole. When both the atria and ventricles are in the diastole or relaxed phase, it is referred to as joint diastole. A complete heartbeat consists of a systole and diastole of both the atria and both the ventricles.
Complete answer:
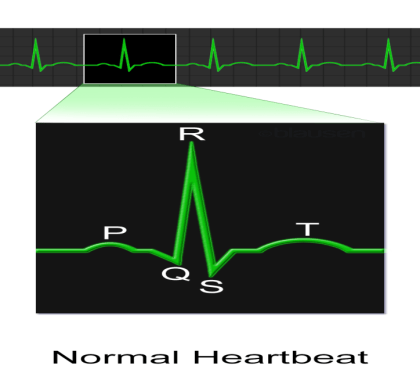
A normal electrocardiogram has a P wave, a QRS complex and a T wave. The QRS complex has three separate Q, R and S waves.
The QRS complex is the longest region of our ECG or electrocardiogram. It begins after a fraction of a second of the P wave. It begins as a small downward deflection (Q), and continues as a large upright (R) and triangular wave, ending as a downward wave (S) at the base and not showing the atrial contraction.
The QRS complex signifies the depolarization of the ventricles, which initiates the ventricle contraction. The contraction starts after Q and marks the starting of the systole.
Time between the S and T are called ST intervals, representing the end of the spread of impulse through ventricles, and its repolarization.
P wave is a small upward wave that indicates the electrical excitation or depolarization of the atria.
So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Note:
ECG is a graphical representation of the electrical activity of the heart during a cardiac cycle. The machine used to record an ECG is called an electrocardiograph.
The first ECG was recorded by Waller in 1887 and the details of the ECG were studied by Einthoven in 1903. He is also considered the “Father of the Electrocardiography”.

Complete answer:
A normal electrocardiogram has a P wave, a QRS complex and a T wave. The QRS complex has three separate Q, R and S waves.
The QRS complex is the longest region of our ECG or electrocardiogram. It begins after a fraction of a second of the P wave. It begins as a small downward deflection (Q), and continues as a large upright (R) and triangular wave, ending as a downward wave (S) at the base and not showing the atrial contraction.
The QRS complex signifies the depolarization of the ventricles, which initiates the ventricle contraction. The contraction starts after Q and marks the starting of the systole.
Time between the S and T are called ST intervals, representing the end of the spread of impulse through ventricles, and its repolarization.
P wave is a small upward wave that indicates the electrical excitation or depolarization of the atria.
So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Note:
ECG is a graphical representation of the electrical activity of the heart during a cardiac cycle. The machine used to record an ECG is called an electrocardiograph.
The first ECG was recorded by Waller in 1887 and the details of the ECG were studied by Einthoven in 1903. He is also considered the “Father of the Electrocardiography”.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




