
Which of the following compounds will most readily be dehydrated to give alkene under acidic condition?
A.2-Hydroxycyclopentanone
B.1-Pentanol
C.3-Hydroxypentan-2-one
D.4-Hydroxypentan-2-one
Answer
585.3k+ views
Hint: The rate of formation of alkene will depend on the stability of alkene. More stable alkene will form rapidly and less stable alkene will take form slowly. The stability of alkene is determined through hyperconjugation.
Complete step by step answer:
When the hydration of alcohol occurs under acidic condition alkene is formed. The ease of dehydration depends upon the stability of the alkene formed. Greater is the stability of alkene, easier it would be to form that alkene.
The stability of alkene depends upon the hyperconjugation. More is the hyperconjugation which will be the stability of alkene. Hyperconjugation depends upon the number of Alpha hydrogens, higher is the number of Alpha hydrogen, more will be hyperconjugation. So we need to check the number of Alpha hydrogen that is present in the alkene that is formed by the given compounds.
Alpha hydrogen is that hydrogen which is attached to carbon next to the double bond.
Dehydration of 2-hydroxycyclopentanone gives the following alkene:
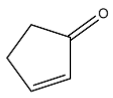
It has 2 carbons next to the double bond. There is no hydrogen on carbon that is on RHS but there are two hydrogen atoms on LHS. So this molecule has 2 alpha hydrogen.
Dehydration of 1-pentanol gives the following alkene:
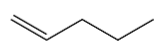
It has 1 carbon next to double bond. There are two hydrogen atoms on the next carbon. So this molecule has 2 alpha hydrogen.
Dehydration of 3-hydroxypentan-2-one gives the following alkene:
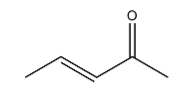
It has 2 carbons next to the double bond. There is no hydrogen on carbon that is on RHS but there are three hydrogen atoms on LHS. So this molecule has 3 alpha hydrogen.
Dehydration of 4-hydroxypentan-2-one gives the following alkene:
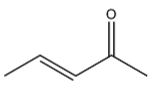
It has 2 carbons next to the double bond. There is no hydrogen on carbon that is on RHS but there are three hydrogen atoms on LHS. So this molecule has 3 alpha hydrogen.
Both C and D will readily form the hydrogen but in the C option the intermediate carbocation formed is less stable than the option D.
Hence, the correct option is option D.
Note:
If the question is asked with multiple answers then we will mark both option C and D correct. If there is only one option to choose from then the option D is marked as correct as the stability of the carbocation formed in option D is higher than the stability of the carbocation formed in option C.
Complete step by step answer:
When the hydration of alcohol occurs under acidic condition alkene is formed. The ease of dehydration depends upon the stability of the alkene formed. Greater is the stability of alkene, easier it would be to form that alkene.
The stability of alkene depends upon the hyperconjugation. More is the hyperconjugation which will be the stability of alkene. Hyperconjugation depends upon the number of Alpha hydrogens, higher is the number of Alpha hydrogen, more will be hyperconjugation. So we need to check the number of Alpha hydrogen that is present in the alkene that is formed by the given compounds.
Alpha hydrogen is that hydrogen which is attached to carbon next to the double bond.
Dehydration of 2-hydroxycyclopentanone gives the following alkene:

It has 2 carbons next to the double bond. There is no hydrogen on carbon that is on RHS but there are two hydrogen atoms on LHS. So this molecule has 2 alpha hydrogen.
Dehydration of 1-pentanol gives the following alkene:

It has 1 carbon next to double bond. There are two hydrogen atoms on the next carbon. So this molecule has 2 alpha hydrogen.
Dehydration of 3-hydroxypentan-2-one gives the following alkene:

It has 2 carbons next to the double bond. There is no hydrogen on carbon that is on RHS but there are three hydrogen atoms on LHS. So this molecule has 3 alpha hydrogen.
Dehydration of 4-hydroxypentan-2-one gives the following alkene:

It has 2 carbons next to the double bond. There is no hydrogen on carbon that is on RHS but there are three hydrogen atoms on LHS. So this molecule has 3 alpha hydrogen.
Both C and D will readily form the hydrogen but in the C option the intermediate carbocation formed is less stable than the option D.
Hence, the correct option is option D.
Note:
If the question is asked with multiple answers then we will mark both option C and D correct. If there is only one option to choose from then the option D is marked as correct as the stability of the carbocation formed in option D is higher than the stability of the carbocation formed in option C.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

Name the part of the brain responsible for the precision class 11 biology CBSE

The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to AEffect class 11 biology CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE




