
Which of the following compounds will exhibit geometrical isomerism?
A. \[2 - phenyl - 1 - butene\]
B. \[1,1 - diphenyl - 1 - propane\]
C. \[1 - phenyl - 2 - butene\]
D. \[\;3 - phenyl - 1 - butene.\]
Answer
584.4k+ views
Hint: Geometrical isomerism is a type of stereoisomerism having the same molecular formula and same structure but differ in the relative arrangement of atoms. Geometric isomerism also known as Cis–Trans isomerism or configurational isomerism.
Complete step by step solution:
To identify geometrical isomerism it follow two conditions -
There are two necessary conditions for a compound to possess geometrical isomerism:
(i) It must contain a carbon-carbon double bond in the molecule.
(ii) Two unlike atoms or groups must be linked to each doubly bonded carbon atom.
Based on the group or atom attached to the carbon on each side with respect to double bond they are differentiate in two types - Cis isomer and –trans isomer.
If the two groups with the higher priorities are on the same side of the double bond, that is described as the (Cis)- isomer. If the two groups with the higher priorities are on opposite sides of the double bond, then this is the (Trans)-isomer.
As per given option – based on the conditions of geometrical isomerism-
\[1 - phenyl - 2 - butene\] satisfies both the conditions.
It has 2 different groups on the left hand side and the right hand side. It has restricted rotation.
Thus this compound shows geometrical isomerism

The other structure in this option doesn’t follow the mentioned conditions in their structure. Its structure is given below –
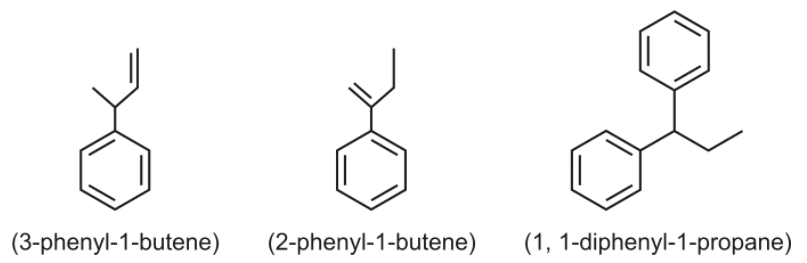
So, option (C) is correct
Note:
In geometrical isomerism, the double bond is planer so there is always \[{180^0}\] rotation during the conversion of Cis to Trans and Trans to Cis. Cis/Trans isomers also have similar chemical properties but different physical properties.
Complete step by step solution:
To identify geometrical isomerism it follow two conditions -
There are two necessary conditions for a compound to possess geometrical isomerism:
(i) It must contain a carbon-carbon double bond in the molecule.
(ii) Two unlike atoms or groups must be linked to each doubly bonded carbon atom.
Based on the group or atom attached to the carbon on each side with respect to double bond they are differentiate in two types - Cis isomer and –trans isomer.
If the two groups with the higher priorities are on the same side of the double bond, that is described as the (Cis)- isomer. If the two groups with the higher priorities are on opposite sides of the double bond, then this is the (Trans)-isomer.
As per given option – based on the conditions of geometrical isomerism-
\[1 - phenyl - 2 - butene\] satisfies both the conditions.
It has 2 different groups on the left hand side and the right hand side. It has restricted rotation.
Thus this compound shows geometrical isomerism

The other structure in this option doesn’t follow the mentioned conditions in their structure. Its structure is given below –

So, option (C) is correct
Note:
In geometrical isomerism, the double bond is planer so there is always \[{180^0}\] rotation during the conversion of Cis to Trans and Trans to Cis. Cis/Trans isomers also have similar chemical properties but different physical properties.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

The largest wind power cluster is located in the state class 11 social science CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

What steps did the French revolutionaries take to create class 11 social science CBSE

Which among the following are examples of coming together class 11 social science CBSE

Why was the Vernacular Press Act passed by British class 11 social science CBSE




